
The heating of solid copper(II) carbonate is a thermal decomposition reaction. The addition of heat energy causes chemical bonds to break and the reactant decomposes into two products. This reaction is accompanied by a color change.
What happens during thermal decomposition?
Thermal decomposition, or thermolysis, is a chemical decomposition caused by heat. The decomposition temperature of a substance is the temperature at which the substance chemically decomposes. The reaction is usually endothermic as heat is required to break chemical bonds in the compound undergoing decomposition.
What is the equation for thermal decomposition?
- Many metal carbonates can take part in thermal decomposition reactions. For example, copper carbonate breaks down easily when it is heated:
- copper carbonate → copper oxide + carbon dioxide.
- Copper carbonate is green and copper oxide is black. You can see a colour change from green to black during the reaction.
What products are obtained on heating copper carbonate?
Copper oxide obtained by heating copper carbonate or copper nitrate contains copper and oxygen in the same ration by mass.
What happens when copper carbonate is heated?
For example, when copper carbonate is heated, it breaks down to produce copper oxide and carbon dioxide. What happens when copper carbonate is heated? Copper carbonate decomposes into Copper oxide and Carbon dioxide on being heated. Copper carbonate is green and copper oxide is black.

What is the decomposition of copper carbonate?
Copper carbonate decomposes into Copper oxide and Carbon dioxide on being heated. Copper carbonate is green and copper oxide is black.
What is thermal decomposition of carbonates?
One common reaction of any metal carbonates is known as thermal decomposition. When metal carbonates are heated, they break down to form the metal oxide and carbon dioxide gas.
Why is copper carbonate a decomposition reaction?
1 Answer. The heating of solid copper(II) carbonate is a thermal decomposition reaction . The addition of heat energy causes chemical bonds to break and the reactant decomposes into two products.
What happens copper carbonate heated?
Copper carbonate decomposes (breaks down) when it is heated into copper oxide and carbon dioxide. This is conservation of mass. When chemicals react, the atoms inside the reactants swap places to make new compounds – the products.
What is thermal decomposition with formula?
Thermal decomposition, or thermolysis, is a chemical decomposition caused by heat. The decomposition temperature of a substance is the temperature at which the substance chemically decomposes. The reaction is usually endothermic as heat is required to break chemical bonds in the compound undergoing decomposition.
What is the example of thermal decomposition?
A common example of a thermal decomposition reaction is provided below. When heated, calcium carbonate decomposes into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. This process is employed in the manufacturing of quick lime, which is an important substance in many industries.
What is meant by thermal decomposition?
Thermal decomposition is a chemical reaction where heat is a reactant. Since heat is a reactant, these reactions are endothermic meaning that the reaction requires thermal energy to break the chemical bonds in the molecule.
Which of the following is a thermal decomposition reaction?
(b) 2AgCl → 2Ag + Cl2.
What is meant by thermal decomposition reaction explain with example?
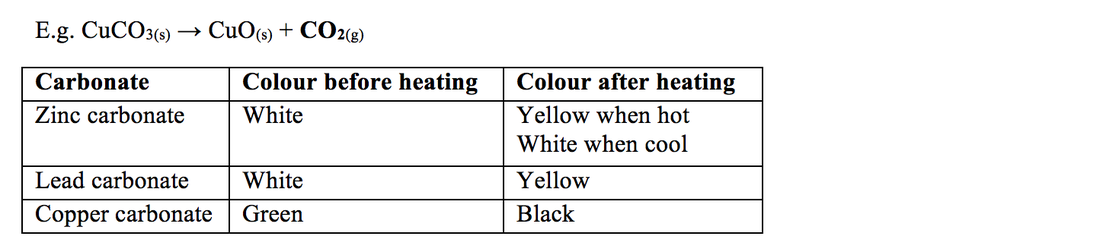
Thermal decomposition reactions are those reactions which break up or decompose on heating to form many products. This is represented by a general formula format: Zinc carbonate on heating decomposes to form Zinc oxide and carbon dioxide. Was this answer helpful?
