What is Stage 1 Labor?
The three stages of labor and childbirth include the following:
- Labor: This includes early, active and transitional labor.
- Pushing and delivery of the baby: This phase of labor begins with pushing and ends with the delivery and birth of your baby.
- Delivery of the placenta: Your placenta will either naturally be expelled or need to be removed by your doctor after your baby is born.
What is the first stage of Labor?
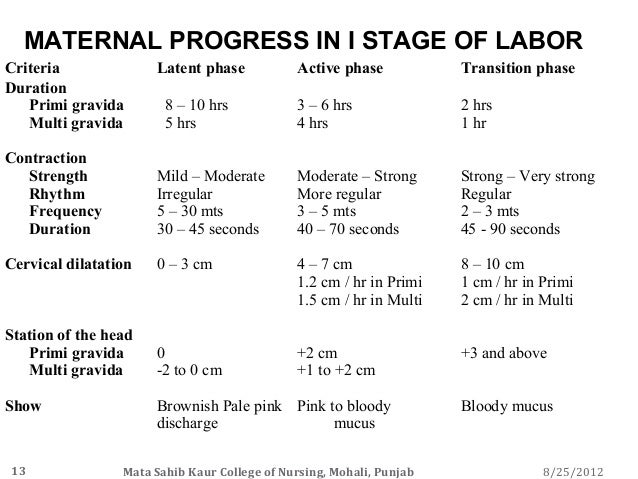
The first stage of labor is divided into three phases: early, active and transition. The first stage of labor is when the cervix dilates (opens) to 10 centimeters. Early labor contractions pull on the cervix, which looks a bit like the neck of a turtleneck sweater. Contractions shorten or thin the cervix.
What are the three phases of transition?
What are the stages of transition?
- Endings. Transition starts with an ending. This is paradoxical but true. ...
- Neutral Zone. The second step of transition comes after letting go: the neutral zone. ...
- New Beginnings. Beginnings involve new understandings, values and attitudes. Beginnings are marked by a release of energy in a new direction – they are an expression of a fresh identity.
What is the transitional stage of Labor?
- First stage of labor. Thinning (effacement) and opening (dilation) of the cervix.
- Second stage of labor. Your baby moves through the birth canal.
- Third stage of labor. Afterbirth.
- Fourth stage of labor. Recovery.

How long is the transition phase of labor?
Transition to the second stage of labor It can last 15 minutes to an hour. During the transition: Contractions come closer together and can last 60 to 90 seconds. You may feel like you want to bear down.
What are the 4 stages of labor?
Labor happens in four stages:First stage: Dilation of the cervix (mouth of the uterus)Second stage: Delivery of the baby.Third stage: Afterbirth where you push out the placenta.Fourth stage: Recovery.
What are the 3 phases in labor?
There are three stages of labour. The first stage is when your cervix is opening and your baby is moving down the birth canal. The second stage is when your baby is being born and the third stage is when the placenta is delivered. Understanding the stages of birth can help you know what is happening during your labour.
What are common maternal characteristics the transition stage of labor?
Many women become restless, irritable, discouraged and confused. During the transition phase, women focus inward and may have a hard time communicating with others or following directions. This is the time during labor when the woman needs the most support for both her physical and psychosocial needs.
What are the 5 P's of labor?
There are five essential factors that affect the process of labor and delivery. They are easily remembered as the five Ps (passenger, passage, powers, placenta, and psychology).
What stage of labor is the longest?
First Stage or Early Labor The first stage of labor, also called early labor, is by far the longest. It begins at the onset of labor and continues until the cervix is fully dilated.
Which client behavior is expected during the transition phase of the first stage of labor?
Which client behavior is expected during the transition phase of the first stage of labor? A client in the transition phase of the first stage of labor has strong uterine contractions, resulting in severe pain. The client may hyperventilate, resulting in nausea and vomiting.
How many stages are there in labor and delivery?
Labour and delivery is divided into three stages, though every woman experiences these stages differently. The first stage of labour lasts from the time when you start having contractions until your cervix is fully dilated. Stage one is broken down into the early phase, the active phase and the transition phase.
What are the interventions a nurse can do during the transition phase?
Transition PhaseInform patient on progress of her labor.Assist patient with pant-blow breathing.Monitor maternal vital signs and fetal heart rate every 30 minutes -1 hour, or depending on the doctor's order. Contraction monitoring is also continued.When perineal bulging is noticeable, prepare for delivery.
