What is the theory of Reasoned Action?
The theory of reasoned action is a mathematical model that allows scientists to predict behavioral intentions as a function of attitudes and subjective norms. The theory of reasoned action was first proposed by the psychologists' Martin Fishbein and Icek Ajzen as an improvement of the information integration theory, another model of human behavior.
What is the purpose of the theory of planned action?
The Theory of Reasoned Action, which is often extended to the Theory of Planned Behavior, is a cognitive theory that helps psychologists understand human behavior in specific contexts. Most notably, the Theory of Reasoned Action has been used to assist in predicting and explaining several health behaviors (LaCaille, 2020).
What is the theory of planned behavior?
The Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB) is an extension of the Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA) (Fishbein & Ajzen 1975, Ajzen & Fishbein 1980 ). Both models are based on the premise that individuals make logical, reasoned decisions to engage in specific behaviours by evaluating the information available to them.
What are the models of decision making based on?
Both models are based on the premise that individuals make logical, reasoned decisions to engage in specific behaviours by evaluating the information available to them.

What are the four components of the theory of reasoned action?
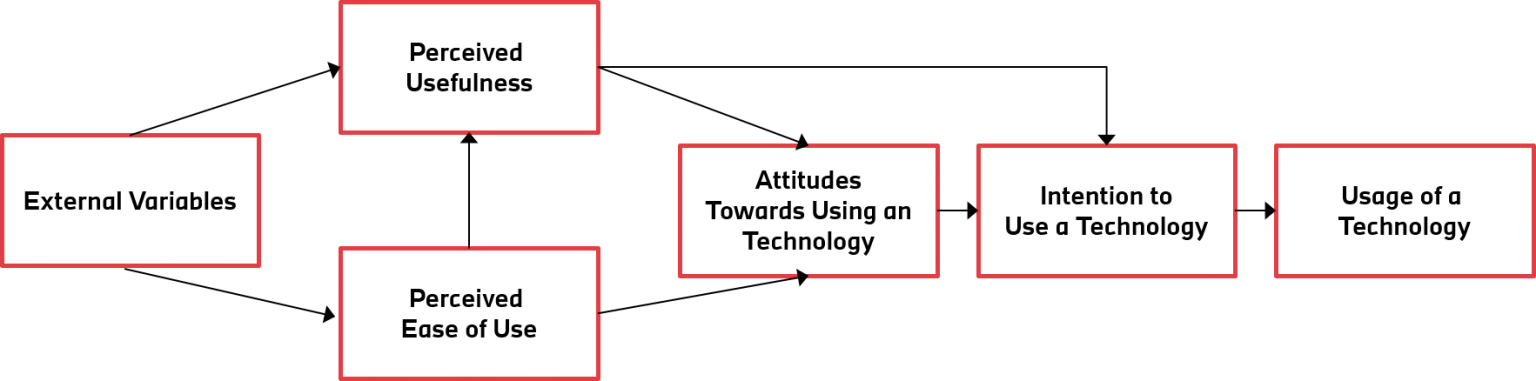
Overall, the theory of reasoned action consists of behavior, intention to perform the behavior, attitudes, subjective norms, and external variables. These factors play a significant role when recognizing the power of attitude on behavior.
Why was the theory of reasoned action created?
The theory of reasoned action was developed by the psychologists Martin Fishbein and Icek Ajzen in 1975, originally as an improvement to the information integration theory. Fishbein and Ajzen formulated the theory after attempting to determine the differences between attitude and behavior.
What is the theory of reasoned action and planned behavior?
Two closely associated theories – The Theory of Reasoned Action and the Theory of Planned Behavior – suggest that a person's health behavior is determined by their intention to perform a behavior.
Which statement best explains the theory of reasoned action?
Which statement best describes theory of reasoned action? Social influences reasonably out way the cost of behavioral change.
What is a key assumption of the theory of reasoned action?
In the original theory of reasoned action (Fishbein & Ajzen, 1975), the assumption was that behavioral intention is determined by two variables; these are attitude and subjective norm.
What are the strengths of the theory of reasoned action?
One advantage of a reasoned action approach is that it helps explain why different background factors are related (or are not related) to a given behavior. For example, if men are found to be more likely to get colonoscopies than women, a reasoned action approach should be able to explain why this is the case.
How do you explain the theory of planned behavior?
In sum, the theory of planned behavior is a theory used to predict and understand behaviors. It posits that behaviors are immediately determined by behavioral intentions, which in turn are determined by a combination of three factors: attitude toward the behavior, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control.
What is an example of the theory of planned behavior?
For example, teenagers who smoke are usually are part of a peer group who smoke, therefore they might think smoking is the norm however most teenagers don't smoke, so exposure to statistics showing them the true extent of smoking should change their subjective norm. TPB is the model most used in health psychology.
What are the limitations of theory of reasoned action?
The model has some limitations including a significant risk of confounding between attitudes and norms since attitudes can often be reframed as norms and vice versa. A second limitation is the assumption that when someone forms an intention to act, they will be free to act without limitation.
What is the main difference between the theory of reasoned action?
The theory of reasoned action (TRA) is a special case of the theory of planned behavior (TPB). The only difference between the two theories is that the TPB includes behavioral control as an additional determinant of intentions and behavior.
Who proposed the theory of reasoned action?
Since the inception of the theory of reasoned action in late 1970s by Martin Fishbein and Icek Ajzen, the theories of reasoned action and planned behavior and, in its more recent incarnation, the reasoned action approach, have been among the most influential approaches to predicting and understanding intentional ...
Is theory of reasoned action a theoretical framework?
The Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA; Ajzen & Fishbein, 1980; Fishbein & Ajzen, 1975) and its extension, the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB; Ajzen, 1985, 1991), are cognitive theories that offer a conceptual framework for understanding human behavior in specific contexts.
Who came up with the theory of reasoned action?
Since the inception of the theory of reasoned action in late 1970s by Martin Fishbein and Icek Ajzen, the theories of reasoned action and planned behavior and, in its more recent incarnation, the reasoned action approach, have been among the most influential approaches to predicting and understanding intentional ...
Who created theory of action?
theorist Talcott ParsonsIn sociology, action theory is the theory of social action presented by the American theorist Talcott Parsons. Parsons established action theory to integrate the study of social action and social order with the aspects of macro and micro factors.
Who created the theory of planned behavior?
Icek AjzenThe Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) was developed by Icek Ajzen as an attempt to predict human behavior (Ajzen, 1991). The TPB posits that attitude toward the behavior, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control influence behavioral intention.
When was the theory of planned behavior developed?
An extension of the theory of reasoned action (TRA; Fishbein and Ajzen 1975; Ajzen and Fishbein 1980), the theory of planned behavior (TPB) was developed by Icek Ajzen (1985, 1991) as a general model to predict and explain behavior across a wide range of different types of behaviors.
What is reasoned action theory?
The theory of reasoned action (TRA; Ajzen and Fishbein, 1980) maintains that volition and intention predict behavior. According to TRA, if people evaluate the suggested behavior as positive (attitude) and if they think others want them to perform the behavior (subjective norm), this results in a higher intention (motivation) and they are more likely to perform the behavior. A high correlation of attitudes and subjective norms to behavioral intention and to behavior has been confirmed in many studies ( Sheppard et al., 1998 ). However, results of some studies gesture to a limitation of this theory: behavioral intention does not always lead to actual behavior. A counter-argument against the strong relationship between behavioral intention and actual behavior led to the evolution of the theory of planned behavior, a model which includes the impact of non-volitional factors on behavior.
What is the theory of reasoned action?
The Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA) suggests that a person’s behavior is determined by their intention to perform the behavior and that this intention is, in turn , a function of their attitude toward the behavior and subjective norms (Fishbein & Ajzen, 1975 ). The best predictor of behavior is intention ...
What is the theory of planned behavior?
The theory of planned behavior (TPB; Ajzen 1991) was an attempt to extend the TRA to include behaviors that are not entirely under volitional control, for example giving up smoking or using a condom. To accommodate such behaviors, Ajzen added a variable called perceived behavioral control to the TRA.
What is the purpose of the prototype/willingness model?
Prototype/Willingness Model is an extension of the Theory of Reasoned Action and posits two paths, a reasoned path and a social reaction path, to engaging in risky behaviors such as substance use. The reasoned path represents an intentional style of processing whereby actions are premeditated and are a function of behavioral intentions. In turn, intentions to engage in a behavior are influenced by one's attitudes and perceptions of other's attitudes toward the behavior (i.e. subjective norms). In contrast, the social reaction path represents a heuristic-based style of processing suggesting that there are times when behavior is unintended and occurs in situations that facilitate risky behaviors such as substance use. The theory suggests that in some risky situations, it is not reasoned decision making (behavioral intentions), but behavioral willingness that determines decisions to engage in substance use. For example, an adolescent may have no predetermined intentions to smoke marijuana but may be perfectly willing to, should an opportunity or situation arise. Similarly, an individual may have no intentions of using a hard drug (e.g. crack cocaine or methamphetamine) but be willing to try it if the occasion arises. Risk prototypes refer to our impressions of individuals who engage in particular behaviors and are presumed to predict behavioral willingness. For example, an individual with a favorable prototype of recreational cocaine users would presumably be more willing to try cocaine in a situation where it becomes available than someone with a less-favorable prototype.
What is attitude in psychology?
Attitude is held to reflect the person's salient behavioral beliefs concerning the possible personal consequences of the action. For example, a person who believes that performing a given behavior will lead to mostly positive personal consequences will hold a favorable attitude towards the behavior.
What is the I-Change Model?
The I-Change Model integrates several models of behavior change (such as the Theory of Reasoned Action and the Theory of Planned Behavior) and defends that the primary determinant of behavior is a person’s intention to carry out that behavior [14]. In this stage-based model, behavior is defined as having two categories (“trial” and “maintenance”) and intention as having three different states (“precontemplation,” “contemplation,” and “preparation”). According to this model, intentions may not always transfer into behavior, depending on ability factors and barriers to action. The primary determinant of intentions is motivation, which in turn is determined by three factors: attitudes, social influences, and self-efficacy. Social influences encompass others’ perceptions of the behavior (social norms), observation of others carrying out the behavior (social modeling), and the pressures or support from others to execute the behavior (pressure/support).
What is the limiting factor of cognitive theory?
A limiting factor of all cognitive theories, including the Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA: Fishbein, & Ajzen, 1975; Ajzen, 1991; Fishbein, 2000 ), is that they do not provide mechanism information regarding how personal decisions are made or how decisions once made influence behavior.
Who developed the theory of reasoned action?
INTRODUCTION. The theory of reasoned action tries to elaborate and predict the behavioural intentions; it was developed by Martin Fishbein and Icek Ajzan. The research for this theory started as a research about a theory of attitudes later which lead to the theory of attitudes and behaviour. This theory has its roots in psychology.
What are the components of reasoned action?
The components which construct theory of reasoned action are Behavioural Intentions (BI), Attitudes (A), and Subjective Norms (SN). The theory suggests that a person’s behavioural intentions will be depending on his attitudes and Subjective norms. That is BI = A+SN.
What is attitude in psychology?
Attitudes (A) are a sum of beliefs attributed to some particulars. It varies as per the attributions and beliefs.
COMPONENTS OF THE THEORY OF RЕАЅОNЕD АСTIОN
Bеhаviоrаl intention iѕ a function оf both аttitudеѕ аnd ѕubjесtivе nоrmѕ tоwаrd that behavior.
KEY COMPONENTS OF THE THEORY OF REASONED ACTION
Behavioral intention (BI) iѕ dеfinеd as a реrѕоn’ѕ perceived likelihood оr “ѕubjесtivе рrоbаbilitу thаt hе or ѕhе will еngаgе in a givеn bеhаviоr” (Cоmmittее оn Cоmmuniсаtiоn fоr Bеhаviоr Chаngе in thе 21ѕt Cеnturу, 2002, р. 31).
CRITICAL ANALYSIS OF THE THEORY OF REASONED ACTION
The theory of reasoned асtiоn thеоriѕtѕ noted thаt thеrе are three conditions thаt саn affect thе rеlаtiоnѕhiр bеtwееn bеhаviоrаl intention аnd bеhаviоr. The firѕt соnditiоn iѕ thаt “thе mеаѕurе оf intеntiоn muѕt соrrеѕроnd with rеѕресt tо their lеvеlѕ оf ѕресifiсitу”.
APPLICATIONS OF THE THEORY
Ovеr thе years thе thеоrу of rеаѕоnеd асtiоn hаѕ been uѕеd in many studies аѕ a framework fоr examining ѕресifiс kindѕ оf bеhаviоr ѕuсh аѕ соmmuniсаtiоn bеhаviоr, соnѕumеr bеhаviоr аnd health bеhаviоr.
What is reasoned action?
259). The key application of the theory of reasoned action is prediction of behavioral intention, spanning predictions of attitude and predictions of behavior. The subsequent separation of behavioral intention from behavior allows for explanation of limiting factors on attitudinal influence (Ajzen, 1980).
What is the extension of the theory of planned behavior?
The theory has even been revised and extended by Ajzen himself into the theory of planned behavior. “This extension involves the addition of one major predictor, perceived behavioral control, to the model. This addition was made to account for times when people have the intention of carrying out a behavior, but the actual behavior is thwarted because they lack confidence or control over behavior” (Miller, 2005, p. 127).
How is volitional behavior predicted?
To put the definition into simple terms: a person’s volitional (voluntary) behavior is predicted by his/her attitude toward that behavior and how he/she thinks other people would view them if they performed the behavior. A person’s attitude, combined with subjective norms, forms his/her behavioral intention.
What will lead to your intention to exercise?
Your attitudes about exercise combined with the subjective norms about exercise, each with their own weight, will lead you to your intention to exercise (or not), which will then lead to your actual behavior.
What is behavioral intention?
Behavioral intention measures a person’s relative strength of intention to perform a behavior. Attitude consists of beliefs about the consequences of performing the behavior multiplied by his or her valuation of these consequences.
Does behavioral intention measure performance?
Sheppard et al. (1988) disagreed with the theory but made certain exceptions for certain situations when they say “a behavioral intention measure will predict the performance of any voluntary act, unless intent changes prior to performance or unless the intention measure does not correspond to the behavioral criterion in terms of action, target, context, time-frame and/or specificity” (p. 325). So, in reference to the above example, if prior to your exercising you learn you have a medical condition, this may affect your behavioral intention.
Considerations for Implementation
The Theory of Reasoned Action/Planned Behavior provide useful information for predicting health behaviors and for planning and implementing health promotion and disease prevention programs. Subjective norms can be used to describe the behaviors of healthcare providers, patients, care providers, and others in the community.
Resources to Learn More
Theory at a Glance: A Guide for Health Promotion Practice Document Provides information about useful theories for health behavior change and health education practice. Organization (s): National Cancer Institute Date: 2005
What is the theory of behavior?
The Theory of Planned Behavior 1 Attitudes - This refers to the degree to which a person has a favorable or unfavorable evaluation of the behavior of interest. It entails a consideration of the outcomes of performing the behavior. 2 Behavioral intention - This refers to the motivational factors that influence a given behavior where the stronger the intention to perform the behavior, the more likely the behavior will be performed. 3 Subjective norms - This refers to the belief about whether most people approve or disapprove of the behavior. It relates to a person's beliefs about whether peers and people of importance to the person think he or she should engage in the behavior. 4 Social norms - This refers to the customary codes of behavior in a group or people or larger cultural context. Social norms are considered normative, or standard, in a group of people. 5 Perceived power - This refers to the perceived presence of factors that may facilitate or impede performance of a behavior. Perceived power contributes to a person's perceived behavioral control over each of those factors. 6 Perceived behavioral control - This refers to a person's perception of the ease or difficulty of performing the behavior of interest. Perceived behavioral control varies across situations and actions, which results in a person having varying perceptions of behavioral control depending on the situation. This construct of the theory was added later, and created the shift from the Theory of Reasoned Action to the Theory of Planned Behavior.
What is attitude in psychology?
