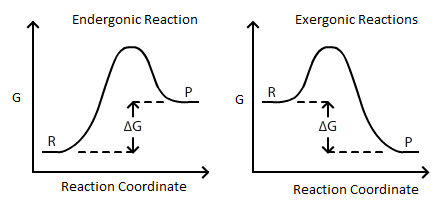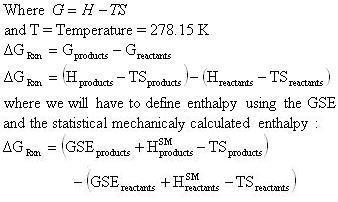
What is the relationship between Delta G and Keq?
When delta G is equal to zero and K is around one, the reaction is at equilibrium. This relationship allows us to relate the standard free energy change to the equilibrium constant. Then, when KEQ is 1 What is Delta G?
How do you calculate Delta G in chemistry?
You can use the thermodynamic equation (delta G = deltaH -- TdeltaS) OR products minus reactants. Or yawn-and-strech then peek at your neighbours paper.
How does Delta G affect Keq?
delta G<0, the reaction is spontaneous. When K<1, the reaction favors the Reactants, so the Reaction is not Spontaneous, making delta G>0. but when K >1, the Reaction favors the Products, so it is Spontaneous, making delta G< 0. Similarly, when Delta G is negative KEQ is? 1 Answer.
What are the units of Delta G?
Δ G is in the units Joules (J). Δ H is in the units of Joules (J). T is in the units of Kelvin (K). Δ S is in the units of Joules per Kelvin (J / K).
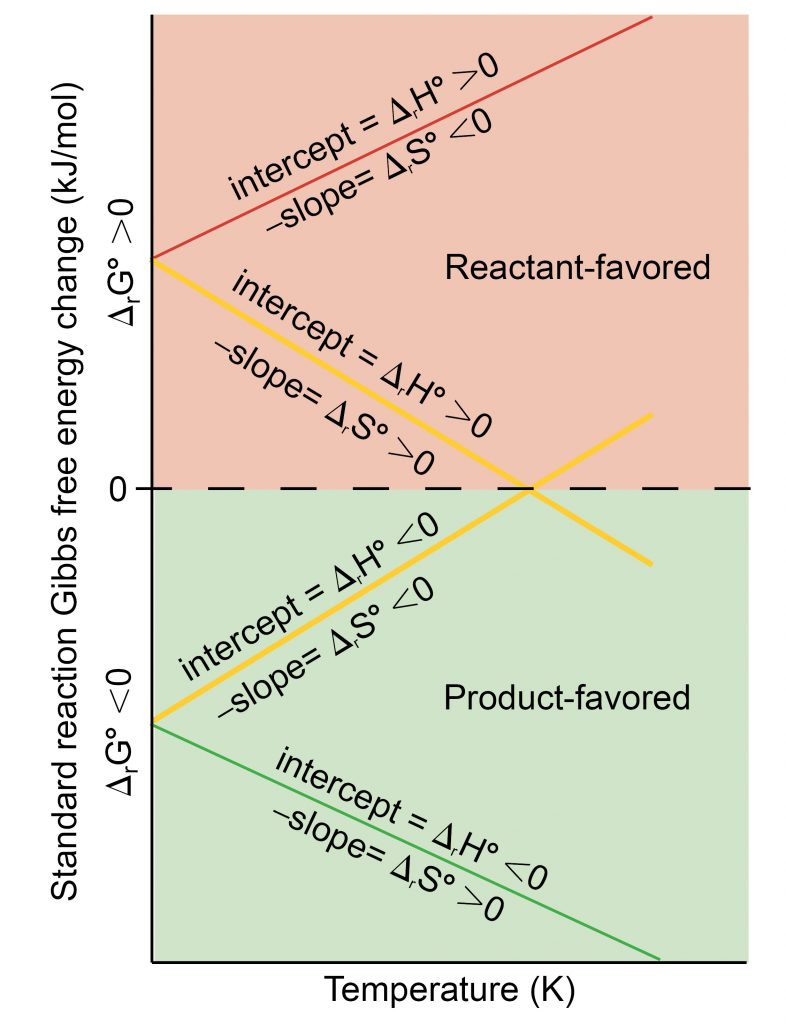
What is the value of Delta G equilibrium?
equal to zeroDelta-G was equal to zero. So, we know, at equilibrium, the change in free energy is equal to zero. So, there's no difference in free energy between the reactants and the products.
Is Delta G zero at equilibrium?
Gibbs free energy is the energy free to do work. At equilibrium, no net energy is being gained or lost (nothing is really changing). Thus, at equilibrium, Delta G is 0.
Is Delta G positive or negative at equilibrium?
As the reaction approaches equilibrium, ΔG becomes less negative and finally reaches zero. At equilibrium ΔG=0 and Q=K, so we can write (must know this!)
Why is Del G at equilibrium zero?
The equilibrium indicated by delta G = 0 is known to be the equilibrium of spontaneity. This implies that the reaction rate will be constant for both the forward reaction and the backward reaction. Was this answer helpful?
