What is translocation in photosynthesis?
Since photosynthesis only occurs in the leaves, plants must have some way of transporting these sugars into other areas of the plant that need it, such as the stems, roots, and flowers. This transport of materials from the leaves to other parts of the plant is known as translocation.
What is translocation of food in plants?
Translocation of food in plants is the process in which food is moved from one part of the plant to another. This can be done through the use of the plant’s vascular system, which consists of the xylem and phloem.
What is the role of the xylem and phloem in translocation?
Translocation occurs in plants through the xylem and phlom, which are the two tissues that carry water and other nutrients from one part of the plant to another. A series of cells known as the phloem pathway are involved in this process. The phloem is responsible for transporting food in vascular plants.
What is translocation or conductance of solutes?
This cell-to-cell movement of food material from one part of the plant to another or through a tissue is the translocation or conductance of solutes. Source is the point where plant synthesis food and sink is the part where plants use food. Translocation of food material takes place in plant in different directions.
Where is translocation in plants?
Translocation occurs in the phloem tissue, which consists of tube-like structures called phloem vessels. These phloem vessels run from the leaves into every other part of the plant and are responsible for transporting dissolved organic solutes, such as sucrose and amino acids, from the sources to the sinks.
What is translocation very short answer?
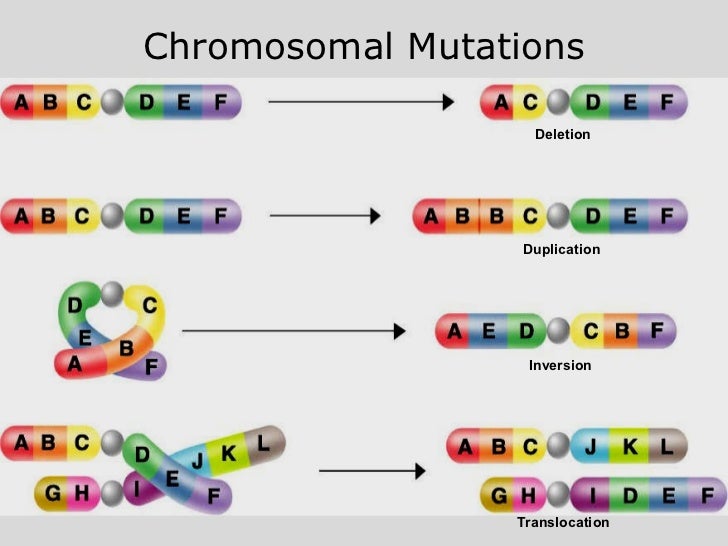
Listen to pronunciation. (TRANZ-loh-KAY-shun) A genetic change in which a piece of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome. Sometimes pieces from two different chromosomes will trade places with each other.
Why is translocation important to the plant?
Because translocation connects distant components of the plant body, xylem and phloem have long been considered to fulfill a role in communicating between organs, through the movement of plant hormones and other signaling molecules. Such signals are envisaged to move with assimilates by mass flow.
What is translocation in phloem?
Translocation is the movement of elements within a plant from leaves to other tissue. Plants' phloem, a type of vascular tissue, is where translocation takes place. Sugars that are produced by photosynthesis or that are stored in plant tissues like roots, bulbs, and tubers are examples of sugar sources.
What is translocation 8th class?
Translocation is the movement of sugar produced in photosynthesis to all other parts of the plant for respiration and the other processes described above. This occurs in phloem cells.
What is a translocation example?
Translocation Mutation Example For example, a person may have a balanced translocation between chromosomes 7 and 21. The q arms of each chromosome have been switched. But this person has all the genetic material required for normal protein synthesis and function.
What are the processes in translocation?
Translocation occurs through part of vascular tissue known as phloem that also transports carbohydrates, amino acids and other substances such as plant hormone which are made in tips of roots and shoots to the storage and growing organs. Was this answer helpful?
What's the difference between transpiration and translocation?
*Transpiration is the evaporation of water from the leaves in the form of water vapour whereas translocation is the transportation of synthesized products (sugars)in a plant. *Transpiration always occurs against the gravity while translocation does not always occur against gravity.
What is the effect of translocation?
Translocations generate novel chromosomes. In a translocation, a segment from one chromosome is transferred to a nonhomologous chromosome or to a new site on the same chromosome. Translocations place genes in new linkage relationships and generate chromosomes without normal pairing partners.
