
What is the time difference between two high tides called?
The time difference between two high tides is called “Tidal Interval”. The tidal cycle in this pattern is called semidiurnal. However, most of the enclosed water bodies or away from the open ocean such as Caribbean sea or Caspian Sea, there are only one high tide and one low tide. This pattern is called Diurnal tides.
How many tides are there in a day?
In most coastal areas around the world there are two tidal cycles (meaning 2 low tides and 2 high tides) over the course of what is called a lunar day (24 h and 50 min) – which is the time it takes for the moon to complete a full rotation around the Earth.
What is the difference between tidal current and incoming tide?
tide. This is called the tidal current. The incoming tide along the coast and into the bays and estuaries is called a flood current; the outgoing tide What is the difference between red tide and blue tide?
How do I find the best time of the tide?
Begin with a tide station next to where the water has to pass through to get to where you want to fish. Then, select a tide station on the other side of where you are fishing. The difference between these two stations will give you an idea of the tide in the area between them. There is no way to uncover the perfect time of the tide.
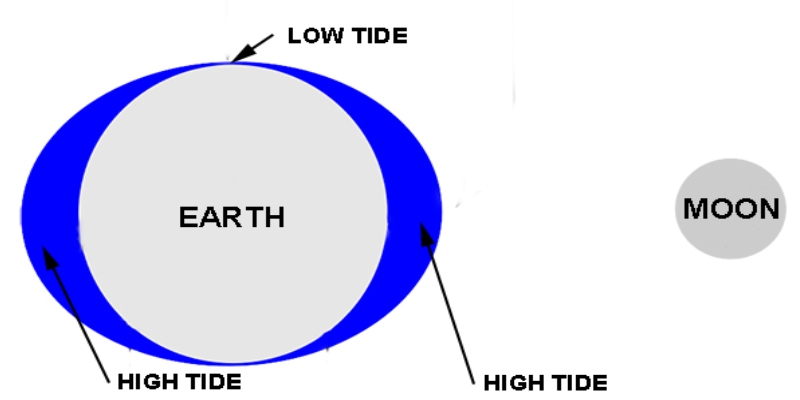
Why are tides 50 minutes apart?
The reason that a lunar day is longer than a normal 24-hour day is because the moon rotates around the Earth in the same direction that the Earth is spinning. It takes the Earth an extra 50 minutes to “catch up” to the moon.
Is the time between tides always the same?
Due to the Moon's orbital prograde motion, it takes a particular point on the Earth (on average) 24 hours and 50.5 minutes to rotate under the Moon, so the time between high lunar tides fluctuates between 12 and 13 hours.
Is tide every 3 or 6 hours?
Because the Earth rotates through two tidal “bulges” every lunar day, coastal areas experience two high and two low tides every 24 hours and 50 minutes. High tides occur 12 hours and 25 minutes apart. It takes six hours and 12.5 minutes for the water at the shore to go from high to low, or from low to high.
Why are tides delayed by 26 minutes?
Periodicity of tides Every place should experience tide after 12 hours but this never happens. Each day tide is delayed by 26 minutes because the moon also rotates on its axis while revolving round the earth.
Are tides the same every day?
It depends. Most coastal locations have two unequal high tides a day. If the Earth were a perfect sphere without large continents, and if the earth-moon-sun system were in perfect alignment, every place would get two equal high and low tides every day.
What is the time interval between one primary and secondary tide?
Hence, the correct answer is 24 hours and 50 minutes.
How do you calculate tide times?
The rule of twelfths works like this; take the difference in height between the high and low tide on that day, and divide that by 12 equal chunks.
What is the time interval between tides name the factors responsible for this time interval?
On account of the continuous rotation of the earth and revolution of the moon around the earth, whenever the moon comes in the front of the earth, tide takes place at an interval of 24 hours and 52 minutes and at the same time on the opposite side of the earth the interval is of 12 hours and 26 minutes.
Answer
The time difference between each tide is approximately 12 hours and 26 minutes if there is a high tide at 8. Am
New questions in Geography
Why could the combination of high rainfall, steep slopes earthquakes be lethal for a populated are near a volcano?
What are tides called?
Tides create a current in the oceans, near the shore, and in bays and estuaries along the coast. These are called "tidal currents.". Tidal currents are the only type of currents that change in a very regular pattern and can be predicted for future dates.
How do tides work?
Tides are characterized by water moving up and down over a long period of time. When used in association with water, the term "current" describes the motion of the water. Oceanic currents are driven by several factors. One is the rise and fall of the tides. Tides create a current in the oceans, near the shore, and in bays and estuaries along ...
What causes tides to move?
Pictured: Lowtide in Islesboro, Maine. Tides are driven by the gravitational force of the moon and sun. Tides are characterized by water moving up and down over a long period of time.
How fast are wind currents measured?
These currents are generally measured in meters per second or in knots (1 knot = 1.85 kilometers per hour or 1.15 miles per hour). Winds drive currents near coastal areas on a localized scale and in the open ocean on a global scale.
What is the third factor that drives currents?
A third factor that drives currents is thermohaline circulation - a process driven by density differences in water due to temperature (thermo) and salinity (haline) in different parts of the ocean. Currents driven by thermohaline circulation occur at both deep and shallow ocean levels and move much slower than tidal or surface currents.
How many high tides and low tides per day?
Tidal forces create 2 high tides and 2 low tides per day. This is due to the fact that the Earth is spinning, so if you are in a part of the Earth…
Why are tides so hard to explain?
Part of the reason tidal forces are so hard to explain is that they are something that only happen out in space. I can’t give you an example or an analogy from down here on Earth that will help you understand it, because here we have the Earth’s gravity.
How many high tides does the Moon have?
The gravitational pull that the Moon exerts on the Earth combined with the Earth’s spin causes 2 high tides and 2 low tides per day.
How long is a tidal cycle?
One tidal cycle comprises two high tides and two low tides. One tidal cycle completes in 24 hours and 50.4 minutes. This is because of the revolution of Moon around the earth and both earth’s rotation and moon revolution are in same direction. The time difference between two high tides is called “Tidal Interval”. The tidal cycle in this pattern is called semidiurnal. However, most of the enclosed water bodies or away from the open ocean such as Caribbean sea or Caspian Sea, there are only one high tide and one low tide. This pattern is called Diurnal tides. At the coast of the oceans, there may be two high tides, of unequal length. This is called Mixed Tides.
Why do tides get bigger?
If there is a place where the water gets funneled (like the Bristol Channel in the UK) then the size of the tide is magnified because the extra water is being squeezed together. Similarly, you can end up with four smaller tides if there is a small island and the water runs round each side of it at different speeds. This can be seen at Bournemouth in the UK because of the Isle of Wight.
How does the Sun affect tides?
When the Earth, Moon and Sun are aligned, tidal forces add up (the high and low tides get accentuated). However, when the Moon is at right angles to the Sun relative to the Earth, tidal forces counteract (the high and low tides are slightly lower). I will probably elaborate more on this in another answer… so don’t forget to keep an eye!
What is the force of gravity that causes tides?
The tidal force is a secondary effect of gravity and it is what causes the phenomenon of tides. It arises because the gravitational force exerted by one body on another is not constant across it, because the force of gravity decreases as the distance between the two bodies increases.
