
Applications
- Human-body emission. Much of a person's energy is radiated away in the form of infrared light. ...
- Temperature relation between a planet and its star. The black-body law may be used to estimate the temperature of a planet orbiting the Sun. ...
- Cosmology. ...
Which makes black body as good absorbers of radiation?
- Particle pairs are spontaneously generated in the vacuum.
- To conserve energy, one of the pair is assumed to have ‘negative energy’.
- Theoretically, negative energy particles cannot ex
What are the examples of black body radiations?
- Low-temperature blackbody with a range of between -40 °C to +150 °C
- High temperature extended area blackbody - from ambient temperature up to +600 °C
- High-temperature cavity blackbody - from ambient temperature up to 1200 °C
What is black body radiation, and how is it produced?
Blackbody radiation is radiation produced by heated objects, particularly from a blackbody. A blackbody is an object that absorbs all radiation ( visible light, infrared light, ultraviolet light, etc.) that falls on it. This also means that it will also radiate at all frequencies that heat energy produces in it.
What mechanism produces black body radiation?
The quick answer to the black body radiation is the motion of atoms due to the non-zero temperature. Why the states for the motion of atoms can not be quantized? If yes, then the atoms jumping from one state to another should emit a discretely distributed electromagnetic waves.
Why is blackbody radiation important?
Blackbody radiation is a cornerstone in the study of quantum mechanics. This experiment is what led to the discovery of a field that would revolutionize physics and chemistry. Quantum mechanics gives a more complete understanding of the fundamental mechanisms at the sub-atomic level.
What is black body example?
A straightforward example of a black body is a cavity with a small hole in it. The light entering the hole undergoes so many reflections within the cavity walls that no light can ever be reflected out. If the walls are painted black, making them absorptive, the cavity represents a perfect black body.
Which law is used in black body radiation?
Planck's lawPlanck's law: The primary law governing blackbody radiation is Planck's Radiation Law. According to Planck's law, every body will emit radiation at all wavelengths and at all times.
Is sun a black body?
Although much hotter on the inside, we can closely approximate the surface of the sun, from which its emission occurs, as a black body at a temperature of about 5800 K. The Stefan-Boltzmann equation then gives the energy flux emitted at the sun's surface.
Who discovered blackbody radiation?
His thesis work on the second law of thermodynamics ultimately became the basis of the research that led Planck to discover the quantum of action - now known as Planck's constant - in 1900. In late 1859, Kirchhoff had defined a black body as an object that is a perfect emitter and absorber of radiation.
Why is it called black body radiation?
A black body or blackbody is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence. The name "black body" is given because it absorbs all colors of light. A black body also emits black-body radiation.
What black body means?
blackbody, also spelled black body, in physics, a surface that absorbs all radiant energy falling on it. The term arises because incident visible light will be absorbed rather than reflected, and therefore the surface will appear black.
Is Earth a blackbody?
Although a blackbody does not really exist, we will consider the planets and stars (including the earth and the sun) as blackbodies. Even though by definition, they are not perfect blackbodies, for the sake of understanding and simplicity we can apply the characteristics of blackbodies to them.
What is black body radiation?
Black-body radiation is the thermal electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, emitted by a black body (an idealized opaque, non-reflective body).
What is the black body spectrum?
An almost perfect black-body spectrum is exhibited by the cosmic microwave background radiation. Hawking radiation is the hypothetical black-body radiation emitted by black holes, at a temperature that depends on the mass, charge, and spin of the hole.
What happens when the body is black?
When the body is black, the absorption is obvious: the amount of light absorbed is all the light that hits the surface. For a black body much bigger than the wavelength, the light energy absorbed at any wavelength λ per unit time is strictly proportional to the black-body curve.
What is the radiation of a baryonic matter?
All normal ( baryonic) matter emits electromagnetic radiation when it has a temperature above absolute zero. The radiation represents a conversion of a body's internal energy into electromagnetic energy, and is therefore called thermal radiation. It is a spontaneous process of radiative distribution of entropy .
What is the temperature of cosmic microwave radiation?
The cosmic microwave background radiation observed today is the most perfect black-body radiation ever observed in nature, with a temperature of about 2.7 K. It is a "snapshot" of the radiation at the time of decoupling between matter and radiation in the early universe. Prior to this time, most matter in the universe was in the form of an ionized plasma in thermal, though not full thermodynamic, equilibrium with radiation.
What is the theory of radiation?
According to the Classical Theory of Radiation, if each Fourier mode of the equilibrium radiation (in an otherwise empty cavity with perfectly reflective walls) is considered as a degree of freedom capable of exchanging energy, then , according to the equipartition theorem of classical physics, there would be an equal amount of energy in each mode. Since there are an infinite number of modes, this would imply infinite heat capacity, as well as a nonphysical spectrum of emitted radiation that grows without bound with increasing frequency, a problem known as the ultraviolet catastrophe .
What is a black body?
Conversely, all normal matter absorbs electromagnetic radiation to some degree. An object that absorbs all radiation falling on it, at all wavelengths, is called a black body. When a black body is at a uniform temperature, its emission has a characteristic frequency distribution that depends on the temperature.
What is a black body?
A blackbody is an idealized physical body, that has specific properties. By definition, a black body in thermal equilibrium has an emissivity of ε = 1.0. Real objects do not radiate as much heat as a perfect black body. They radiate less heat than a black body and therefore are called gray bodies. The surface of a blackbody emits thermal radiation ...
What is the emissive power of a blackbody?
The blackbody emissive power, Eb [W/m2], from a blackbody to its surroundings is proportional to the fourth power of the absolute temperature and can be expressed by the following equation:
Which law describes the spectrum of blackbody radiation, which depends only on the object’s temperature?
This law gives the relationship between the emissivity and absorptivity of an object. Planck’s law. This law describes the spectrum of blackbody radiation, which depends only on the object’s temperature. Wien’s displacement law. This law determines the most likely frequency of the emitted radiation.
Is a blackbody an emitter or absorber?
Its absorptivity is therefore equal to unity, which is also the highest possible value. That is, a blackbody is a perfect absorber (and a perfect emitter ).
Does the magnitude of the emitted radiation increase with temperature?
At any wavelength the magnitude of the emitted radiation increases with increasing temperature. The spectral region in which the radiation is concentrated depends on temperature, with comparatively more radiation appearing at shorter wavelengths as the temperature increases ( Wien’s Displacement Law ).
Is a black body an absorber of electromagnetic radiation?
Since the absorptivity and the emissivity are interconnected by the Kirchhoff’s Law of thermal radiation, a blackbody is also a perfect absorber of electromagnetic radiation. For an arbitrary body emitting and absorbing thermal radiation in thermodynamic equilibrium, the emissivity is equal to the absorptivity.
Definition of Black Body Radiation
Black Body Radiation: When radiant energy falls on the surface of anybody, a part of it is reflected, a part is absorbed, and the rest is transmitted. The whole energy is not absorbed because generally, the surfaces of ordinary bodies are not perfect absorbs of radiation.
Summary
When solids are heated, they emit radiations over a wide range of wavelengths. For example, when an iron bar is heated in a furnace, it emits radiation and becomes dull red and then progressively becomes redder and redder as the temperature increases.
Further Explanation of Black Body Radiation
At a given temperature, the intensity of radiation emitted from a black body increases with wavelength decrease. It reaches a maximum value at a given wavelength and then decreases with a further reduction of wavelength.
History of Black Body Radiation
In late 1859, Kirchhoff had defined a black body as an object that is a perfect emitter and absorber of radiation. He guessed, that he should recombine these two expressions in the simplest possible way. And thus transform the result into a formula relating the energy of the radiation to its frequency.
Sources of Black Body Radiation
Blackbody radiation sources are utilized in thermal imagers testing and calibrating. When the source has been incorporated as an optical test bench automated testing using CI Systems Computerized Test Executive Software. It may be employed to determine the thermal imager operational characteristics or Unit Under Test.
What is the definition of black body radiation?
Black-body radiation, also termed Planck’s law, determines the intensity of a radiation ( Ie) at a wavelength ( λ) from the temperature ( T) of the emitter, if the latter is a perfect absorber and emitter (black body):
How is laser energy absorbed?
