Beta-agonists, corticosteroids Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range …Corticosteroid
Sevoflurane
Sevoflurane is a sweet-smelling, nonflammable, highly fluorinated methyl isopropyl ether used as an inhalational anaesthetic for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia. After desflurane, it is the volatile anesthetic with the fastest onset and offset.
How to cure asthma naturally permanently?
How to Cure Asthma Naturally Permanently – 5 Powerful Strategies
- Fitness Is Key To Controlling Asthma. When professional athletes get exhausted and out of breath in the middle of a game, they know they need to improve their cardio.
- Diet Will Help Keep Asthma Under Control. We’ve all heard “you are what you eat.” And it’s so true. ...
- Let The Feelings Of Asthma Pass. ...
- TLDR; Natural Asthma Cure Quick FAQ. ...
What is the best way to control asthma?
Of course, there is no cure for asthma but the symptoms can be effectively controlled with natural methods in many cases. Asthma can be cured naturally permanently with a combination of lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, meditation, breathing exercises and herbal teas.
What is the most common treatment for asthma?
bronchodilators (such as salbutamol), that open the air passages and relieve symptoms; and. steroids (such as beclometasone), that reduce inflammation in the air passages. This improves asthma symptoms and reduces the risk of severe asthma attacks and death. People with asthma may need to use their inhaler every day.
What are signs that you have asthma?
Signs of an asthma emergency include:
- Rapid worsening of shortness of breath or wheezing
- No improvement even after using a quick-relief inhaler
- Shortness of breath when you are doing minimal physical activity

Which is first line drug for status asthmaticus?
Beta Agonists Short-acting inhaled beta-agonists are the drug of the first choice in acute asthma. [21] Albuterol is preferred over metaproterenol in that class because of its higher beta 2 selectivities and longer duration of action.
What is the difference between status asthmaticus and asthma?
Status asthmaticus is an older, less precise term for what's now more commonly known as acute severe asthma or a severe asthma exacerbation. It refers to an asthma attack that doesn't improve with traditional treatments, such as inhaled bronchodilators.
What is an emergency care of patients with status asthmaticus?
At the hospital, your treatment may include continuous use of an asthma nebulizer, and also epinephrine and corticosteroids to stop the attack. The doctor at the hospital may also give you terbutaline shots and magnesium sulfate to help the muscles around your airways relax.
How do you diagnose status asthmaticus?
The common diagnostic signs of status asthmaticus include:Breathlessness at rest.Inability to speak in sentences or not being able to speak at all.Increased respiratory rate at rest (greater than 30 breaths per minute)Elevated pulse rate at rest (greater than 120 beats per minute)Agitation and irritability.More items...•
What triggers status asthmaticus?
Causes and triggers An upper respiratory infection is one of the most common causes of a status asthmaticus attack. The infection increases the amount of mucus in a person's lungs, making it harder for them to breathe. Other potential causes include: allergic reactions to foods. chlamydial pneumonia.
What are the complications of status asthmaticus?
Status asthmaticus can vary from a mild form to a severe form with bronchospasm, airway inflammation, and mucus plugging that can cause difficulty breathing, carbon dioxide retention, hypoxemia, and respiratory failure.
Is status asthmaticus reversible?
The disease of asthma does not go away. It is not reversible.
Can an asthmatic patient take oxygen?
Oxygen therapy for severe asthma attacks supplies a person with additional oxygen. There are various oxygen therapy devices a doctor can use to treat an asthma attack. Oxygen therapy can also treat other conditions that cause low oxygen levels. Oxygen therapy is generally safe.
Why don't you intubate an asthmatic?
Intubation for acute asthma Mechanical ventilation is not an ideal therapy for potentially fatal asthma. Because serious complications may occur in association with intubation and positive pressure ventilation, all efforts should be made to avoid unnecessary intubation in this setting.
Is there wheezing in status asthmaticus?
Patients are usually tachypneic upon examination and, in the early stages of status asthmaticus, may have significant wheezing. Initially, wheezing is heard only during expiration, but wheezing later occurs during expiration and inspiration.
What if my inhaler isn't helping?
Take one puff of a reliever or rescue inhaler every 30 to 60 seconds, with a maximum of 10 puffs. If symptoms get worse or do not improve after 10 puffs, seek emergency medical care. If it takes longer than 15 minutes for help to arrive, repeat step 2.
What are the 4 categories of asthma?
The EPR-3 guideline classification divides asthma severity into four groups: intermittent, persistent-mild, persistent-moderate, and persistent-severe.
What are the 3 types of asthma?
Types of asthmaDifficult to control asthma.Severe asthma.Occupational asthma.
What is Asthmaticus in medical terms?
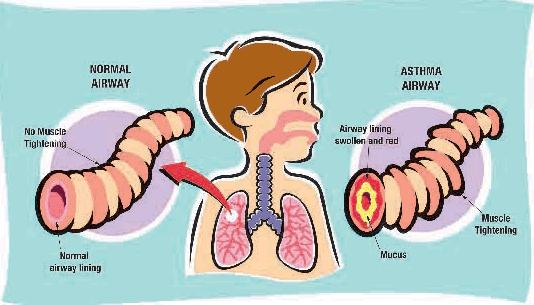
(AZ-muh) A chronic disease in which the bronchial airways in the lungs become narrowed and swollen, making it difficult to breathe.
Is status asthmaticus reversible?
The disease of asthma does not go away. It is not reversible.
What lung sounds do you hear with asthma?
This is the most commonly heard breath sound associated with asthma. While not all people with asthma wheeze, the majority do. Wheezing is generally a higher-pitched whistling sound that occurs most commonly when you breathe out.
How can asthmaticus be prevented?
Status asthmaticus can be prevented if triggers and stress factors are avoided, and compliance with the medicines is good. Identify those individuals who are at a greater risk of exacerbation, such as extremes of ages. Environmental management is essential in patients with environmental allergies. Inpatient education by trained laypeople resulted in improvement in compliance with inhaler management and post-discharge care. [37]
What is status asthmaticus?
Status asthmaticus is a medical emergency, an extreme form of asthma exacerbation characterized by hypoxemia, hypercarbia, and secondary respiratory failure. All patients with bronchial asthma are at risk of developing an acute episode with a progressive severity that is poorly responsive to standard therapeutic measures, regardless of disease severity or phenotypic variant. This is also known as status asthmaticus.
Why should a ventilator be kept in moderation in status asthmaticus patients?
Ventilator applied PEEP should be kept in moderation in status asthmaticus patients because of the risk of barotrauma and hypotension.
What percentage of asthma deaths are slow onset?
Eighty percent to 85% of asthma fatalities are in the subgroup of slow-onset asthma exacerbation, perhaps reflecting an inadequate disease control over time. In contrast to the sudden onset of exacerbation phenotype, which presents mostly with clear airways, slow-onset exacerbation patients have extensive airway inflammation and mucus plugging. [2]
What is the primary player in asthma?
Increasing understanding of the pathophysiology of asthma at the histological level over the last two decades has emphasized airway inflammation as the primary player, over and above smooth muscle contraction, and airway hyperresponsiveness. An interplay of mast cells, T lymphocytes, and epithelial cells result in a circulatory surge of inflammatory cells and cytokines. Histamines, leukotrienes, and platelet-activating factors are found in increased concentrations locally and systemically. Lymphocytic and eosinophilic submucosal infiltrates in tracheal and bronchial biopsy specimens is reportedly associated with poorer outcomes in adult patients with asthma. [7]
What are the two phases of asthma?
Physiologically, acute asthma is divided into two phases. An early bronchospastic phase is observed within minutes after exposure to the allergen with mast cell degranulation and release of inflammatory mediators like histamine, prostaglandin D2, and leukotriene C4. A later inflammatory phase causing airway swelling and edema due to eosinophils released eosinophilic cationic proteins (ECP) and major basic protein (MBP).
What is the phenotype of sudden onset asthma?
The other phenotype, known as “sudden onset asthma exacerbation, ” presents with severe deterioration within hours. They often correlate with sudden massive exposure to external triggers like predisposed allergens, food articles, sulfites, among others.
What is the best treatment for asthma?
Glucocorticosteroids are the most important treatment for status asthmaticus. [ 30] . These agents can decrease mucus production, improve oxygenation, reduce beta-agonist or theophylline requirements, and activate properties that may prevent late bronchoconstrictive responses to allergies and provocation.
