What is operant conditioning in psychology?
Operant conditioning, sometimes referred to as instrumental conditioning, is a method of learning that uses rewards and punishment to modify behavior. Through operant conditioning, behavior that is rewarded is likely to be repeated, and behavior that is punished will rarely occur.
What is Skinner's operant conditioning?
Skinner - Operant Conditioning. By Saul McLeod, updated 2018. Operant conditioning is a method of learning that occurs through rewards and punishments for behavior. Through operant conditioning, an individual makes an association between a particular behavior and a consequence (Skinner, 1938).
What is operant conditioning by Saul McLeod?
By Saul McLeod, updated 2018. Operant conditioning is a method of learning that occurs through rewards and punishments for behavior. Through operant conditioning, an individual makes an association between a particular behavior and a consequence (Skinner, 1938).
How does operant behavior occur?
The operant behavior occurs due to an association between behavior and consequence. There are broadly three types of operant conditioning. These might result in a change of behavior in an organism. They are as follows – 1. Reinforcement It is anything within the environment that gives strength to a behavior.

What is operant conditioning example?
By contrast, a dog might learn that, by sitting and staying, it will earn a treat. If the dog then gets better at sitting and staying in order to receive the treat, then this is an example of operant conditioning.
What is Skinner's theory of operant learning?
Skinner in his theory of operant conditioning. In positive reinforcement, a response or behavior is strengthened by rewards, leading to the repetition of desired behavior. The reward is a reinforcing stimulus. Skinner showed how positive reinforcement worked by placing a hungry rat in his Skinner box.
What are the 4 types of operant conditioning according to Skinner?
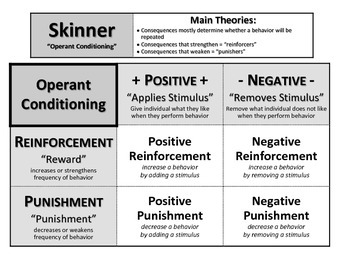
In Operant Conditioning Theory, there are essentially four quadrants: Positive Reinforcement, Positive Punishment, Negative Reinforcement, and Negative Punishment.
Why is it called operant conditioning?
Operant, or instrumental, conditioning is so called because, in making their responses, learners provide the instrument by which a problem is solved. Such learning is more important to schoolwork, for teachers are concerned ultimately with drawing forth new responses from their students.
What is Skinner's behaviorism theory?
Skinner's behavior theory was based on two assumptions, firstly that human behavior follows 'laws' and that the causes of human behavior are something outside of a person, something in their environment. He believed that these environmental 'causes' of behavior could always be observed and studied.
What is Skinner's operant conditioning theory explain its educational importance?
Skinner called his theory as operant conditioning as it is based on certain operations or actions which an organism has to carry out. The term 'operant' stresses that behaviour operates upon the environment to generate its own consequences. An operant is a set of acts which conditions an organism in doing something.
What are the main characteristics of Skinner's studies on learning?
Skinner held that science has three principal characteristics: (1) its findings are cumulative, (2) it rests on an attitude that values empirical observation, and (3) it searches for order and reliable relationships. You just studied 78 terms!
Why is Skinner's theory important?
Evaluation. Skinner's theory of operant conditioning played a key role in helping psychologists to understand how behavior is learnt. It explains why reinforcements can be used so effectively in the learning process, and how schedules of reinforcement can affect the outcome of conditioning.
What is operant conditioning theory of learning?
Operant conditioning, sometimes referred to as instrumental conditioning, is a method of learning that occurs through rewards and punishments for b...
What is Skinner's theory of operant conditioning?
Operant conditioning is a method of learning that occurs through rewards and punishments for behavior. Through operant conditioning, an individual...
What is positive reinforcement?
Positive reinforcement is a term described by B. F. Skinner in his theory of operant conditioning. In positive reinforcement, a response or behavio...
What are some examples of operant conditioning?
Positive ReinforcementFor example, if your teacher gives you £5 each time you complete your homework (i.e., a reward) you will be more likely to re...
What is operant conditioning?
Operant conditioning, also known as instrumental conditioning, is a method of learning normally attributed to B.F. Skinner, where the consequences of a response determine the probability of it being repeated. Through operant conditioning behavior which is reinforced (rewarded) will likely be repeated, and behavior which is punished will occur less ...
How can operant conditioning be used to produce complex behavior?
Skinner argues that the principles of operant conditioning can be used to produce extremely complex behavior if rewards and punishments are delivered in such a way as to encourage move an organism closer and closer to the desired behavior each time.
How did Skinner show positive reinforcement?