Can you sleep through contractions?
These contractions may be slightly uncomfortable and feel like mild to moderate menstrual cramps. Usually, they're intermittent and variable, seven to ten or even twenty or more minutes apart. You may be able to sleep or do other activities while experiencing them.
How long does it take to push a baby out?
For first-time mothers the average length of pushing is one-to-two hours. In some instances, pushing can last longer than two hours if mother and baby are tolerating it. Normally, the baby is born with his face looking toward mother's back (referred to as an anterior position).
What are the 7 cardinal movements of labor?
Anglo-American literature lists 7 cardinal movements, namely engagement, descent, flexion, internal rotation, extension, external rotation, and expulsion.
How long can pre labor last?
It may last up to 2 to 3 days. Contractions are mild to moderate and shorter (about 30 to 45 seconds). You can usually keep talking during them. Contractions may also be irregular, about 5 to 20 minutes apart.
Stage 1: Early Labor and Active Labor
The first stage of labor and birth occurs when you begin to feel regular contractions, which cause the cervix to open (dilate) and soften, shorten...
Stage 2: The Birth of Your Baby
It's time! You'll deliver your baby during the second stage of labor.How long it lasts: It can take from a few minutes up to a few hours or more to...
Stage 3: Delivery of The Placenta
After your baby is born, you'll likely feel a great sense of relief. You might hold the baby in your arms or on your abdomen. Cherish the moment. B...
How long does the transition phase of labor last?
However, it is also the shortest phase of the first stage generally lasting approximately 20 to 90 minutes.
What is the most intense phase of labor?
Transition can be the most intense phase of labor, but it is also usually the shortest. In first pregnancies, transition generally lasts no more than a couple of hours. Transition is when many women will consider having an epidural, so it is important to keep in mind that this is the home stretch, with your body having already accomplished most of the daffy cult work. During this phase, contractions are stronger, longer, and more frequent as they dilate your cervix and move your baby down the birth canal. Contractions may come so close together that they seem to merge into one long one with an overwhelming urge to push. Do whatever makes you feel more comfortable and helps you handle the intensity of labor.#N#At this point, comfort items such as mood music, a favorite pillow, or a photograph of your dog may become distracting and annoying, and even words of encouragement from your birthing partner may grate on your nerves. You may be irritable, nauseated, or shaky, with trembling thighs and knees. You may vomit, panic, or feel out of control.
What happens during a woman's transition?
In addition to the intense contractions most women experience nausea and vomiting, burping, hiccups, shaking of the body, hot and cold feelings, or sensitivity to touch during transition. Many women become restless, irritable, discouraged and confused. During the transition phase, women focus inward and may have a hard time communicating ...
What are the stages of labor and birth?
Stages of labor and birth: Baby, it's time! Labor is a natural process. Here's what to expect during the three stages of labor and birth — and what you can do to promote comfort. Every woman's labor is unique, even from one pregnancy to the next. Sometimes labor is over in a matter of hours.
What is the name of the contraction that opens and thins out during labor?
Close. Cervical effacement and dilation. Cervical effacement and dilation. During the first stage of labor, the cervix opens (dilates) and thins out (effaces) to allow the baby to move into the birth canal. In figures A and B, the cervix is tightly closed.
What happens when you have a cervix?
Early labor. During early labor, your cervix dilates and effaces. You'll feel mild, irregular contractions. As your cervix begins to open, you might notice a clear, pink or slightly bloody discharge from your vagina. This is likely the mucus plug that blocks the cervical opening during pregnancy.
How long does it take for a placenta to be delivered?
How long it lasts: The placenta is typically delivered in five to 30 minutes, but the process can last as long as an hour.
How to stay motivated after delivery?
To stay motivated, you might ask to feel the baby's head between your legs or see it in a mirror. After your baby's head is delivered, the rest of the baby's body will follow shortly. His or her airway will be cleared if necessary. Your health care provider or labor coach will then cut the umbilical cord.
How long does it take to deliver a baby?
It's time! You'll deliver your baby during the second stage of labor. How long it lasts: It can take from a few minutes up to a few hours or more to push your baby into the world. It might take longer for first-time moms and women who've had an epidural.
What is the longest stage of birth?
This allows the baby to move into the birth canal. The first stage is the longest of the three stages. It's actually divided into two phases of its own — early labor (latent phase) and active labor.