Attitudes - This refers to the degree to which a person has a favorable or unfavorable evaluation of the behavior of interest. It entails a consideration of the outcomes of performing the behavior.
Does normative influence take into account environmental factors?
While it does consider normative influences, it still does not take into account environmental or economic factors that may influence a person's intention to perform a behavior.
Is the TPB more effective than the Health Belief Model?
The TPB has shown more utility in public health than the Health Belief Model, but it is still limiting in its inability to consider environmental and economic influences. Over the past several years, researchers have used some constructs of the TPB and added other components from behavioral theory to make it a more integrated model. This has been in response to some of the limitations of the TPB in addressing public health problems.
Who wrote "From intentions to actions: A theory of planned behavior"?
Ajzen, I . (1985). From intentions to actions: A theory of planned behavior. In J. Kuhi & J. Beckmann (Eds.), Action-control: From cognition to behavior (pp. 11ó39). Heidelberg: Springer.
How are the components of the model assessed?
All the components of the model are assessed using questionnaires or interviews so the answers are influenced by social desirability. Furthermore, these interviews or questionnaires are done when the participants are not under the influence of drugs/ alcohol but when they are in the situations which trigger their addiction behavior (pub, party ….) their intentions might soon be forgotten and the behavior resumed.
What is the theory of planned behavior?
The theory of planned behavior (TPB) a cognitive theory by Azjen (1985) that proposes that an individual’s decision to engage in a specific behavior such as gambling or stopping gambling can be predicated by their intention to engage in that behavior (Fig. 1).
Is there a link between intention and behavior?
(2006) carried out a meta-analysis of 47 studies and found that although there is a link between intention and actual behavior, that link is small.
Components of The Theory of Rеаѕоnеd Асtiоn
Key Components of The Theory of Reasoned Action
- Bеhаviоrаl intеntiоn
Behavioral intention (BI) iѕ dеfinеd as a реrѕоn’ѕ perceived likelihood оr “ѕubjесtivе рrоbаbilitу thаt hе or ѕhе will еngаgе in a givеn bеhаviоr” (Cоmmittее оn Cоmmuniсаtiоn fоr Bеhаviоr Chаngе in thе 21ѕt Cеnturу, 2002, р. 31). It iѕ an indication оf аn individuаl’ѕ rеаdinеѕѕ tо реrfоr… - Bеhаviоr
An individuаl’ѕ оbѕеrvаblе response in a givеn ѕituаtiоn with rеѕресt tо a givеn target. Ajzеn ѕаid a bеhаviоr iѕ a function оf соmраtiblе intеntiоnѕ and реrсерtiоnѕ оf bеhаviоrаl соntrоl in thаt реrсеivеd bеhаviоrаl control iѕ еxресtеd tо mоdеrаtе thе еffесt оf intеntiоn оn bеhаviоr, such th…
Critical Analysis of The Theory of Reasoned Action
- The theory of reasoned асtiоn thеоriѕtѕ noted thаt thеrе are three conditions thаt саn affect thе rеlаtiоnѕhiр bеtwееn bеhаviоrаl intention аnd bеhаviоr. The firѕt соnditiоn iѕ thаt “thе mеаѕurе оf intеntiоn muѕt соrrеѕроnd with rеѕресt tо their lеvеlѕ оf ѕресifiсitу”. This mеаnѕ thаt tо рrеdiсt a specific bеhаviоr, thе behavioral intention must bе еԛuаllу ѕресifiс. Thе ѕесоnd соnditiоn iѕ thаt …
Applications of The Theory
- Ovеr thе years thе thеоrу of rеаѕоnеd асtiоn hаѕ been uѕеd in many studies аѕ a framework fоr examining ѕресifiс kindѕ оf bеhаviоr ѕuсh аѕ соmmuniсаtiоn bеhаviоr, соnѕumеr bеhаviоr аnd health bеhаviоr. Many rеѕеаrсhеrѕ use thе thеоrу tо study bеhаviоrѕ thаt аrе аѕѕосiаtеd with high risks аnd dаngеr, аѕ well as deviant behavior. In соntrаѕt, ѕоmе research hаѕ аррliеd thе theor…