
How do you calculate sampling distribution?
This tutorial explains how to do the following with sampling distributions in Excel:
- Generate a sampling distribution.
- Visualize the sampling distribution.
- Calculate the mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution.
- Calculate probabilities regarding the sampling distribution.
What is the sampling distribution's true purpose?
A sampling distribution is a probability distribution of a statistic obtained through a large number of samples drawn from a specific population. The sampling distribution of a given population is the distribution of frequencies of a range of different outcomes that could possibly occur for a statistic of a population.
Why sampling distribution of sample means is normal?
as sample size 'n' increases the sampling distribution of 'x-bar' becomes approximately normal regardless of the shape of the underlying population. The distribution of the sample mean, x-bar, will be normally distributed if the sample is obtained from a population that is normally distributed, regardless of the sample size.
What is the mean of the sampling distribution equal to?
While the mean of a sampling distribution is equal to the mean of the population, the standard error depends on the standard deviation of the population, the size of the population and the size of...

How is sampling distribution used in real life?
The sampling distribution of a proportion is when you repeat your survey or poll for all possible samples of the population. For example: instead of polling asking 1000 cat owners what cat food their pet prefers, you could repeat your poll multiple times.
What is sampling and why is it used?
Sampling is a tool that is used to indicate how much data to collect and how often it should be collected. This tool defines the samples to take in order to quantify a system, process, issue, or problem. To illustrate sampling, consider a loaf of bread. How good is the bread?
Why is sampling important in statistics?
In statistics, a sample is an analytic subset of a larger population. The use of samples allows researchers to conduct their studies with more manageable data and in a timely manner. Randomly drawn samples do not have much bias if they are large enough, but achieving such a sample may be expensive and time-consuming.
What are the advantages of sampling?
Advantages of Sampling MethodReduce Cost. It is cheaper to collect data from a part of the whole population and is economically in advance.Greater Speed. ... Detailed Information. ... Practical Method. ... Much Easier.
What is sampling explain?
Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students. In statistics, sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population.
What is sampling in a research?
Sampling is the selection of a subset of the population of interest in a research study. In the vast majority of research endeavors, the participation of an entire population of interest is not possible, so a smaller group is relied upon for data collection.
What is the meaning of sampling in research?
In research terms a sample is a group of people, objects, or items that are taken from a larger population for measurement. The sample should be representative of the population to ensure that we can generalise the findings from the research sample to the population as a whole.
What is sample explain?
Definition: A sample is defined as a smaller set of data that a researcher chooses or selects from a larger population by using a pre-defined selection method. These elements are known as sample points, sampling units, or observations. Creating a sample is an efficient method of conducting research.
What Is a Sampling Distribution?
A sampling distribution is a probability distribution of a statistic obtained from a larger number of samples drawn from a specific population. The sampling distribution of a given population is the distribution of frequencies of a range of different outcomes that could possibly occur for a statistic of a population .
What is the distribution of a sample?
Each sample has its own sample mean and the distribution of the sample means is known as the sample distribution.
What is the standard deviation of a sampling distribution?
The standard deviation of a sampling distribution is called the standard error. While the mean of a sampling distribution is equal to the mean of the population, the standard error depends on the standard deviation of the population, the size of the population and the size of the sample.
What is the majority of data analyzed by researchers?
The majority of data analyzed by researchers are actually drawn from samples, and not populations.
Does a sample have a bell curve?
However, because a sampling distribution includes multiple sets of observations, it will not necessarily have a bell-curved shape.
Why is sampling distribution important?
This is also called a probability distribution because it relies on probability to inform the data scientist of sample statistics. Using a sampling distribution simplifies the process of making inferences about large amounts of data. For this reason, it is used often as a statistical resource in data science.
Why do data scientists use sampling distributions?
When data scientists work with large quantities of data they sometimes use sampling distributions to determine parameters of the group of data, like what the mean or standard deviation might be. Parameters are facts about data in the form of statistical values. This is also called a probability distribution because it relies on probability ...
What is the most common type of sampling distribution?
The most common type of sampling distribution is of the mean . It focuses on calculating the mean of every sample group chosen from the population and plotting the data points. The graph shows a normal distribution where the center is the mean of the sampling distribution, which represents the mean of the entire population.
