What charge does a proton give off?
A proton is a subatomic particle that has a positive charge of +1 e. An "e" is defined as the elementary electrical charge that a proton possesses, measured at approximately 1.6 x 10^-19 coulombs. The positive electrical charge of a proton is opposed by negative charge of an electron.
What are some characteristics of a proton?
Characteristics of a Proton. Protons are positively charged. protons are located inside the nucleus. Protons have a rest mass of 1.67262 × 10−27 kg(~ 1 a.m.u. which is 1.836 times the mass of an electron. The charge on 1 proton is 1.6 x 10-19 C. One coulomb is equal to the charge on 6.241 x 1018 protons.
What is a non example for proton?
The definition of a proton is a particle with a positive charge that is in the nucleus of an atom. An example of a proton is the single proton in the nucleus of a hydrogen atom. Similarly, it is asked, what is a non example of a proton? Neutrons, electrons, and photon are non-examples of a proton.
What is charge to mass ratio of proton?
The ratio of proton mass to Planck mass is dimensionless, while the proton charge measured in Coulombs depends on this completely arbitrary unit. Hence, the coincidence is completely arbitrary. There is a natural dimensionless expression for the proton charge, in which it is approximately 0.3 --- quite a few orders of magnitude off.
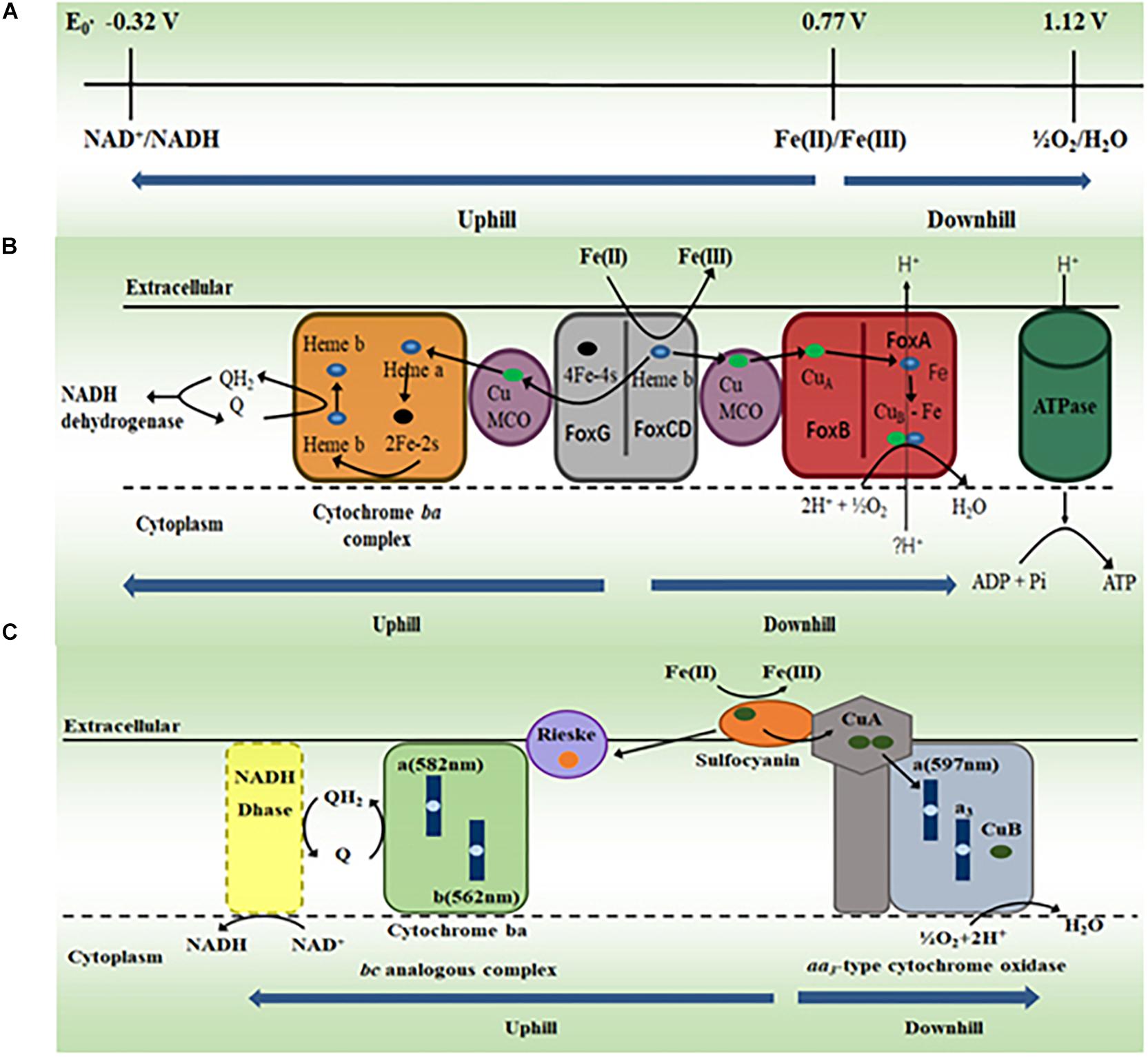
What is the significance of proton motive force in the electron transport chain?
