The following are the key applications of photoelectric sensors:
- Detect changes in a target’s color, contrast and luminescence
- Detect porous targets, and invisible markings on products
- Detect the presence or movement of an object within a defined sensing area or zone
- Detect the level of contents in a hopper
- Check products passage in a rinsing process
- Locate the position of an automated storage and retrieval system
Full Answer
How does a photoelectric smoke detector work?
Photoelectric smoke detectorsoperate with a continuous, focused beam of light onto a mirror from an LED light source that is aimed directly into a sensing chamber, away from the sensor. If smoke enters the chamber, the light that is reflected onto the light sensor is interrupted, scattering light in many directions and triggers the alarm.
What is optical and electrical sensor?
The function of an optical sensor is to convert a ray of light into an electronic signal. The main purpose of an optical sensor is to measure the physical amount of light and, depending on the type of sensor, then translate it into a form that can be read by an integrated measuring device.
What did photoelectric effect prove?
This phenomenon is the photoelectric effect, and the electrons are called photoelectrons. Experiments indicate that by increasing light frequency, the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons increases, and by intensifying the light, the current increases.
What is an opto sensor?
An opto electronic sensors is a device that is capable of producing an electrical signal that is proportional to the amount of light incident on the active area of the device. Integrated opto electronic sensors are designed to recognize fundamental stimuli such as patterns, images, motion and intensity and colour. Opto Electronics materials

What does photoelectric sensor sense?
A photoelectric sensor is a device that detects a difference in the light level received from the light source. The sensor is made up of a light source, an amplifier, signal converter, and an output.
What are the 4 types of photoelectric sensors?
There are many different styles of photoelectric sensors, but really only four basic technologies: through-beam, reflective, diffuse, and background suppression.
Is a photoelectric sensor a camera?
0:082:53What is a Photoelectric Sensor? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPresent or absence of a material photoelectric sensors do this through the use of a transmitter thatMorePresent or absence of a material photoelectric sensors do this through the use of a transmitter that emits light to a receiver.
How does a photoelectric work?
When light shines on a metal, electrons can be ejected from the surface of the metal in a phenomenon known as the photoelectric effect. This process is also often referred to as photoemission, and the electrons that are ejected from the metal are called photoelectrons.
What is the range of photoelectric sensor?
With this optical system, the distance range in which regular-reflective light from the object can be detected consistently is the sensing distance. As such, the sensing distance can range from 10 to 35 mm depending on the upper and lower limits.
Do photoelectric sensors work in the dark?
The "Dark-ON" operating mode is when a Through-beam Sensor produces an output when the light entering the Receiver is interrupted or decreases....Photoelectric Sensors.IntroductionFeaturesExplanation of TermsTroubleshooting2 more rows
Which sensor is used in camera?
CMOS sensors have also been adopted by the commercial imaging industry, meaning that nearly every smartphone camera, digital camera, or imaging device uses a CMOS sensor.
Which sensor is used to detect light?
Photoelectric sensors use a beam of light to detect the presence or absence of an object. It emits a light beam (visible or infrared) from its light-emitting element. A reflective-type photoelectric sensor is used to detect the light beam reflected from the target.
Which sensor type is best for camera?
The 35mm full-frame sensor type is the gold standard among professional photographers who want the highest-quality images. The dimensions of a 35mm sensor are typically 36×24mm.
What are photoelectric devices?
Photoelectric devices refer to devices that can realize the conversion function between light radiation energy and signal or the transmission, processing and storage of photoelectric signals.
What is photoelectric effect in short?
photoelectric effect, phenomenon in which electrically charged particles are released from or within a material when it absorbs electromagnetic radiation. The effect is often defined as the ejection of electrons from a metal plate when light falls on it.
What is an example of a device that uses the photoelectric effect?
Totally transparent photoelectric devices can be used in photodetectors and transparent solar cells to improve UV light detection. Photoelectric devices, which include solar cells, LEDs, and photosensors, convert electric power to light, or vice versa. One everyday example is the cell phone.
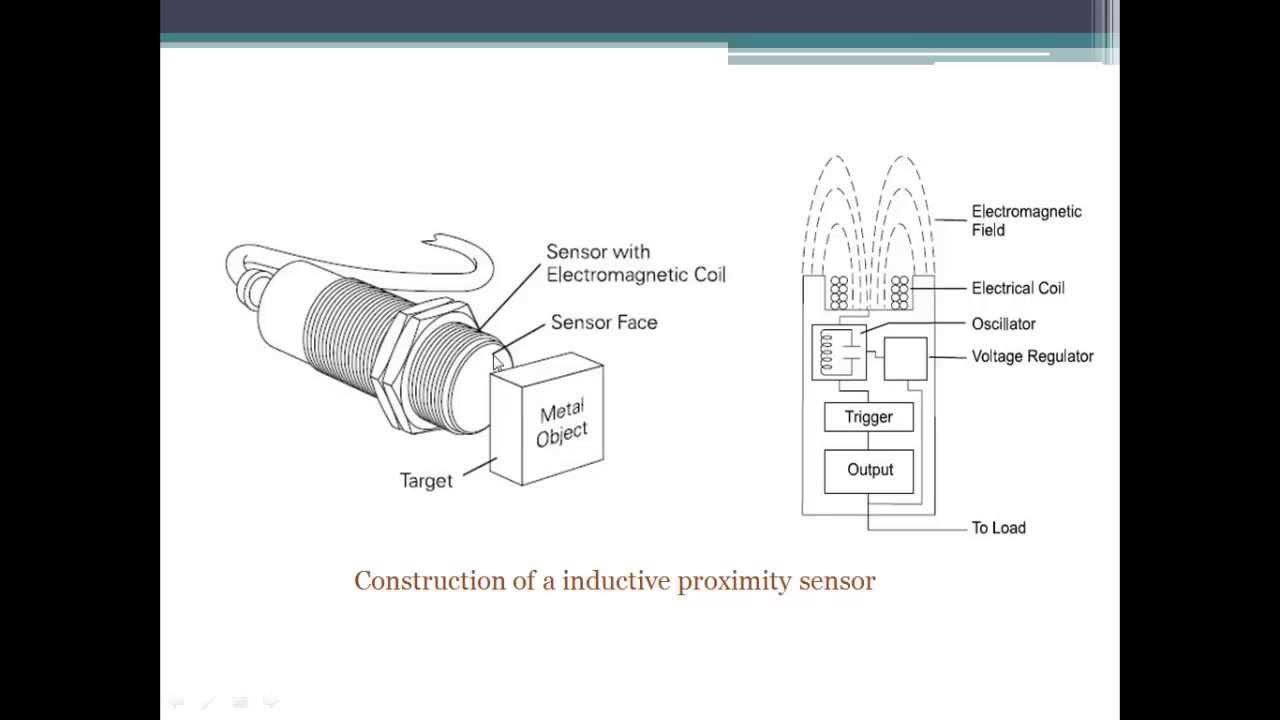
What are the different types of proximity sensors?
According with the non contact object detection method, there are five types of proximity sensor....They are,Inductive Proximity Sensor.Optical Proximity Sensor.Capacitive Proximity Sensor.Magnetic Proximity Sensor.Ultrasonic proximity Sensor.
How do I choose a photoelectric sensor?
Take into consideration the following variable when selecting an photoelectric sensor.Location. Select a sensor family that physically fits in the application location.Sensor detection mode. ... Sensor to target distance. ... Beam size. ... Sensor output requirements. ... Output configuration. ... Interface requirements.
What is a photoelectric device?
A device which gives an electrical signal in response to visible, infrared, or ultraviolet radiation. They are often used in systems which sense objects or encoded data by a change in transmitted or reflected light.
What is photoelectric proximity sensor?
One of the most common types of proximity sensor is the photoelectric sensor. These sensors detect objects directly in front of them by the detecting the sensor's own transmitted light reflected back from an object's surface.
Through (or opposed) beam
The emitter and receiver on through-beam sensors are aligned contrary to one another. The benefit of that is that the light reaches the receiver without delay and lengthy detection levels and excessive extra benefit can consequently be completed.
Retro-reflective
The emitter and receiver are aligned in a housing such that the retroreflective sensors are smooth to install.
Diffuse (proximity sensing)
Diffuse mode sensors are especially smooth to install, considering the most effective tool must be outfitted and no reflector is required.
Working Principles
A sensor is made of an irradiating detail, a specific kind of light, and detail photosensitive to the irradiated light.
Applications for photoelectric sensors
The complete programs listing for photoelectric sensors are just too lengthy to list off in a single article, so we’ve selected seven becoming examples.
The future marketplace of Photoelectric Sensors
Photoelectric sensors are more and more getting used inside the business area in which they may be used for detecting function misalignments.
Conclusion
Sometimes referred to as image sensors, photoelectric sensors emit a ray of light that is used to hit upon the presence or absence of objects and systems or modifications in floor conditions.
How Does a Photoelectric Sensor Work?
The Time of Flight (TOF) technology sends out a massive spot infrared laser and measures how long does it take the light to travel back to the receiver.
What Are the Types of Photoelectric Sensors and How These Work?
There are various types of optical sensors available and each of them works on different models, distinct housing styles, sizes, and operating styles. There are 3 primary forms types of photoelectric or Optical sensors:
Conclusion
The photoelectric technique has the benefits of precision, quick response, non-contact, etc.
What is a photoelectric sensor?
A Photoelectric Sensor is a device that uses light to detect the presence or absence of an object. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
How does a diffused photoelectric sensor work?
For the Diffused sensor to work, the sensor’s emitter needs to be pointed at an object so the light travels from the sensor’s emitter to the object and then bounces back to the sensor’s receiver.
What are the disadvantages of using a through beam sensor compared to a retroreflective sensor?
Some disadvantages of using a Through-Beam sensor compared to using a Retroreflective or Diffused sensor are they cost a little more, they require more room to mount correctly, and they do not detect thin clear objects well.
How does a retroreflective sensor work?
For the Retroreflective Sensor to work, the sensor’s emitter needs to be pointed at a reflector and aligned, so the light travels from the sensor’s emitter to the reflector and then bounces back to the sensor’s receiver.
How does a through beam sensor work?
For the Through-Beam sensor to work, the emitter and receiver have to be pointed at each other and be aligned. When they are aligned and nothing is blocking the light, the output of the sensor will be on.
Why are retroreflective sensors shorter than through beam sensors?
This is because the light has to travel to a reflector and then back to the sensor instead of just traveling straight to the receiver.
What are the disadvantages of retroreflective sensors?
Some disadvantages of using a Retroreflective sensor are you have to install the sensor with a reflector, if the object is shiny it might turn on the sensor’s output instead of the reflector, and the light beam is not as focused as a Through-Beam sensor’s light beam.