What is translocation in xylem and phloem?
Phloem consists of living cells arranged end to end. Unlike xylem, phloem vessels contain cytoplasm, and this goes through holes from one cell to the next. Phloem transports sucrose and amino acids up and down the plant. This is called translocation .
What is translocation in xylem?
Xylem is associated with translocation of mainly water, mineral salts, some organic nitrogen and hormones from roots to the aerial parts of the plants. While the phloem translocates a variety of organic and inorganic solutes mainly from the leaves to other parts of the plants.
What is translocation and its types?
The term translocation is used when the location of specific chromosome material changes. There are two main types of translocations: reciprocal and Robertsonian. In a reciprocal translocation, two different chromosomes have exchanged segments with each other.
What is translocation in class 7th?
Translocation is the movement of materials from leaves to other tissues throughout the plant. Plants produce carbohydrates (sugars) in their leaves by photosynthesis, but nonphotosynthetic parts of the plant also require carbohydrates and other organic and nonorganic materials.
What is translocation 12th?
The products of metabolic processes, particularly photosynthesis, are moved from leaves, where they are formed, to other parts of the plant. This transport of soluble products of photosynthesis is called translocation and it occurs in the part of the vascular tissue known as phloem.
What is translocation BYJU's?
The movement of materials such as carbohydrates and amino acids through the vascular bundles (xylem and phloem) produced as a result of photosynthesis from the leaves to the rest of the plant is known as translocation.
What is translocation English?
translocation in American English 1. a change of location. 2. Genetics. a chromosomal rearrangement in which a segment of genetic material from one chromosome becomes heritably linked to another chromosome.
What is an example of translocation in plants?
An example of translocation in plants is the movement of sugars from sugar sources to sugar sinks. Sugar sources include sugars either created thro...
What is translocation in DNA?
DNA translocation can cause a chromosomal abnormality when a piece of one chromosome breaks and fuses with a different chromosome. This abnormality...
What is a simple definition of translocation?
A simple definition of translocation is the movement of materials from one area to another. In plants, plant translocation involves the movement of...
How is translocation done in plants?
Translocation in plants is achieved by the movement of sugars through the phloem. The mass flow hypothesis, or pressure flow model, explains that s...
What is the process of transporting materials from the leaves to other parts of the plant?
Translocation is the movement of materials in plants from the leaves to other parts of the plant. Nutrients, mainly sugars, are created in the leaves during photosynthesis. These are then transported throughout the plant through phloem, which are a long series of connected cells.
How Does It Move?
In some plants, it's directly transported into the phloem using sugar transport proteins. In others, it makes its way in through small openings in the phloem cell walls and is then converted into larger forms so that it cannot move back out.
How does water move through a plant?
The entrance of the water causes pressure to build and forces the water and dissolved materials to move through the phloem from the leaves into the rest of the plant, where it can be stored or turned into energy. The materials move from sugar sources, which have an abundance of sugar following photosynthesis (such as leaves), into sugar sinks, which are areas where there's a lack of sugar (such as the stems and flowers).
How do materials move in the phloem?
The most widely accepted hypothesis about how these materials move within the phloem is the mass flow hypothesis . Sugars enter the phloem either through sugar transport proteins or by going through small openings and then being transformed to larger forms so they cannot move back out. This causes sugar to build up in the phloem in the leaves, and water enters via osmosis, or when a material, such as water, moves from an area where there is more of it into an area where there is less.
How do nutrients flow through plants?
The nutrients the plant creates can't simply stream through the leaves to the other parts of the plant. They're moved through special tubes that run all throughout the plant, known as phloem. These long, continuous tubes extend from the leaves into every part of the plant, and new phloem are added as the plant grows, so the flow of nutrients is never interrupted.
What is the process of water moving from an area where there is more of it to an area where there is less?
Osmosis is when a material (such as water) moves from an area where there is more of it into an area where there is less. The entrance of the water causes pressure to build inside the phloem. This, in turn, forces the water and dissolved materials to begin moving out of the leaves and into the areas where the sugar is needed.
How does food get to where it needs to go?
When you eat, how does the food get where it needs to go? It starts at your mouth and is moved by a series of mechanisms that turn it into energy and transport nutrients throughout your body. A similar thing happens in plants. Even though plants don't have mouths, they still need to transport nutrients throughout their system, just as people do.
How does food material travel in a plant?