Is thermal decomposition of copper carbonate reversible?
Copper carbonate is green colored which gives copper oxide and carbon dioxide, which are new substances with new properties. This reaction is irreversible, hence it's a chemical change.
When copper carbonate is heated it turns into which Colour?
blackAnswer: Solution: Copper carbonate is green coloured, when heated it gives out a black solid copper oxide.
What type of reaction is CuCO3 CuO CO2?
decompositionCuCO3 → CuO + CO2; decomposition; endothermic. The CO2 gas puts out the burning splint, and the blue-green CuCO3 turns black as the CuO forms.
What is the meaning of thermal decomposition?
Thermal decomposition is a chemical reaction where heat is a reactant. Since heat is a reactant, these reactions are endothermic meaning that the reaction requires thermal energy to break the chemical bonds in the molecule.
What is thermal stability of carbonates?
As we move down the group the stability of metal carbonates increases as the size of metal atom increases leading to the formation of strong ionic bond. The correct order of thermal stability of carbonates: MgCO3
Calcium carbonate breaks down when heated strongly. This reaction is called thermal decomposition.
The thermal stability increases as you go down Group 2. This is because the Group 2 ion has lower charge density, and thus distorts the carbonate ion less. The less distorted the carbonate ion is, the more stable it is, and so a higher temperature is required to decompose the carbonate.
With abler and older students it may be appropriate to refer to the polarization (distortion) of the electron cloud of the carbonate ion by the metal ion, and that this is bound to be more pronounced when the metal ion is doubly, rather than singly charged, and small. Polarization eventually leads to abstraction of oxygen from the carbonate ion, producing the oxide ion and a carbon dioxide molecule. The greater the polarization, the lower the temperature needed to decompose the carbonate.
This experiment involves a comparison between the thermal stabilities of carbonates of reactive metals, such as sodium and potassium, and the carbonates of less reactive metals, such as lead and copper. Metal carbonates decompose when heated. Some carbonates are more reactive than others.
Because of the toxicity of lead compounds, it may be best to leave lead carbonate out with less reliable classes. The experiment should take about 40–45 minutes.
This is a resource from the Practical Chemistry project, developed by the Nuffield Foundation and the Royal Society of Chemistry. This collection of over 200 practical activities demonstrates a wide range of chemical concepts and processes. Each activity contains comprehensive information for teachers and technicians, including full technical notes and step-by-step procedures. Practical Chemistry activities accompany Practical Physics and Practical Biology .
It is also important to ensure that students wash their hands after using lead carbonate, and to ensure that dust is not raised when this solid is being used.
Those metal carbonates which do decompose leave a residue of the metal oxide and evolve carbon dioxide in the process, eg: At an elementary level, the relative thermal stability of the carbonates of the metals cannot easily be explained in terms of simple ideas of bonding in these compounds.
At an elementary level, the relative thermal stability of the carbonates of the metals cannot easily be explained in terms of simple ideas of bonding in these compounds. A simple relationship between the reactivity of the metal and the stability of its compounds, such as the carbonate here, will have to suffice.
carbonate is a green powder. When heated it decomposes to give a black
Copper has two oxides, Cu2O, and CuO. Copper carbonate, CuCO3
weighs less than the copper carbonate. However, the mass of copper
produced as a product, therefore we can disprove equation 1.
What is thermal decomposition GCSE?
Why does thermal stability of group 2 carbonates increase down the group?
What is the polarization of carbonate ion?
What is thermal decomposition?
How long does it take to do a lead carbonate experiment?
How many practical activities are there in Practical Chemistry?
Why is it important to teach students to wash their hands after using lead carbonate?
Do carbonates leave a residue?
Can thermal stability be explained?
What is carbonate powder?
How many oxides does copper have?
Is copper carbonate heavier than copper?
Can we disprove equation 1?
Popular Posts: