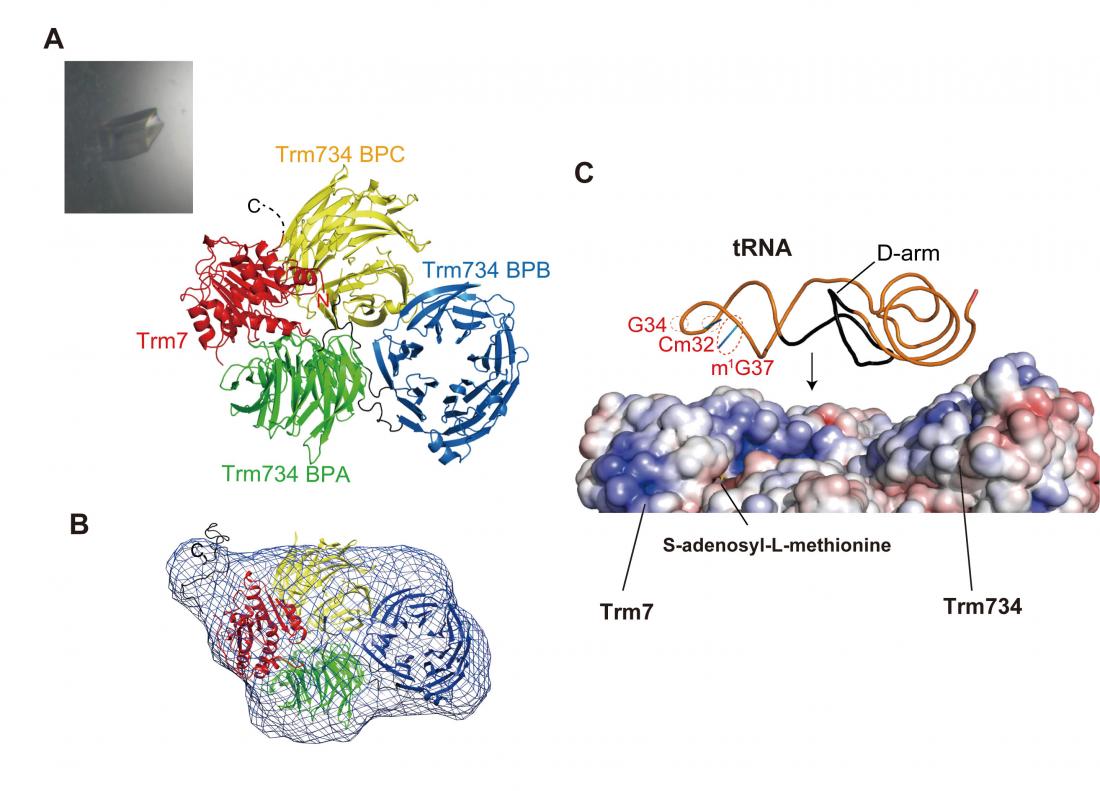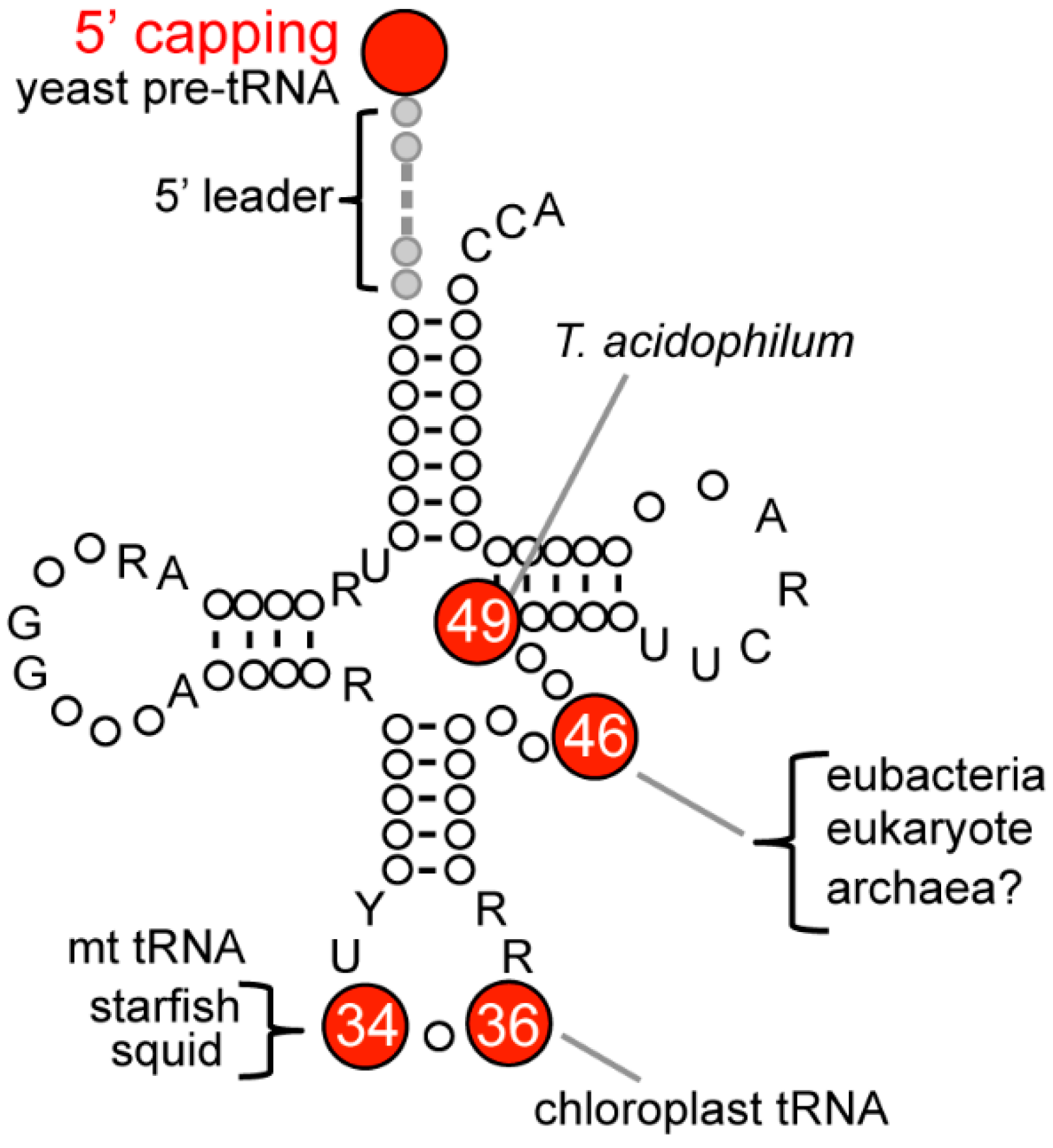
What is the tRNA anticodon for methionine?
UACThe anticodon on the tRNA that delivers the methionine to the ribosome is UAC, whereas tRNAs with anticodons of AAU, AAC, GAA, GAG, GAU, and GAC deliver leucine.
What is the tRNA of Aug?
The AUG start codon signals the ribosome to place in the amino acid methionine because the tRNA that has methionine attached to it has the anticodon sequence UAC.
What is the codon for methionine?
codon AUGMethionine is specified by the codon AUG, which is also known as the start codon. Consequently, methionine is the first amino acid to dock in the ribosome during the synthesis of proteins. Tryptophan is unique because it is the only amino acid specified by a single codon.
Can you translate tRNA to amino acids?
transfer RNA (tRNA) – a type of RNA that is folded into a three-dimensional structure. tRNA carries and transfers an amino acid to the polypeptide chain being assembled during translation. translation – the process in which a cell converts genetic information carried in an mRNA molecule into a protein.
How do you write a tRNA anticodon?
4:4627:26Transfer RNA (tRNA), Codons, and Anticodons - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipCode you'd look at the complement complementary nucleotides so for example if I want to know theMoreCode you'd look at the complement complementary nucleotides so for example if I want to know the anticodon that binds to Aug. Well you just look at the complementary bases.
What is the tRNA anticodon for AUG?
The anticodon for AUG is UAC. Here's a tRNA with the anticodon UAC, and it's bringing in a methionine attached to its other end. Codon recognition happens when tRNA pairs with the mRNA inside the ribosome.
What is a tRNA anticodon?
An anticodon is a trinucleotide sequence located at one end of a transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule, which is complementary to a corresponding codon in a messenger RNA (mRNA) sequence.
Is methionine always a start codon?
The start codon is the first codon of a messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript translated by a ribosome. The start codon always codes for methionine in eukaryotes and Archaea and a N-formylmethionine (fMet) in bacteria, mitochondria and plastids.
What do UGA UAA and UAG code for?
STOP codonsThere are 3 STOP codons in the genetic code - UAG, UAA, and UGA. These codons signal the end of the polypeptide chain during translation. These codons are also known as nonsense codons or termination codons as they do not code for an amino acid.
How do you convert mRNA to tRNA?
Each tRNA is attached to an amino acid, so the ribosome moves down the mRNA transcript, positioning a matching tRNA codon next to each mRNA codon and linking the amino acids before ejecting the tRNA. Since each codon has three bases, you'll move down the mRNA transcript three bases at a time.
Is tRNA a protein?
Definition. Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA) is a small RNA molecule that plays a key role in protein synthesis. Transfer RNA serves as a link (or adaptor) between the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule and the growing chain of amino acids that make up a protein.
What is the code for mRNA?
Six codons: Arg, Leu, Ser....DNACoding Strand (Codons)5' > > > - - - - - - T T C - - - - - - > > > 3'mRNAMessage (Codons)5' > > > - - - - - - U U C - - - - - - > > > 3'3 more rows
What is a tRNA anticodon?
An anticodon is a trinucleotide sequence located at one end of a transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule, which is complementary to a corresponding codon in a messenger RNA (mRNA) sequence.
How many tRNA are there?
The human genome contains more than 500 tRNA genes to decode 61 codons.
What is the meaning of tRNA?
Transfer RNATransfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA) is a small RNA molecule that plays a key role in protein synthesis. Transfer RNA serves as a link (or adaptor) between the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule and the growing chain of amino acids that make up a protein.
How many tRNA types are there?
The majority of cells have 40 to 60 types of tRNAs because most of the 61 sense codons have their own tRNA in the eukaryotic cytosol. The tRNAs, which accept the same amino acid are known as isoaccepting tRNAs. In the human mitochondria, there are only 22 different tRNAs and in plant chloroplasts, about 30.
What Is Methionine Used For?from yourhealthremedy.com
The sulfur in methionine provides the body with many potential health benefits. 1 These may include:
How much methionine should I take daily?from verywellhealth.com
The recommended daily intake for methionine is 10.4mg per kilogram of body weight or 4.5mg per pound. A person weighing 70kg (~154 pounds) should consume around 728mg of methionine per day. ( 4) Below is a list of the top 10 foods highest in methionine with the %RDI calculated for someone weighting 70kg (154lbs).
How to lower methionine levels?from yourhealthremedy.com
Since this amino acid is found mainly in food, a good strategy may be to lower methionine levels by lowering methionine consumption, completely eliminating high methionine foods to control cancer growth as well as improve our lifespan.
What are the most common complications of methionine loading?from pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
For each sex, the patients and controls exhibited the same proportion of complications. The most common symptom, dizziness, was attributable to methionine loading. In addition, isolated sleepiness, nausea, polyuria and decreased or increased blood pressure were observed in part of the subjects.
What enzymes are not altered after nitrous oxide anesthesia?from pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
The activity of the other cobalamin-dependent enzyme, methylmalony l coenzyme A mutase, in the mononuclear white blood cells, and the serum concentration of the cobalamin marker methylmalonic acid, were not altered after nitrous oxide anesthesia or methionine loading or both... PMID:8017644.
How long does it take for methionine to reduce BOD?from pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
AEROBIC: In a laboratory activated sludge system, (L)-methionine had an 80% theoretical BOD reduction after 16 days of incubation (1). In a Warburg respirometer study using activated sludge, (L)-methionine (at a concn of 500 mg/L) had a theoretical BOD of 2.6% over a 24-hr incubation period (2). In an activated sludge system that had been acclimated to phenol, (L)-methionine had a theoretical oxidation of 16% after 12 hrs of aeration (3).
How are amino acids selected for protein synthesis?from pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Amino acids are selected for protein synthesis by binding with transfer RNA (tRNA) in the cell cytoplasm. The information on the amino acid sequence of each individual protein is contained in the sequence of nucleotides in the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules, which are synthesized in the nucleus from regions of DNA by the process of transcription. The mRNA molecules then interact with various tRNA molecules attached to specific amino acids in the cytoplasm to synthesize the specific protein by linking together individual amino acids; this process, known as translation, is regulated by amino acids (e.g., leucine ), and hormones. Which specific proteins are expressed in any particular cell and the relative rates at which the different cellular proteins are synthesized, are determined by the relative abundances of the different mRNAs and the availability of specific tRNA-amino acid combinations, and hence by the rate of transcription and the stability of the messages. From a nutritional and metabolic point of view, it is important to recognize that protein synthesis is a continuing process that takes place in most cells of the body. In a steady state, when neither net growth nor protein loss is occurring, protein synthesis is balanced by an equal amount of protein degradation. The major consequence of inadequate protein intakes, or diets low or lacking in specific indispensable amino acids relative to other amino acids (often termed limiting amino acids), is a shift in this balance so that rates of synthesis of some body proteins decrease while protein degradation continues, thus providing an endogenous source of those amino acids most in need. /Protein synthesis/