Common Causes
But with a normal junctional rhythm, the inherent heart rate should be between 40 and 60. With accelerated, it's between 60 and 100. With junctional tachycardia, the heart rate will be over 100. In this case, we have approximately 115 beats per minute, so that fits the bill for junctional tachycardia.
Related Conditions
So it is a junctional rhythm. But with a normal junctional rhythm, the inherent heart rate should be between 40 and 60. With accelerated, it's between 60 and 100. With junctional tachycardia, the heart rate will be over 100.
What is the difference between junctional rhythm and junctional tachycardia?
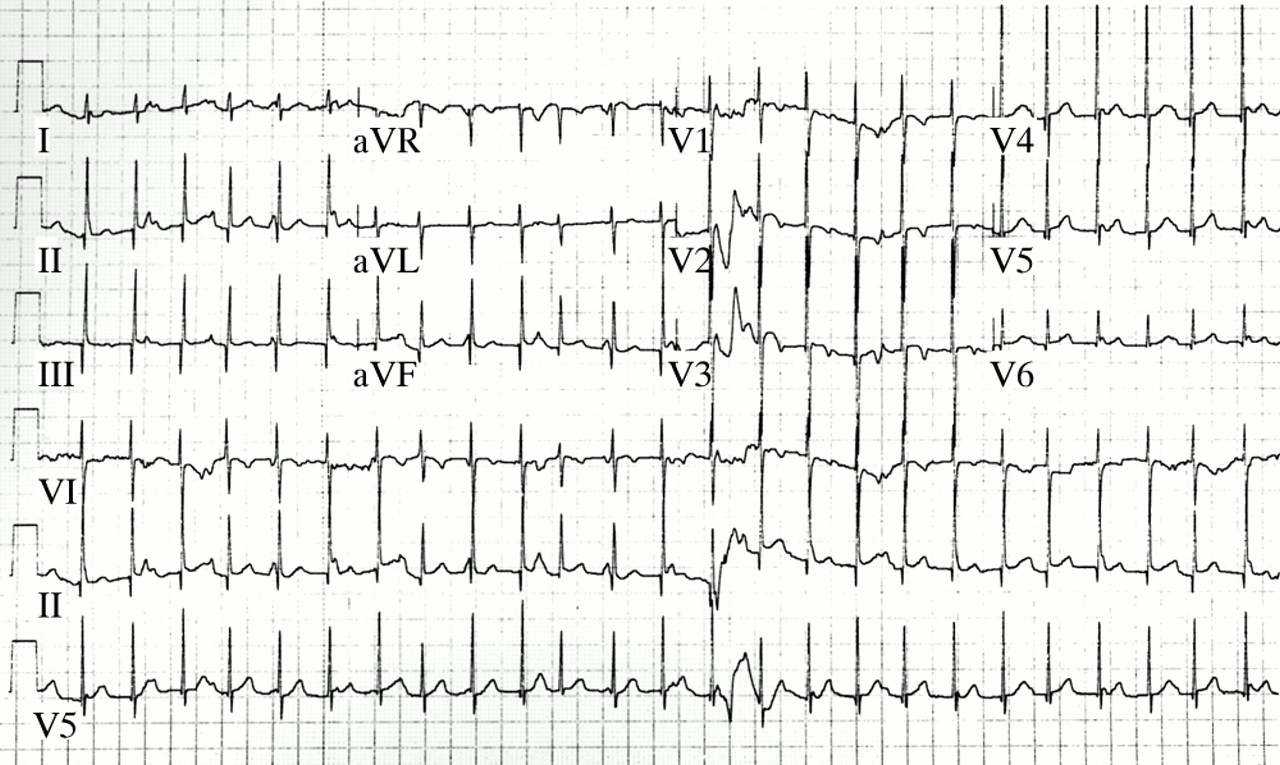
We are finally looking at a junctional tachycardia strip. We can see that it's a very regular strip, but it's very fast. So since we're dealing with a regular rhythm, we can do the small box method to calculate the heart rate. We have approximately 13 small boxes between R waves. So if we take 1,500, divide it by 13, we get 115 beats per minute.
What is the normal range of heart rate with accelerated tachycardia?
The outlook for junctional tachycardia is different depending on the type. Primary or congenital (since birth) junctional tachycardia is harder to treat and can lead to heart failure, complete heart block or ventricular fibrillation. Up to 9% of cases are fatal without treatment.
How do you calculate the heart rate on a junctional tachycardia strip?
What is the prognosis of junctional tachycardia?

Is junctional tachycardia ventricular rhythm?
If the QRS complex is wide, an accelerated junctional rhythm resembles an accelerated ventricular rhythm. The rate of the ectopic ventricular rhythm is usually 70 to 110 beats/min.
What is junctional tachycardia rhythm?
Junctional tachycardia (junctional ectopic tachycardia) is a rare heart rhythm that starts from a natural pacemaker, but not the one your heart normally uses. Usually, your heartbeat starts in your sinoatrial node and travel down through your heart. This is called normal sinus rhythm.
What is the ventricular rate for junctional bradycardia?
The junctional rate is usually 40 to 60 bpm. It can serve as an escape rhythm (Fig. 3.14) in cases of SB or AV block. Holter monitoring may be useful to document the presence of sinus node dysfunction and the cause of any symptoms that might result from the rhythm.
What is the difference between atrial tachycardia and junctional tachycardia?
Atrial fibrillation is also considered to be an atrial tachycardia. Junctional tachycardias originate from within the AV node or involve re-entrant circuits within the AV node. Supraventricular tachycardias are also known as narrow-complex tachycardias, as the QRS complex resembles normal sinus complexes.
What does a junctional tachycardia look like?
Junctional tachycardia is a form of supraventricular tachycardia characterized by involvement of the AV node....Junctional tachycardiaECG showing junctional tachycardia. Narrow complex QRS. No P waves. Heart rate fast.TreatmentAmiodarone to control the rhythm, electrical cardioversion is not used.1 more row
How do you read a junctional rhythm?
0:586:33Junctional Rhythms - EKG Interpretation - @Level Up RNYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipI get 44 beats per minute which is right in that range we talked about with junctional rhythms rightMoreI get 44 beats per minute which is right in that range we talked about with junctional rhythms right junctional rhythms will have an inherent rate between 40 and 60 beats per minute.
What is a junctional bradycardia?
Junctional bradycardia (JB) involves cardiac rhythms that arise from the atrioventricular junction at a heart rate of <60/min. In patients with retrograde atrioventricular nodal conduction, a retrograde P wave can be accompanied with JB.
What is the difference between junctional rhythm and junctional escape rhythm?
Junctional beats and junctional rhythm Less than three consecutive beats are referred to as junctional beats (also called junctional escape beats). Three or more consecutive junctional beats are referred to as junctional rhythm (also called junctional escape rhythm).
Is junctional tachycardia a type of SVT?
Junctional tachycardia is a form of supraventricular tachycardia, a type of racing pulse caused by a problem in the area between the upper and lower chambers of your heart.
Is junctional tachycardia life threatening?
But in more severe cases, you may have symptoms like shortness of breath or fatigue. A junctional rhythm usually isn't life-threatening, but if you have symptoms that interfere with your daily life, you may need treatment.
How do you treat junctional tachycardia?
Congenital junctional ectopic tachycardia (JET) is usually initially treated with antiarrhythmic therapy, with the choice of medication guided by the degree of coexisting ventricular dysfunction. Congenital JET has been successfully controlled with amiodarone, propafenone, or cautious combinations of both medications.
What are the three types of junctional rhythms?
Types of Junctional Rhythm. The three types of junctional rhythm are categorized according to the resulting heart rate. In order of ascending beats per minute (bpm), these are junctional rhythm (or junctional escape rhythm), accelerated junctional rhythm, and junctional tachycardia.
What is the dangerous condition of ventricular tachycardia?