There, the material is heated, vaporized and transformed in a low density, hot expanding plasma. At the second step, the remaining part of the laser pulse propagates through this plasma and is partially absorbed near its reflection point, called the critical density. For the laser wavelengths in the optical domain, that is, from 0.3 to 1 μm, the plasma critical density is very low, 10–100 times smaller than the solid density. The absorbed laser energy is transported further from this low density hot plasma to the cold solid material by electrons and partially by X-ray radiation. The energy flux arriving on the cold dense material causes its ablation and ejection of the vapors. This is the final step of the laser energy absorption process—the reaction force of ablated vapors creates a pressure on the remaining solid part of the shell.
How does the transmission of solar radiation affect the spectral distribution of the Sun?
Transmission through the atmosphere changes the spectral distribution of solar radiation due to the selective absorption of radiation. It also varies with the composition of the atmosphere and the length of the path through the atmosphere, which is determined by the position of the sun.
What is the peak of the sun's UV radiation?
As a result, the sun emits UV/visible radiation with a peak at 500 nm which is based on the sun's surface temperature ( Tsun) = 5780 K. The earth's average temperature ( T) = 290 K, and its black body emission curve peaks at about 10,000 nm, which is 20 time longer than the sun's peak radiation.
Is the Sun a black body?
The Sun is very similar to a black body. Despite significant variations of the solar spectrum near the surface due to many atmospheric processes, especially clouds, total solar radiation in space has been found to be fairly constant. For example, at 645 km ASL, the daily average total solar radiation ranged from 1357 to 1362 W m−2, ...
What is black body radiation?
Black body radiation is the emission of electromagnetic energy by an object which is in a thermodynamic equilibrium. The blackbody emits an amount of energy depends on its temperature, with ideal blackbody absorbing and re-emitting all the incident radiations it receives at any wavelength.
What are black bodies used for?
Applications. The blackbodies are used for lighting, heating, security, thermal imaging, as well as testing and measurement applications. Since the intensity of the energy at any temperature and wavelength and can be determined using the Planck Law of radiation. A blackbody radiation source with a known temperature, or, ...
What are the factors that determine the blackbody radiation source?
The choice of the blackbody radiation sources depends on the temperature, type of the application and environment. The major factors considered include; The temperature depends on the object under test. For example, a low-temperature blackbody is suitable for applications such as calibrating IR sensor that looks at buildings, vehicles, ...
What are some examples of blackbody radiators?
Some examples of blackbody radiators that emit visible light or whose radiation is used for other processes include the electric heaters, incandescent light bulbs, stoves, the sun, the stars, night vision equipment, burglar alarms, warm-blooded animals, etc. Typical blackbody radiations:
Why do welders wear dark goggles?
Due to this, welders usually use dark goggles to prevent damage to their eyes. An object that is not very hot still emits radiation, but in the infrared region. This is utilized in night vision equipment which is used to detect the infrared radiation and convert this into a visible image.
What is the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation?
The electromagnetic radiation occupies a wide spectrum, both in the visible and invisible regions depending on the temperature of the object and amount of radiation.
Can you see black body radiation with the naked eye?
The black body radiation from animals is usually in the infrared radiation, and cannot be seen with the naked eye ; however, a thermal camera can be used to see the thermal radiation from an animal.
Why is black body radiation important?
Why is the black body radiation so important? In the derivation of the black-body radiation formula the assumption is made that the system is an electromagnetic cavity, so that it can be considered in thermal equilibrium.
What is blackbody radiation?
2. Blackbody radiation is characteristic of every object in thermodynamic equilibrium and black bodies at constant uniform temperature. At any temperature objects emit thermal radiation. EM radiation is emitted because inside the object, due to thermal motion of particles charged particles/dipoles start to oscillate, ...
Why is a cavity with a small hole with EM radiation inside it a near perfect blackbody?
So a cavity with a small hole with EM radiation inside it is appropriate to study mathematically and is a near perfect blackbody because the hole allows negligible radiation to enter the cavity so that it affects negligibly the thermal equilibrium ...