Translocation of food material takes place in plant in different directions. Mainly, food material travels in a downward and upward direction. The path of food flow is not constant throughout the life of the plant. At one time, the flow of the food is upwards, and at other times its direction is downward. The plant manufactures food material in leaves and that material travels downward to the stem and root. The synthesized food nourishes old cells and builds new ones. Plant stores some food in storage organs. In these cases, food is rapidly migrating from the seeds or the vegetative storage organs to the growing tips where they use it rapidly.
What is the dominant part of the phloem?
Sieve tubes are the most dominant part of the phloem, and are the only living element that are present in vascular plants.
What direction does food flow?
We know that the direction of the flow of food substance is from the region of higher concentration of solutes to lower concentration. Translocation continues as long as there is positive concentration gradient from supply end to consumption end. Moreover, the rate of translocation increases with the increase in steepness of gradient.
What is the point where plants use food?
Source is the point where plant synthesis food and sink is the part where plants use food.
How do plants get food?
All parts of the plant require a continuous supply of food for their nutrition and development,this is referred to as translocation. Plants differ in their cell arrangement. In simple plants like spirogyra, all cells are green, and each cell can make enough food for its requirement. The higher plants have a great differentiation of structure and division of labor. In higher plants, green cells mainly stick to the leaves, which make up the chief center where synthesis of carbohydrates takes place. The non-green parts of the plant like stem and root get their food supply from leaves. Before food can reach the non-green parts, there must be a proper infrastructure for transferring food. It must travel from leaves through intervening cells and tissues. The food material travels within the plant in the form of a solution in water.
Which process involves the movement of nutrients both outward to the cortex and inward to the center?
Lateral translocation involves the movement of nutrients both outward to the cortex and inward to the center.
Where does upward movement of food take place?
After that plant reverses the direction of translocation. Upward movement takes place during the development of cereal grains where the ear head is terminal. Another instance of upward movement of food is in the stems of woody plants. The food stored in older parts move upward to the sprouting buds. So we can understand that the direction of transport of food is from the region of higher concentration towards lower concentration.
What are the nutrients that are translocated in phloem sap?
The major nutrients that are translocated from the phloem sap are the sugars along with amino acids and minerals. This is due to the reason that sugars are the major solute found in the phloem sap. Throughout the plant, various plant hormones, nucleic acids, and proteins are also moved via translocation. Through the process of photosynthesis, plants in their leaves produce carbohydrates (sugars). These carbohydrates are required by other non-photosynthetic parts of the plant as well along with other materials. Due to this, the translocation occurs from the source (leaves) to the sink (roots, flowers, fruits, stems, and developing leaves) to deliver nutrients to every part of the plant. The process of translocation occurs through the phloem transport system, which is a series of cells. The phloem is formed of still-living cells, the dead cells are found in the xylem. In phloem, the nutrients are translocated as solutes in a solution known as phloem sap.
How does phloem sap flow?
The phloem sap can flow within the source to sink regions with the help of a pathway that is continuous and membrane-bound. The sugar pumped into the phloem is produced in the mesophyll cells (composing the middle layer) with the help of metabolic energy. The energy is also used to concentrate the sugar. The water enters the cells through osmosis when the sugar gets concentrated in cells. Due to the presence of rigid cell walls in the plant cells, the internal pressure is created with the increase of water. Because of this pressure, the sap moves down the tube from the pores of the sieve element.
What is the process of translocation in plants?
Translocation in plants is the movement of nutrients, like sucrose and amino acids, through phloem vessels inside the plant, usually taking place between the source, where these nutrients are produced, and the sink, where they are utilized and stored. It is the movement of some mineral ions and organic molecules in vascular plants.
What is the tissue that moves nutrients?
Phloem is the tissue through which the movement of nutrients takes place. It consists of vascular bundles that are organized in long and consecutive strands. The veins found in the leaves are the vascular bundles that have originated from the roots and stems. The sieve elements are found as sieve cells in the gymnosperms, whereas existing as sieve tube membranes in the angiosperms are responsible for transferring the nutrients to the different regions of the plants that are located at distant regions.
Why are sieve elements alive?
The interior of the cell is open due to the lack of nucleus and other substances, and the end walls of the sieve elements are perforated by large pores that help in the flow of the solution through the tube. The sieve elements remain alive due to the presence of companion cells that are closely associated with them. The transfer and movement of small and large molecules are regulated by the plasmodesmata as it is responsible for joining the sieve elements to the companion cells.