How to measure variability in a sampling distribution?
The variability of a sampling distribution can be measured either by standard deviation or variance, de pending on the context and inferences you are trying to draw. There are three primary factors that influence the variability of a sampling distribution. They are:
What does the central limit theorem say about sampling distribution?
The central limit theorem says the sampling distribution showing mean of any variables, independent and random, will be normal or close to it when a large enough sample is used.
What happens when you do a sampling distribution of proportion?
When you do a sampling distribution of proportion you can gauge things like probability of passing an exam. Imagine you have a group of data broken into all possible samples. In each sample group, you find the probability of students passing the exam.
What is a t distribution?
A T-distribution is a sampling distribution that helps data professionals determine the population size or the population variance. The T-distribution uses a t-score to evaluate data that wouldn't be appropriate for a normal distribution. For instance, when analyzing a very small sample. The formula for t-score looks like this:
What is sampling distribution?
What is a Sampling Distribution? A sampling distribution can be defined as a probability distribution. A Probability Distribution Probability distribution is the calculation that shows the possible outcome of an event with the relative possibility of occurrence or non-occurrence as required.
Why do researchers go ahead with sampling distribution?
go ahead of sampling distribution instead of choosing the entire population. This makes the data set easy and also manageable. To make it easier, suppose a marketer wants to do an analysis of the number of youth riding a bicycle between two regions within the age limit 13-18.
What is the role of binomial distribution?
Here the role of binomial distribution comes into play. Generally, it responds to the laws of the binomial distribution, but as the sample size increases, it usually becomes normal distribution again .
What is the prime factor of sampling?
The prime factor involved here is the mean of the sample and the standard error, which, if estimates, help us calculate the sampling distribution too . There are various types of distribution techniques, and based on the scenario and data set, each is applied.
Why is it important to analyze a static distribution?
This is important because it simplifies the path to statistical inference. Moreover, it allows analytical considerations to be focussed upon a static distribution rather than the mixed probabilistic spread of each chosen sample unit.
Why is the conclusion important in statistics?
Conclusion. This is key in statistics because they act as a major guideline to statistical inference. They basically guide the researcher, academicians, or statisticians about the spread of the frequencies, signaling a range of varied probable outcomes that could be further tagged to the entire population.
When is a chi square distribution used?
This type of distribution is used when the data set involves dealing with values that include adding up the squares. The set of squared quantities belonging to the variance of samples is added, and thus a distribution spread is made, which we call as chi-square distribution.
Sampling Distribution of the Mean Example
For starters, I want you to fully understand the concept of a sampling distribution. So, here’s a simple example!
Sampling Distributions of the Mean for Normal Distributions
As you saw in the apple example, sampling distributions have their own overall shape, central tendency and variability. Let’s start exploring this for cases where the parent distribution is normal.
Standard Errors and Sample Sizes in a Sampling Distribution
As I mentioned above, the standard error of a sampling distribution depends on the sample size. Here’s the formula for the standard error of the mean: σ / √n
Sampling Distributions for Nonnormal Distributions
Sampling distributions for nonnormal data tend to follow the parent’s skewed distribution for very small sample sizes. However, as the sample size increases, the sampling distribution converges on a symmetric normal distribution with a mean = µ and a standard error of σ/√n—just like they do for normal distributions!
Sampling Distributions in Hypothesis Tests
All hypothesis tests calculate a test statistic. Their calculations take your sample data and boil them down to a single number indicating how your data compare to the null hypothesis. These are the z-scores, t-values, F-values, and chi-square values, which you probably know.
What is sampling distribution?
Sampling distribution is a key tool in the process of drawing inferences from statistical data sets. Here, we'll take you through how sampling distributions work and explore some common types.
Why Are Sampling Distributions Important?
Sampling distributions are closely linked to one of the most important tools in statistics: the central limit theorem. There is plenty to say about the central limit theorem, but in short, and for the sake of this article, it tells us two crucial things about properly drawn samples and the shape of sampling distributions:
What is the standard deviation of a sampling distribution?
Both of these sampling distributions approach a normal distribution with a particular mean and standard deviation. The standard deviation of a sampling distribution is called the standard error.