Skinner showed how positive reinforcement worked by placing a hungry rat in his Skinner box. The box contained a lever on the side, and as the rat moved about the box, it would accidentally knock the lever. Immediately it did so a food pellet would drop into a container next to the lever.
Why did the Skinner study show that rats learned to repeat behavior?
In the Skinner study, because food followed a particular behavior the rats learned to repeat that behavior, e.g., operant conditioning. • There is little difference between the learning that takes place in humans and that in other animals. Therefore research (e.g., operant conditioning) can be carried out on animals (Rats / Pigeons) ...
What is Skinner's view of behavior?
He believed that the best way to understand behavior is to look at the causes of an action and its consequences. He called this approach operant conditioning. YouTube.
How did Skinner teach rats to avoid electric current?
In fact Skinner even taught the rats to avoid the electric current by turning on a light just before the electric current came on . The rats soon learned to press the lever when the light came on because they knew that this would stop the electric current being switched on.
What did Skinner believe about the mind?
Skinner believed that we do have such a thing as a mind, but that it is simply more productive to study observable behavior rather than internal mental events.
Who developed operant conditioning theory?
In the 1930s, B. F. Skinner, who had become familiar with the work of these researchers and others, continued the exploration of how organisms learn. Skinner studied and developed the operant conditioning theory that is popular today.
What is operant conditioning?
The basic concept behind operant conditioning is that a stimulus (antecedent) leads to a behavior, which then leads to a consequence. This form of conditioning involves reinforcers, both positive and negative, as well as primary, secondary, and generalized.
What is the importance of reinforcement in operant conditioning?
Reinforcements and reinforcement schedules are crucial to using operant conditioning successfully. Positive and negative punishment decreases unwanted behavior, but the effects are not long lasting and can cause harm. Positive and negative reinforcers increase the desired behavior and are usually the best approach.
What is classical conditioning?
An easy way to think about classical conditioning is that it is reflexive. It is the behavior an organism automatically does. Pavlov paired a bell with a behavior a dog already does (salivation) when presented with food. After several trials, Pavlov conditioned dogs to salivate when the bell dinged.
What did Thorndike learn?
Thorndike also established that learning is the result of a trial-and-error process. This process takes time, but no conscious thought. He studied and developed our initial concepts of operant conditioning reinforcement and how various types influence learning. Thorndike’s principles of learning include:
What is the relationship between the discriminative stimulus, response, and reinforcer?
The relationship between the discriminative stimulus, response, and reinforcer is what influences the likelihood of a behavior happening again in the future. A reinforcer is some kind of reward, or in the case of adverse outcomes, a punishment.
How many types of reinforcement are there?
There are four types of reinforcement divided into two groups. The first group acts to increase a desired behavior. This is known as positive or negative reinforcement.
Why is operant conditioning considered incomplete?
First, operant conditioning is accused of being an incomplete explanation for learning because it neglects the role of biological and cognitive elements.
How is operation conditioning used?
Operant conditioning is also used in behavior modification, an approach to the treatment of numerous issues in adults and children, including phobias, anxiety, bedwetting, and many others. One way behavior modification can be implemented is through a token economy, in which desired behaviors are reinforced by tokens in the form of digital badges, buttons, chips, stickers, or other objects. Eventually these tokens can be exchanged for real rewards.
What is shaping in behavioral science?
Behavior Shaping. Operant conditioning can lead to increasingly complex behaviors through shaping, also referred to as the “method of approximations.”. Shaping happens in a step-by-step fashion as each part of a more intricate behavior is reinforced. Shaping starts by reinforcing the first part of the behavior.
Why is Skinner's observation about operant conditioning flawed?
Finally, because Skinner’s observations about operant conditioning relied on experiments with animals, he is criticized for extrapolating from his animal studies to make predictions about human behavior. Some psychologists believe this kind of generalization is flawed because humans and non-human animals are physically and cognitively different.
What is the process of learning through reinforcement and punishment?
Operant conditioning is the process of learning through reinforcement and punishment.
How did Skinner study operant conditioning?
To study operant conditioning, Skinner conducted experiments using a “Skinner Box,” a small box that had a lever at one end that would provide food or water when pressed. An animal, like a pigeon or rat, was placed in the box where it was free to move around. Eventually the animal would press the lever and be rewarded. Skinner found that this process resulted in the animal pressing the lever more frequently. Skinner would measure learning by tracking the rate of the animal’s responses when those responses were reinforced.
Why are conditional reinforcers not innately desirable?
Conditioned reinforcers reinforce behavior not because they are innately desirable, but because we learn to associate them with primary reinforcers. For example, Paper money is not innately desirable, but it can be used to acquire innately desirable goods, such as food and shelter.
What is Operant Conditioning?