Where does phloem unloading take place?
Phloem unloading takes place in the consumption end or the sink. Sucrose is transferred to the receiver cells of the sink from the sieve tube, and this is facilitated by the unloading of the sieve elements. In this, the sugars exit from the sieve elements present in the sink tissues. After this, the movement within short distances occurs in which the sugars are transported by a short distance pathway to cells in the sink. Lastly, sugars either get metabolized in the sink cells or get stored there.
What is the movement of sugar produced in photosynthesis to all other parts of the plant for respiration and the other processes?
Translocation is the movement of sugar produced in photosynthesis to all other parts of the plant for respiration and the other processes described above. This occurs in phloem cells.
What is the process of photosynthesis?
During photosynthesis, plants produce glucose from simple inorganic molecules - carbon dioxide and water - using light energy. Some of the glucose produced by photosynthesis is used for respiration. This releases energy for the seven life processes. Translocation is the movement of sugar produced in photosynthesis to all other parts ...
Which tissue is grouped into vascular bundles?
In the stem, the transport tissues of the xylem and phloem are grouped into vascular bundles.
What are the organs of plants?
Plant cells, tissues and organs are adapted to their functions. The stem, root and leaves form an organ system that transports substances into, around and out of a plant. The leaves are the main organ of photosynthesis.
Which tube has no nuclei?
Sieve tubes - specialised for transport and have no nuclei. Each sieve tube has a perforated end so its cytoplasm connects one cell to the next.
Where does transport take place in the phloem?
Transport in the phloem therefore takes place both up and down the stem - in contrast to transport in the xylem, which is just upwards. Transport of substances in the phloem is called translocation. Phloem consists of living cells. The cells that make up the phloem are adapted to their function:
What is the rate of absorption of water?
The rate of absorption is fast. It occurs in rapidly transpiring plants. The movement of plants is through apoplast and it is absorbed due to transpiration pull and it is created due to the stress created in xylem sap. The rate of absorption significantly depends upon the rate of transpiration. The force required for the absorption of water is mainly generated in the mesophyll cells.
How do antiport proteins exchange solutes?
Antiport proteins exchange the solutes by transporting them in and out of the cell. The main function of uniport protein is to carry single solute across the membrane. Symport proteins transfer two different solutes simultaneously in the same direction.
How is water absorbed in the symplast?
In the case of active absorption, water moves through symplast and it is absorbed according to the Diffusion Pressure Deficit changes. The rate of absorption is slow. It comprises osmotic and non-osmotic forces.
What is the driving force behind uptake and transport of water?
Transpiration is the driving force behind uptake and transport of water. It is the process of water evaporation through openings called stomata. This creates a pull by replacing the water that has evaporated. This pull in the xylem tissues extends all the way down due to the cohesive forces.
What is the perfect system for the absorption and translocation of water?
Plants contain a vast network of conduits which consist of xylem and phloem. This is more like the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the human body. Similar to the circulatory system in humans, ...
What is the xylem composed of?
The xylem is also composed of elongated cells like the phloem. However, xylem is especially accountable for transporting water to all plant parts from the roots. Since they serve such an important function, a single tree would have a lot of xylem tissues.
How does the xylem work?
Xylem is a long, non-living tube running from the roots to the leaves through the stem. The water is absorbed by the root hair and undergoes cell to cell movement by osmosis until it reaches the xylem. This water is then transported through the xylem vessels to the leaves and is evaporated by the process of transpiration.
What is a translocation in a fusion product?
A translocation is a chromosomal abnormality whereby there's a break in the chromosome, one particular chromosome, and that chromosome will then fuse to a different chromosome. And then you have what we call a fusion product. Chromosomal translocations are typically seen in cases of leukemia, like, for instance, in acute myeloid leukemia.
What is a translocation?
Translocation is a type of chromosomal abnormality in which a chromosome breaks and a portion of it reattaches to a different chromosome. Chromosomal translocations can be detected by analyzing karyotypes of the affected cells.
What is chromosomal translocation?
Chromosomal translocations are typically seen in cases of leukemia, like, for instance, in acute myeloid leukemia. For instance, you have different types of chromosomal translocation where part of Chromosome 8, for instance, will break off and fuse with part of Chromosome 11, so you have what we call an 8/11 translocated product.