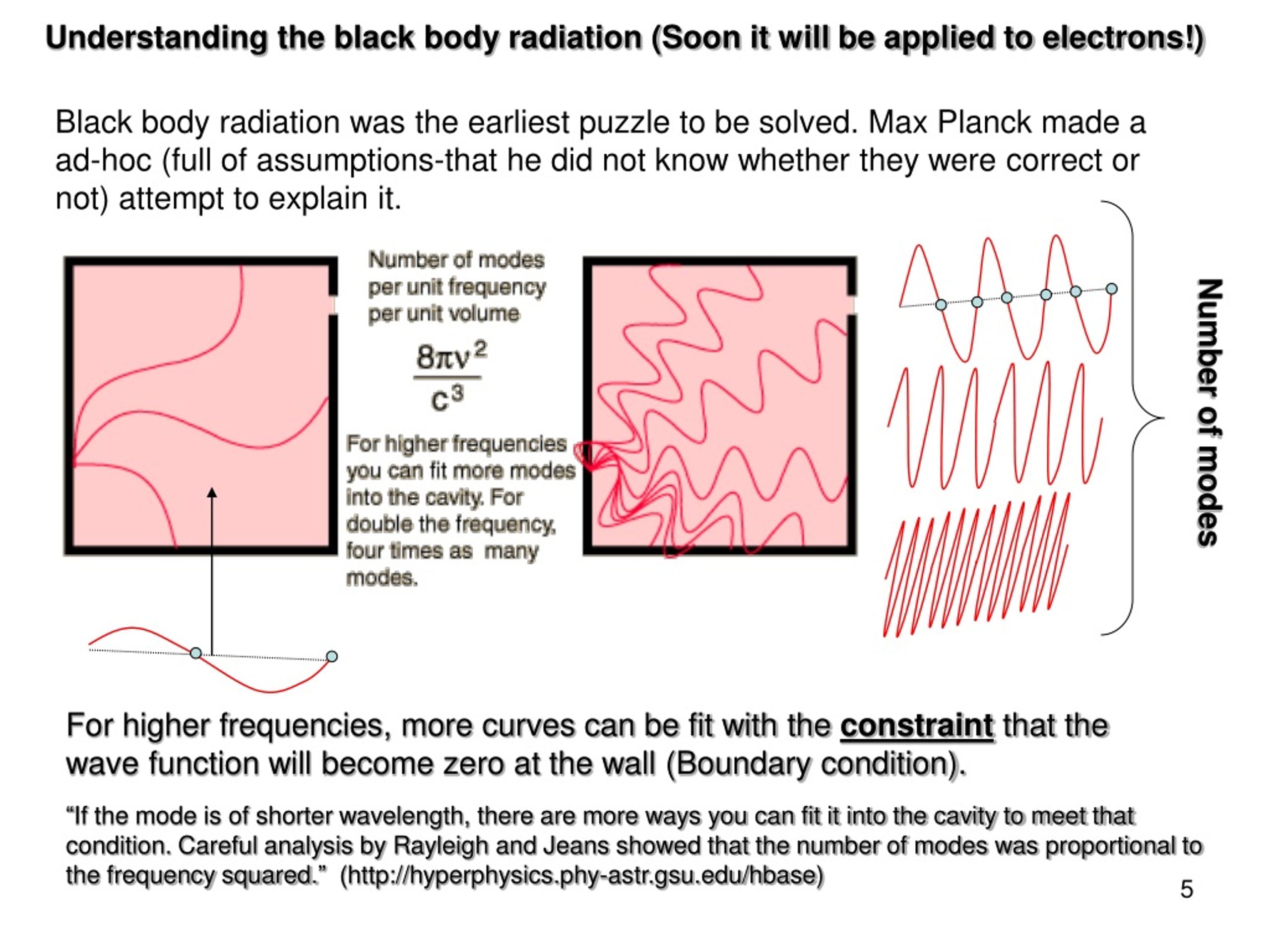
Did Rayleigh and Jeans explain the blackbody spectrum?