What is transitional labor?
During the third and final phase of labor, called transitional labor , your cervix will dilate to 10 centimeters as you experience strong contractions about every two to three minutes, though it can vary.
What is the first phase of labor?
Phase 1: early (latent) labor. The first of the three stages of labor, called the latent phase, is usually the longest. Thankfully, it's also the least intense by far. Over a span of time from several hours to several weeks, often without noticeable or bothersome contractions (or over a period of no-doubt-about-it contractions), ...
What happens during the other two stages of labor and childbirth?
The three phases of labor are the first part of a larger picture: The three stages of childbirth. Once you’ve made it through labor, the two other childbirth stages include:
What are the three stages of labor?
The three stages of labor and childbirth include the following:
What is active labor?
During active labor, your cervix dilates to about 7 to 8 centimeters. Contractions will be more evenly spaced, intense, and frequent, coming about every three to four minutes apart. Active labor usually lasts from two to three-and-a-half hours (with a wide range of what's considered normal).
How long do labor contractions last?
They generally last 30 to 45 seconds and can be regular or irregular. They’ll gradually become more frequent, spaced up to about 20 minutes apart at first to about five minutes apart by the end of early labor.
How to know if you are in early labor?
You'll experience mild to moderate contractions that last 30 to 45 seconds, though they can be shorter, and might be regular or irregular. They may be spaced around 20 minutes apart and become progressively closer together, but not necessarily in a consistent pattern.
What is transitional labor?
Image: Getty Images. Transitional labor is a pretty intense time during the whole labor process. It’s the stage between active labor —when you’re hanging out in the hospital having contractions maybe three to five minutes apart—and actually starting to push for delivery.
How long does it take to get through transitional labor?
And don’t worry—transitional labor is typically pretty short (about 15 minutes to an hour), and once you get through it, you’re almost there!
What is the transition phase?
Transition is the final phase of the first stage of labour, following early and active labour. At this point, a woman progresses from seven to 10 centimetres, often in less than an hour. The word transition means that her body is making the shift from opening the cervix to the beginning of the baby’s descent. ...
What is the new sensation in labor?
Your job is to follow your body’s lead: Accept, and work with, the sensations that are bringing your baby to you. In transition, a new sensation is rectal pressure. Some women tense with this sensation, but your body needs to relax to it.
What are the emotional challenges of transition?
But transition is best known for its emotional challenges. Nanaimo, BC, labour nurse Andrea Wing says Parkinson’s responses were typical. “A woman’s behaviour may change. She doesn’t know what to do. She may be panicked or scared, and nothing helps. At this point, some women say, “I can’t do this” or “I need something for the pain.”
What is the active phase of labor?
This is also known as the latent phase of the first stage of labor. Second, a much shorter and rapid dilational phase is also known as the active phase of the first stage of labor. Third, a pelvic division phase, which takes place during the second stage of labor. [1]
How many stages of labor are there?
Labor is the process through which a fetus and placenta are delivered from the uterus through the vagina.[1] . Human labor divides into three stages. The first stage is further divided into two phases.
How long does the second stage of labor last?
The second stage of labor commences with complete cervical dilation to 10 centimeters and ends with the delivery of the neonate. This was also defined as the pelvic division phase by Friedman. After cervical dilation is complete, the fetus descends into the vaginal canal with or without maternal pushing efforts. The fetus passes through the birth canal via 7 movements known as the cardinal movements. These include engagement, descent, flexion, internal rotation, extension, external rotation, and expulsion.[1] In women who have delivered vaginally previously, whose bodies have acclimated to delivering a fetus, the second stage may only require a brief trial, whereas a longer duration may be required for a nulliparous female. In parturients without neuraxial anesthesia, the second stage of labor typically lasts less than three hours in nulliparous women and less than two hours in multiparous women. In women who receive neuraxial anesthesia, the second stage of labor typically lasts less than four hours in nulliparous women and less than three hours in multiparous women.[1] If the second stage of labor lasts longer than these parameters, then the second stage is considered prolonged. Several elements may influence the duration of the second stage of labor, including fetal factors such as fetal size and position, or maternal factors such as pelvis shape, the magnitude of expulsive efforts, comorbidities such as hypertension or diabetes, age, and history of previous deliveries. [8]
How does labor start?