What happens if you draw a large enough random sample from a population?
If you draw a large enough random sample from a population, the distribution of the sample should resemble the distribution of the population.
How many standard deviations does a normal distribution lie within?
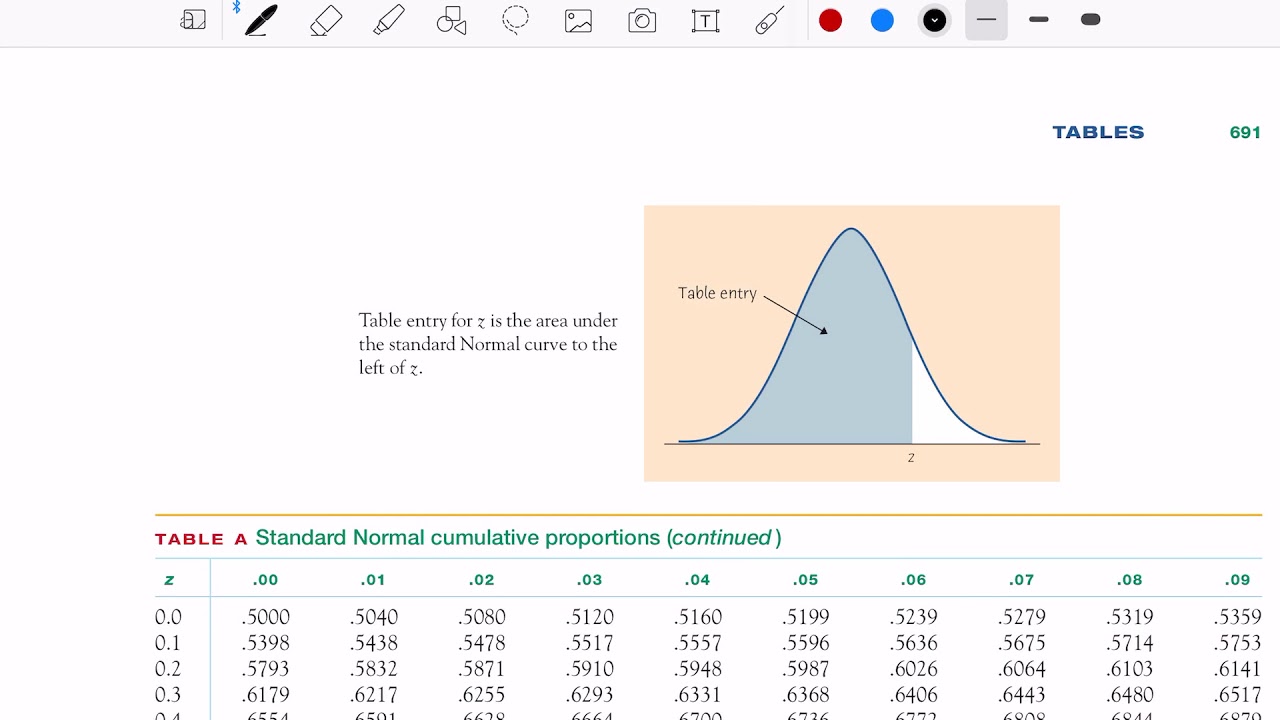
The empirical rule tells us that 68% of all observations in a normal distribution lie within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% of all observations lie within two standard deviations of the mean, and 99.7% of all observations lie within three standard deviations of the mean.
Can a normal distribution be mapped to a standard normal distribution?
Any value from a normal distribution can be mapped to a value on the standard normal distribution using a z-transformation.
Is sampling distribution the same as probability distribution?
Don’t get confused! The sampling distribution is not the same thing as the probability distribution for the underlying population or the probability distribution of any one of your samples.
What is sampling distribution?
read more. of sample means. The sampling distribution forms base for several statistical concepts that may be used by the researchers to facilitate their hypothesis.
What is standard deviation of sample size?
Standard Deviation of Sample Size Sample Size The sample size formula depicts the relevant population range on which an experiment or survey is conducted. It is measured using the population size, the critical value of normal distribution at the required confidence level, sample proportion and margin of error. read more will be –
Is the mean of a sample the same as the mean of the population?
The mean of the sample is equivalent to the mean of the population since the sample size is more than 30.