Operant conditioning, also known as instrumental conditioning or Skinnerian conditioning, is a learning theory in behavioral psychology. It can be used to increase or decrease the frequency of certain behaviors through the introduction of consequences.
What is the difference between classical and operant conditioning?
The main difference here is that one leads to an unconscious effect (classical) and the other involves a conscious choice (operant).
What can a mental health professional do to help you shift unwanted behaviors into more desired behaviors?
If you live with a mental health condition, mental health professionals can introduce reinforcers or punishers to help shift certain unwanted behaviors into more desired behaviors.
What are the two types of behavioral modifiers in operant conditioning?
The two main types of behavioral modifiers in operant conditioning are called reinforcers and punishers. Reinforcement and punishment can also be further broken down into two subtypes: positive and negative.
What is the difference between a punisher and a reinforcer?
Essentially, reinforcers will encourage behaviors, whereas punishers will discourage them. And depending on the schedule of reinforcement, those behaviors can either increase or decrease in frequency and consistency.
How did the Skinner box work?
In an experiment known as the “Skinner box,” Skinner placed a rat in a box with a lever that released food into the box. After the rat accidentally hit the lever enough times, it ultimately learned that its behavior (pulling the lever) led to a specific consequence (receiving food).
What happens when a behavior isn't reinforced?
And when a behavior isn’t reinforced or rewarded for an extended period of time, it may eventually lead to the extinction of that response.
What Is Operant Conditioning?
Most people remember watching or reading about the experiments involving rats in a maze that get treats by pushing a lever. The experiment was trying to prove the concept of operant conditioning.
Operant Conditioning Experiment
Remember the rat in the maze? B.F. Skinner was the person who devised an experiment involving rats and operant conditioning. His experiment involved a rat in a box, which is known as an operant conditioning chamber and is often referred to as a Skinner box.
B. F. Skinner's Operant Conditioning Theory
Operant conditioning is more complex than simply rewarding and punishing behavior. There are many different effects and conditions that are present in the process. The first step in understanding the theory is to know the three general responses that occur as a result of natural stimulus:
Operant Conditioning Word Search Activity
This activity will help you assess your knowledge of the definition, theory, and examples of operant conditioning in psychology.
Which theory of operant conditioning was used to learn the most difficult and complex series of responses?
With the help of such experiments, Skinner put forward his theory of operant conditioning for learning not only the simple responses like pressing of the lever but also for learning the most difficult and complex series of responses.
How can Operant Conditioning be used for shaping behaviour?
Operant conditioning can be used for shaping behaviour of children by appropriate use of reinforcement or rewards. Behaviour can be shaped through successive approximation in terms of small steps.
What is reinforcement in operant conditioning?
Reinforcement is a special kind or aspect of conditioning within which the tendency for a stimulus to evoke a response on subsequent occasions is increased by reduction of a bond.
What is the term for the process of a set of actions that conditions an organism in doing something?
Skinner called his theory as operant conditioning as it is based on certain operations or actions which an organism has to carry out. The term ‘operant’ stresses that behaviour operates upon the environment to generate its own consequences. An operant is a set of acts which conditions an organism in doing something.
What is the process of learning that plays the part in learning such behaviour?
The occurrences of such behaviour was named as operant behaviour and the process of learning that plays the part in learning such behaviour was named by him as operant conditioning.
Why should teachers reinforce behaviour immediately after it occurs?
The teacher should reinforce a behaviour immediately after it occurs because the association between a behaviour and the reward is easily made at this time .
What did Skinner argue about the no stimulus no response mechanism?
Based on the findings of his experiments, skinner concluded that “behaviour is shaped and maintained by its consequences. It is operated by the organism and maintained by its result. ”.

Origins
- Skinner distinguished between two different types of behaviors 1. Respondent behaviorsare those that occur automatically and reflexively, such as pulling your hand back from a hot stove or jerking your leg when the doctor taps on your knee. You don't have to learn these behaviors. They simpl…
Reinforcement and Punishment
Behavior Shaping
Schedules of Reinforcement
Examples of Operant Conditioning
- Through his experiments, Skinner identified the different kinds of reinforcement and punishment that encourage or discourage behavior.
Critiques
- Operant conditioning can lead to increasingly complex behaviors through shaping, also referred to as the “method of approximations.” Shaping happens in a step-by-step fashion as each part of a more intricate behavior is reinforced. Shaping starts by reinforcing the first part of the behavior. Once that piece of the behavior is mastered, reinforceme...
Sources
- In the real world, behavior is not constantly reinforced. Skinner found that the frequency of reinforcement can impact how quickly and how successfully one learns a new behavior. He specified several reinforcement schedules, each with different timing and frequencies. 1. Continuous reinforcementoccurs when a particular response follows each and every performan…