Why is Gibbs free energy 0 at equilibrium?
If the difference in Gibbs energy for the forward reaction is G, so the change in Gibbs energy is -G for the backward reaction. This is why energy from Gibbs is zero at equilibrium.
What happens to Gibbs free energy at equilibrium?
GIbbs free energy is a measure of how much potential a reaction has left to do a net something. So the free energy is zero at equillibrium and no more work can be done.
When Delta G is positive the reaction is?
If the delta G is positive, that means that the forward reaction is not favored (the backwards reaction is favored) and that the reactants will be favored because K<1. (You could then say that the reaction shifts to the left.)
When Delta G is negative the reaction is?
A negative delta (∆) G in a reaction usually means that the reaction can occur without any energy input. Thus, the reactions with a negative ∆G will be spontaneous as there is a release of energy (in the form of heat mostly). The reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
Is Delta G zero during a phase change?
ΔG is zero for a phase change at the normal phase change temperature.
Which of the following is always zero at equilibrium?
At equilibrium, the total entropy change is zero.
Which quantity out of Delta G and Delta G not will be zero at equilibrium?
1 Answer. ΔrG will always be zero. ΔrGΘ is zero for K = 1 because ΔGΘ = – RT lnK, ΔGΘ will be non zero for other values of K.
What happens if Delta G is negative?
A negative delta (∆) G in a reaction usually means that the reaction can occur without any energy input. Thus, the reactions with a negative ∆G will be spontaneous as there is a release of energy (in the form of heat mostly). The reaction will be spontaneous at all temperatures.
What does Delta G mean?
Delta G is the difference in Gibbs free energy between the products and reactants of a reaction. If Delta G is positive, the reaction is non-sponta...
How do you know if Delta G is positive or negative?
Using the Equation dG = dH - dS*T, if dH is positive and dS is negative, then delta G is positive. If dH is negative and dS is positive, delta G is...
How is Gibbs free energy calculated?
Gibbs free energy is calculated using the equation dG = dH - dS*T, where dH is the change in enthalpy, dS is the change in entropy, and T is temper...
What happens if a negative g° is negative?
As Q gets larger (i.e., as we get more products), the term ‘RT ln Q’ gets increasingly positive, and eventually adding that term to a negative ∆G°, will make ∆G = 0, equilibrium will be established and no further change occurs.
What happens when Q gets smaller?
As Q gets smaller (i.e., as we get more reactants), the term ‘RT ln Q’ gets increasingly negative, and eventually adding that term to a positive ∆G°, will make ∆G = 0, equilibrium will be established and no further change occurs.
Is K a constant?
Since K is the equilibrium constant, we are at equilibrium, the amounts of products and reactants in the mixture are fixed, and the sign of ∆G ° can be thought of as a guide to the ratio of the amount of products to the amount of reactants at equilibrium and therefore the thermodynamic favorability of the reaction.
Is G° a zero?
If it so happens that products and reactants are equally favored at equilibrium, then ∆G° is zero, BUT ∆G° is not *necessarily* ZERO at equilibrium.
Is Q too large for a positive reaction?
It is possible that Q could already be too large and therefore ∆G is positive. IF so, then the reaction will need to from more reactants, reduce the value of Q, and allow ∆G to reach zero, i.e., allow equilibrium to be established.
What is equilibrium constant?
Equilibrium constant (K): A number that expresses the relationship between the amounts of products and reactants present at equilibrium in a reversible chemical reaction at a given temperature.
What is Gibbs free energy change?
Gibbs free energy change (G): thermodynamic property defined in terms of system enthalpy and entropy; all spontaneous processes involve a decrease in G.
What is the difference between a negative and positive value of a free energy change?
The free energy change for a process may be viewed as a measure of its driving force. A negative value for ΔG represents a finite driving force for the process in the forward direction, while a positive value represents a driving force for the process in the reverse direction. When ΔG is zero, the forward and reverse driving forces are equal, and so the process occurs in both directions at the same rate (the system is at equilibrium).
When the reaction quotient is lesser than the equilibrium constant, a chemical reaction will proceed in the forward direction?
When the reaction quotient is lesser than the equilibrium constant, a chemical reaction will proceed in the forward direction until equilibrium is reached and Q = K; however, if Q < K, the process will proceed in the reverse direction until equilibrium is achieved.
What is the gas constant of R?
R is the gas constant (8.314 J/K mol), T is the kelvin or absolute temperature, and Q is the reaction quotient.
What is the standard free energy of formation?
Standard free energy of formation (ΔG∘f): change in free energy accompanying the formation of one mole of substance from its elements in their standard states
What happens to reactants at equilibrium?
At equilibrium, the reactants are converted in to products at a rate equal to the reverse process, so that at equilibrium, .
Why is the original state not an equilibrium state?
The original state is not really an equilibrium state of the system because the reaction is not at equilibrium. So, calculating the G of the system in the original state (or in any subsequent state different from chemical equilibrium) is problematic.
What direction is a spontaneous reaction?
So if , is negative, and the reaction is spontaneous in the forward direction. If , is positive, and the reaction is spontaneous in the opposite direction.