What is thoracostomy for asthma?
For example, thoracostomy is indicated in pneumothoraces. Some children may have asthma that is primarily exacerbated by gastroesophageal reflux disease. Some patients can be treated with a combination of antireflux (eg, proton pump inhibitors) and histamine 2 (H2)–receptor antagonist agents.
What is the best way to administer beta2?
The nebulized, inhaled route of administration is generally the most effective route of delivery for beta2-agonists. Inhaled beta-agonists can be administered intermittently or as continuous, nebulized aerosol in a monitored setting. Some patients with severe, refractory status asthmaticus may benefit from the addition of beta-agonists delivered intravenously.
How long does it take to respond to albuterol?
The dose is 4 puffs, repeated at 15- to 30-minute intervals as needed. Most patients respond within 1 hour of treatment. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of the R isomer of albuterol, known as levalbuterol, for treating patients with acute asthma.
What is the first line of therapy for bronchospasm?
Beta2-Agonists. The first line of therapy is bronchodilator treatment with a beta2-agonist, typically albuterol. Handheld nebulizer treatments may be administered either continuously (10-15 mg/h) or by frequent timing (eg, q5-20min), depending on the severity of the bronchospasm.
What masks are used for hypoxemia?
In the event of significant hypoxemia, non-rebreathing masks may be used to deliver as much as 98% oxygen. Tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation are indicated for respiratory failure.
How do anticholinergic agents work?
Anticholinergic agents are believed to work centrally by suppressing conduction in vestibular cerebellar pathways. They may have an inhibitory effect on parasympathetic nervous system. They may also decrease mucus production and improve mucociliary clearance
How long does it take for asthma medication to work?
They will not immediately relieve asthma symptoms, but they will begin to help in the 24 hours after a person starts treatment. Whenever possible, a doctor will try to avoid intubation.
When was asthma last reviewed?
The earlier a person can seek treatment, the more likely their symptoms will resolve. Last medically reviewed on June 18, 2019. Asthma.
What to do if your inhaler doesn't work?
If a person’s inhaler does not relieve their breathing symptoms, they should obtain immediate medical assistance. When a person has asthma, their doctor typically prescribes an inhaler that contains long-acting medications to keep the airways open. They may also prescribe a short-acting inhaler that a person can use if they have significant ...
Why does asthma attack?
An upper respiratory infection is one of the most common causes of a status asthmaticus attack. The infection increases the amount of mucus in a person’s lungs, making it harder for them to breathe. Other potential causes include: allergic reactions to foods. chlamydial pneumonia.
What are the symptoms of asthma?
A person with status asthmaticus will usually have a fast respiratory rate, rapid heart rate, and a low pulse oximetry reading.
How to tell if you have asthma?
When a person is in status asthmaticus, they may experience some of the following symptoms: 1 anxiety 2 blue tinge to lips and fingernails 3 diminished breath sounds 4 decreased alertness 5 fatigue 6 shortness of breath 7 sweating 8 trouble taking deep breaths 9 wheezing
Is asthma a life threatening condition?
Although status asthmaticus can be life-threatening, it is treatable, so it is essential that a person seeks emergency care.
What is the best treatment for asthma?
At the hospital, your treatment may include continuous use of an asthma nebulizer, and also epinephrine and corticosteroids to stop the attack. The doctor at the hospital may also give you terbutaline shots and magnesium sulfate to help the muscles around your airways relax.
How to manage asthma?
It’s important to follow the asthma action plan that you made with your doctor, avoid your triggers, take your medicine, and keep up with your doctor appointments.
What is Status Asthmaticus?
Status asthmaticus is respiratory failure that comes with the worst form of acute severe asthma, or an asthma attack. If an attack comes on quickly and it doesn’t respond to regular treatment, it can lead to status asthmatiscus, If it happens, you may have to go to the hospital to get it treated. If you have a bad asthma attack and your rescue inhaler or your nebulizer doesn't help, you need medical care right away.
What is the name of the condition where you hear a severe asthma attack?
You may hear a severe asthma attack called a “severe asthma exacerbation.” In its most severe form, you may hear it called status asthmaticus.
How to tell if you have asthma?