What is the mean of a distribution of the sample mean?
The distribution of the sample mean will have a mean equal to µ.
When is sample proportion normally distributed?
The sample proportion is normally distributed if n is very large and isn’t close to 0 or 1. We can also use the following relationship to assess normality when the parameter being estimated is p, the population proportion:
What would happen if we created 100 confidence intervals of the same size from the same population?
If we created 100 confidence intervals of the same size from the same population, we would expect 95 of them to contain the true parameter (the population mean weight). We also expect five of the intervals would not contain the parameter.
What is the sample mean in inferential testing?
Inferential testing uses the sample mean ( x̄) to estimate the population mean ( μ ). Typically, we use the data from a single sample, but there are many possible samples of the same size that could be drawn from that population. As we saw in the previous chapter, the sample mean ( x̄) is a random variable with its own distribution.
Why was the Student's t distribution created?
He found errors in his testing and he knew it was due to the use of s instead of σ. He created this distribution to deal with the problem of an unknown population standard deviation and small sample sizes. A portion of the t-table is shown below.
Is the assumption of a normally distributed population still important?
The assumption of a normally distributed population is still important, even though the parameter has changed.
Can you use standard deviation in real life?
Typically, in real life we often don’t know the population standard deviation (σ). We can use the sample standard deviation ( s) in place of σ. However, because of this change, we can’t use the standard normal distribution to find the critical values necessary for constructing a confidence interval.
How Does It Work?
- Select a random sample of a specific size from a given population.
- Calculate a statistic for the sample, such as the mean, median, or standard deviation.
- Develop a frequency distribution of each sample statistic that you calculated from the step above.
- Select a random sample of a specific size from a given population.
- Calculate a statistic for the sample, such as the mean, median, or standard deviation.
- Develop a frequency distribution of each sample statistic that you calculated from the step above.
- Plot the frequency distribution of each sample statistic that you developed from the step above. The resulting graph will be the sampling distribution.
Types of Sampling Distribution
- 1. Sampling distribution of mean
As shown from the example above, you can calculate the mean of every sample group chosen from the population and plot out all the data points. The graph will show a normal distribution, and the center will be the mean of the sampling distribution, which is the mean of the entire populati… - 2. Sampling distribution of proportion
It gives you information about proportions in a population. You would select samples from the population and get the sample proportion. The mean of all the sample proportions that you calculate from each sample group would become the proportion of the entire population.
Practical Example
- Suppose you want to find the average height of children at the age of 10 from each continent. You take random samples of 100 children from each continent, and you compute the mean for each sample group. For example, in South America, you randomly select data about the heights of 10-year-old children, and you calculate the mean for 100 of the children. You also randomly select d…
Central Limit Theorem
- The central limit theorem helps in constructing the sampling distribution of the mean. The theorem is the idea of how the shape of the sampling distribution will be normalized as the sample size increases. In other words, plotting the data that you get will result closer to the shape of a bell curve the more sample groups you use. The more sample groups you use, the less varia…
Additional Resources
- CFI is the official provider of the Business Intelligence & Data Analyst (BIDA)®certification program, designed to transform anyone into a world-class analyst. To keep learning and developing your knowledge of business intelligence, we highly recommend the additional resources below: 1. Basic Statistics Concepts for Finance 2. Hypothesis Testing 3. Median 4. Sa…
What Is A Sampling Distribution?
- A sampling distribution is a probability distribution of a statistic obtained from a larger number of samples drawn from a specific population. The sampling distribution of a given population is the distribution of frequencies of a range of different outcomes that could possibly occur for a statistic of a population.1 In statistics, a population is...
Understanding Sampling Distribution
- A lot of datadrawn and used by academicians, statisticians, researchers, marketers, analysts, etc. are actually samples, not populations. A sample is a subset of a population. For example, a medical researcher that wanted to compare the average weight of all babies born in North America from 1995 to 2005 to those born in South America within the same time period cannot …
Special Considerations
- A population or one sample set of numbers will have a normal distribution. However, because a sampling distribution includes multiple sets of observations, it will not necessarily have a bell-curvedshape. Following our example, the population average weight of babies in North America and in South America has a normal distribution because some babies will be underweight (belo…