This proton motive force provides the energy necessary for enzymes called ATP synthases, also located in the membranes mentioned above, to catalyze the synthesis of ATP from ADP and phosphate.
What does proton motive force synthesize?
A Protonmotive Force Drives ATP Synthesis in Bacteria. (themiosmotic hypothesis/membrane-bound ATPase/membrane potential/valinomycin/ATPase-negative mutants)
Why is proton motive force a form of energy?
energy that is generated by the transfer of protons or electrons across an energy-transducing membrane and that can be used for chemical, osmotic, or mechanical work.
What is proton motive force in bacteria?
In bacteria, the extrusion of protons by the electron transport chain results in an electrochemical gradient of protons, known as the proton motive force (PMF), generated across the cell membrane.
What are the two components of the proton motive force?
The protonmotive force across the inner mitochondrial membrane (Δp) has two components: membrane potential (ΔΨ) and the gradient of proton concentration (ΔpH).
How do you find proton motive force?
The sign of the force is negative for exergonic transformations in which exergy is lost or dissipated, ∆mFH+b, and positive for endergonic transformations which conserve exergy in a coupled exergonic process, ∆mFH+a = -∆mFH+b.
How does pH affect proton motive force?
At a pH of less than 5.7, there was a large decrease in proton motive force, and this decrease corresponded to the inhibition of cellobiose utilization.
Is proton motive force in photosynthesis?
The thylakoid proton motive force (pmf) generated during photosynthesis is the essential driving force for ATP production; it is also a central regulator of light capture and electron transfer.
How is proton motive force generated in fermentation?
In fermentative bacteria, a proton motive force is generated by fermentation of weak acids, such as malate and citrate. The two components of the pmf, the membrane potential and the pH gradient, are generated in separate steps.
Do flagella use proton motive force?
A protonmotive force drives bacterial flagella.
What is a motive force?
In science, motive force is the conjunction term referring to the force or forces that cause something to move or, in a sense, the force that induces motor action. Its use can be found in terms such as electro-motive force, proton motive force, among others.
Does ATP synthase pump protons?
The ATP synthase enzyme is reversible and can also serve as a proton pump by coupling ATP hydrolysis to proton translocation. Each of the respiratory enzymes uses a different strategy for performing proton pumping.
How does the proton motive force result in ATP biosynthesis?
The proton gradient produced by proton pumping during the electron transport chain is used to synthesize ATP. Protons flow down their concentration gradient into the matrix through the membrane protein ATP synthase, causing it to spin (like a water wheel) and catalyze conversion of ADP to ATP.
What is the name of the enzyme that uses the proton motive force to synthesize ATP?
ATP SynthaseThe ATP synthase is a mitochondrial enzyme localized in the inner membrane, where it catalyzes the synthesis of ATP from ADP and phosphate, driven by a flux of protons across a gradient generated by electron transfer from the proton chemically positive to the negative side.
What is synthesis of ATP?
ATP synthesis involves the transfer of electrons from the intermembrane space, through the inner membrane, back to the matrix. The transfer of electrons from the matrix to the intermembrane space leads to a substantial pH difference between the two sides of the membrane (about 1.4 pH units).
Is proton motive force in photosynthesis?
The thylakoid proton motive force (pmf) generated during photosynthesis is the essential driving force for ATP production; it is also a central regulator of light capture and electron transfer.
What is the purpose of protons motive force?
Proton motive force is the force created by the transfer of protons or electrons across a membrane that can be used for chemical, mechanical or osmotic processes. It promotes the movement of electrons against the electrochemical potential.
How is the proton motive force formed?
The proton motive force is formed when the cell membrane gains energy due to the reactions caused by the transport of electron carriers. This energy is either stored in ATP or is used immediately.
Why do bacteria need proton motive force?
All bacteria require a proton motive force to grow and replicate. Energy is conserved during respiration, by the generation of a proton motive force across a membrane impermeable to protons. Dissolution of the force leads to a rapid loss in cell viability and even cell death.
Where do protons enter the matrix?
protons enter the half channel facing the proton-rich intermembrane space, bind to an aspartate residue on one of the subunits of the c ring, and then leave the c subunit once they rotate around to face the matrix half channel
Where is the proton channel located?
the proton channel and is embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane (flow)