A severe asthma attack can cause symptoms such as: 1 Shortness of breath 2 Can’t speak in full sentences 3 Feel breathless even when you lie down 4 Chest feels tight 5 Bluish tint to your lips 6 Feel agitated, confused, or can’t concentrate 7 Hunched shoulders, and strained muscles in your stomach and neck 8 Feel that you need to sit or stand up to breathe more easily
How to check if your lungs are working?
Take your asthma medication as often as your doctor recommends. Use a peak flow meter several times a day. These devices help to check on how well your lungs are working. Start treatment immediately, according to your asthma action plan, if you notice a lower reading, even if you feel fine.
Where to start asthma treatment?
With any asthma attack, you must start treatment right away, at the first sign of symptoms, either at home or in your doctor's office.
What is status asthmaticus?
Excerpt. Status asthmaticus is a medical emergency, an extreme form of asthma exacerbation characterized by hypoxemia, hypercarbia, and secondary respiratory failure. All patients with bronchial asthma are at risk of developing an acute episode with a progressive severity that is poorly responsive to standard therapeutic measures, ...
Is asthma a cause of emergency department visits?
Despite advances in pharmacotherapy and access to early diagnosis and treatment of asth ma itself, it remains one of the most common causes of emergency department visits. No single clinical or diagnostic index has been known to predict clinical outcome in status asthmaticus. Hence, a multi-pronged and time-sensitive approach combining symptoms and signs, assessing airflow and blood gas, and a rapid escalation of treatment based on initial treatment response is favored to diagnose and manage the condition.
Can asthma cause death?
If not recognized and managed appropriately, asthmatics portends the risk of acute ventilatory failure and even death. Despite advances in pharmacotherapy and access to early diagnosis and treatment of asthma itself, it remains one of the most common causes of emergency department visits.
What is the best treatment for asthma?
In order to treat severe asthma, intravenous corticosteroids and methylxanthines are often given. Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates and also the synthetic analogues of these hormones.
What are the Symptoms of Status Asthmaticus?
Some of the symptoms are so dangerous that Status Asthmaticus is considered as a medical emergency. Persistent shortness of breath is one of the symptoms of Status Asthmaticus in which a person runs out of breath in spite of living a normal life and not doing any heavy work might suffer from Status Asthmaticus. The symptoms of Status Asthmaticus also include breathlessness while lying down in conventional posture, chest may feel closed and lips might also have a bluish tinge.
Why do some people get asthma attacks?
Doctors do not know why some people get such severe asthma attacks. However some of the causes of status asthmaticus might be like
How common is asthma in the US?
Asthma affects up to 10% of the population in the United States Of America. Prevalence has increased by 60% in all ages in the past 20 years. Status asthmaticus is usually more common among persons in low socioeconomic groups, regardless of race; as they have less access to regular specialist medical care. Individuals living alone are partially affected.
How much oxygen does a non-rebreathing mask deliver?
In the event of significant hypoxemia, non-rebreathing masks may be used for delivering as much as 98% oxygen.
Is status asthmaticus a medical emergency?
Status asthmaticus is known to be a medical emergency and it is the extreme form of an asthma exacerbation that can lead to hypoxemia, hypercarbia and secondary respiratory failure. More about the condition, its symptoms, causes, risk factors and treatments are discussed in the following array of the article.
What is the best medication for dilating the airways?
Interventions include IV or intravenous medications like magnesium sulfate, aerosolized medications like albuterol or salbutamol for dilating the airways.
What is a severe asthmatic?
Acute severe asthma, formerly known as status asthmaticus, is defined as severe asthma unresponsive to repeated courses of beta-agonist therapy. It is a medical emergency that requires immediate recognition and treatment.
How long does ipratropium last?
Oral or parenteral corticosteroids should be administered to all patients with acute severe asthma as early as possible because clinical benefits may not occur for a minimum of 6 to 12 hours.
Is albuterol a medical emergency?
It is a medical emergency that requires immediate recognition and treatment. Albuterol in combination with ipratropium bromide in the emergency department …. Acute severe asthma, formerly known as status asthmaticus, is defined as severe asthma unresponsive to repeated courses of beta-agonist therapy. It is a medical emergency that requires ...