The first stage of labor begins when labor starts and ends with full cervical dilation to 10 centimeters.[1] Labor often begins spontaneously or may be induced medically for a variety of maternal or fetal indications.[5] Methods of inducing labor include cervical ripening with prostaglandins, membrane stripping, amniotomy, and intravenous oxytocin.[5] Although precisely determining when labor starts may be inexact, labor is generally defined as beginning when contractions become strong and regularly spaced at approximately 3 to 5 minutes apart.[1] Women may experience painful contractions throughout pregnancy that do not lead to cervical dilation or effacement, referred to as false labor. Thus, defining the onset of labor often relies on retrospective or subjective data. Friedman et al. were some of the first to study labor progress and defined the beginning of labor as starting when women felt significant and regular contractions.[6] He graphed cervical dilation over time and determined that normal labor has a sigmoidal shape. Based on the analysis from his labor graphs, he proposed that labor has three divisions. First, a preparatory stage marked by slow cervical dilation, with large biochemical and structural changes. This is also known as the latent phase of the first stage of labor. Second, a much shorter and rapid dilational phase is also known as the active phase of the first stage of labor. Third, a pelvic division phase, which takes place during the second stage of labor. [1]
How is labor monitored?
Clinicians monitor fetal heart tracings to evaluate for any signs of fetal distress that would warrant intervention as well as the adequacy or inadequacy of contractions. Vital signs of the mother are taken at regular intervals and whenever concerns arise regarding a clinical status change. Laboratory testing often includes the hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet count and is sometimes repeated following delivery if significant blood loss occurs. Cervical exams are usually performed every 2 to 3 hours unless concerns arise and warrant more frequent exams. Frequent cervical exams are associated with a higher risk of infection, especially if a rupture of membranes has occurred. Women should be allowed to ambulated freely and change positions if desired.[3] An intravenous catheter is typically inserted in case it is necessary to administer medications or fluids. Oral intake should not be withheld. If the patient remains without food or drink for a prolonged period of time, intravenous fluids should be considered to help replace losses but do not need to be used continuously on all laboring patients.[3] Analgesia is offered in the form of intravenous opioids, inhaled nitrous oxide, and neuraxial analgesia in those who are appropriate candidates.[4] Amniotomy is considered on an as-needed basis for fetal scalp monitoring or labor augmentation, but its routine use should be discouraged.[3] Oxytocin may be initiated to augment contractions found to be inadequate.
What is the first stage of labor?
Labor is a process that subdivides into three stages. The first stage starts when labor begins and ends with full cervical dilation and effacement. The second stage commences with complete cervical dilation and ends with the delivery of the fetus. The third stage initiates after the fetus is delivered and ends when the placenta is delivered.
What are the vital signs of a woman in labor?
When women first present to the labor and delivery unit, vital signs, including temperature, heart rate, oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, and blood pressure, should be obtained and reviewed for any abnormalities. The patient should be placed on continuous cardiotocographic monitoring to ensure fetal wellbeing.
What is the first stage of labor?
The first stage of labor is the longest and involves three phases: Early Labor: The onset of labor until the cervix is dilated to 3-6 centimeters. Active Labor Phase: Continues from 3 cm until the cervix is dilated to 7 centimeters. Transition Phase – Continues from 7 cm until the cervix is fully dilated to 10 centimeters.
How long does the transition phase last?
Transition Phase – Continues from 7 cm until the cervix is fully dilated to 10 centimeters
How long does labor last?
What to expect: Early labor will last approximately 8-12 hours. Your cervix will efface and dilate to 4 centimeters. Contractions will last about 30-45 seconds, giving you 5-30 minutes of rest between contractions. Contractions are typically mild and somewhat irregular but become progressively stronger and more frequent.
What is it called when water breaks during labor?
Your water might break – this is known as amniotic sac rupture and can happen anytime within the first stage of labor
What to do when you have contractions?
It is very important that you have plenty of support. It is also a good time to start your breathing techniques and try a few relaxation exercises between contractions.
What to do during early labor?
What to do: During this phase, you should just try to relax. It is not necessary to rush to the hospital or birth center. Try to enjoy the comfort of the familiar surroundings at home. If early labor occurs during the day , do some simple routines around the house. Keep yourself occupied while conserving your energy.
Do babies descend before they are fully dilated?
Some babies descend earlier and the mom feels the urge to push before she’s fully dilated. Other babies descend later and the mom reaches full dilation without feeling pressure.