Rayleigh and jeans couldn't explain blackbody spectrum at higher frequencies, their law predicted infinte spectral radiance at infinite frequencies . Planck gave the solution to the ultraviolet catastrophe (infinite spectral radiance at infinite frequencies) and explained the spectrum of blackbody radiation by assuming the energy ...

Testing Thermal Radiation
Radiancy, Temperature, and Wavelength
- Performing the experiment for a number of different temperatures, we obtain a range of radiancy vs. wavelength curves, which yield significant results: 1. The total intensity radiated over all wavelengths (i.e. the area under the R(λ) curve) increases as the temperature increases. This is certainly intuitive and, in fact, we find that if we take the integral of the intensity equation above, …
Blackbody Radiation
- The above description involved a bit of cheating. Light is reflected off objects, so the experiment described runs into the problem of what is actually being tested. To simplify the situation, scientists looked at a blackbody, which is to say an object that does not reflect any light. Consider a metal box with a small hole in it. If light hits the ...
Failure of Classical Physics
- The data (the other three curves in the graph) actually show a maximum radiancy, and below the lambdamax at this point, the radiancy falls off, approaching 0 as lambdaapproaches 0. This failure is called the ultraviolet catastrophe, and by 1900 it had created serious problems for classical physics because it called into question the basic concepts of thermodynamicsand elec…
Planck’s Theory
- Max Planck suggested that an atom can absorb or reemit energy only in discrete bundles (quanta). If the energy of these quanta is proportional to the radiation frequency, then at large frequencies the energy would similarly become large. Since no standing wave could have an energy greater than kT, this put an effective cap on the high-frequency radiancy, thus solving th…
Consequences
- While Planck introduced the idea of quanta to fix problems in one specific experiment, Albert Einstein went further to define it as a fundamental property of the electromagnetic field. Planck, and most physicists, were slow to accept this interpretation until there was overwhelming evidence to do so.
Overview
Black-body radiation is the thermal electromagnetic radiation within, or surrounding, a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, emitted by a black body (an idealized opaque, non-reflective body). It has a specific, continuous, spectrum of wavelengths, inversely related to intensity, that depend only on the body's temperature, which is assumed, for the sake of calculations and theory, to be uniform and constant.
Theory
Black-body radiation has a characteristic, continuous frequency spectrum that depends only on the body's temperature, called the Planck spectrum or Planck's law. The spectrum is peaked at a characteristic frequency that shifts to higher frequencies with increasing temperature, and at room temperature most of the emission is in the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. As the temperature increases past about 500 degrees Celsius, black bodies start to emit significant am…
Equations
Planck's law states that
where
is the spectral radiance (the power per unit solid angle and per unit of area normal to the propagation) density of frequency radiation per unit frequency at thermal equilibrium at temperature . Units: power / [area * solid angle * frequency]. is the Planck constant; is the speed o…
Applications
The human body radiates energy as infrared light. The net power radiated is the difference between the power emitted and the power absorbed:
Applying the Stefan–Boltzmann law,
where A and T are the body surface area and temperature, is the emissivity, and T0 is the ambient temperature.
History
In his first memoir, Augustin-Jean Fresnel (1788–1827) responded to a view he extracted from a French translation of Isaac Newton's Optics. He says that Newton imagined particles of light traversing space uninhibited by the caloric medium filling it, and refutes this view (never actually held by Newton) by saying that a black body under illumination would increase indefinitely in heat.
In 1858, Balfour Stewart described his experiments on the thermal radiative emissive and absorp…
Doppler effect
The relativistic Doppler effect causes a shift in the frequency f of light originating from a source that is moving in relation to the observer, so that the wave is observed to have frequency f':
where v is the velocity of the source in the observer's rest frame, θ is the angle between the velocity vector and the observer-source direction measured in the reference frame of the source, and c is the speed of light. This can be simplified for the special cases of objects moving directl…
See also
• Bolometer
• Color temperature
• Infrared thermometer
• Photon polarization
• Planck's law
Further reading
• Kroemer, Herbert; Kittel, Charles (1980). Thermal Physics (2nd ed.). W. H. Freeman Company. ISBN 0-7167-1088-9.
• Tipler, Paul; Llewellyn, Ralph (2002). Modern Physics (4th ed.). W. H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-4345-0.