A dangerous condition related to ventricular tachycardia is ventricular fibrillation (V-fib). In V-fib, your lower heart chambers contract in a very rapid and uncoordinated manner. This abnormal rhythm happens most often in people with heart disease or a prior heart attack.
What causes ventricular tachycardia?
Causes. Ventricular tachycardia is caused by a disruption in the normal electrical impulses that control the rate of your heart's pumping action. Many things can cause or contribute to problems with the heart's electrical system.
What causes a heart to beat faster?
In ventricular tachycardia, an abnormal electrical impulse originating in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) causes the heart to beat faster. The problem may involve either a small cluster of cells or a large area of scar tissue.
How many times does the heart beat in a minute?
A healthy heart normally beats about 60 to 100 times a minute at rest. In ventricular tachycardia, the heart beats faster than normal, usually 100 or more beats a minute. The chaotic heartbeats prevent the heart chambers from properly filling with blood. As a result, your heart may not be able to pump enough blood to your body and lungs.
What is the heart rhythm?
Normal heartbeat. In a normal heart rhythm, a cluster of cells at the sinus node sends out an electrical signal. The signal then travels through the atria to the atrioventricular (AV) node and then passes into the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump out blood.
What causes scarring in the heart?
Abnormalities of the heart that result in scarring of heart tissue (sometimes called "structural heart disease"), the most common cause is a prior heart attack. Poor blood flow to the heart muscle due to coronary artery disease. Congenital heart conditions, including long QT syndrome.
How many chambers does the heart have?
Your heart is made up of four chambers — two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles).
How long does it take for junctional tachycardia to show?
If surgery caused your junctional tachycardia, symptoms will typically show up 6 to 72 hours after the procedure. Special machines in the hospital will spot it. Your doctor might also notice a fall in both blood pressure and the heart’s pumping power.
How long does it take for a tachycardia to show up after surgery?
The tests include: If surgery caused your junctional tachycardia, symptoms will typically show up 6 to 72 hours after the procedure.
What is the name of the condition where the heart beats faster than normal?
Diagnosis. Treatment. Tachycardia is when your heart beats faster than normal, even when you’re not doing anything. Junctional tachycardia is a form of supraventricular tachycardia , a type of racing pulse caused by a problem in the area between the upper and lower chambers of your heart. It’s known as the atrioventricular node, or AV node.
What can help lower your pulse?
Medication. In some cases, prescription drugs like calcium channel blockers, amiodarone, digoxin, beta-blockers, or calcium channel blockers can help lower your pulse. Catheter ablation. If your symptoms don’t get better, your doctor might suggest a procedure called catheter ablation.
What does an EKG look for in a sinus node?
They’ll do an electrocardiogram -- sometimes called an EKG or ECG -- to look at the electrical pulsing of your heart. They’ll also look for signs that your AV node has taken over the rhythm-setting job of the heart. That’s normally the sinus node’s job.
What is junctional tachycardia?
Junctional tachycardia. Junctional tachycardia is caused by abnormal automaticity in the atrioventricular node, cells near the atrioventricular node or cells in the bundle of His. It is very rare among adults and elderly, but is relatively common in children. When occurring in adults and elderly it is referred to as nonparoxysmal junctional ...
What is the primary objective of junctional tachycardia?
Treatment of junctional tachycardia. The primary objective is to treat the underlying cause and/or eliminate provocative medications. Electrical cardioversion is ineffective and should be avoided (electrical cardioversion may be pro-arrhythmogenic in patients on digoxin).
What is the difference between JET and NPJT?
When occurring in adults and elderly it is referred to as nonparoxysmal junctional tachycardia (NPJT) whereas it is referred to as junctional ectopic tachycardia (JET) in children. NPJT is caused by ischemia, digoxin overdose, theophylline, overdose cathecholamines, electrolyte disorders and perimyocarditis.
What is the most common rhythm in the AV node?
The most common rhythm arising in the AV node is junctional rhythm , which may also be referred to as junctional escape rhythm. Junctional tachycardia is less common. Basic knowledge of arrhythmias and cardiac automaticity will facilitate understanding of this article.
What is the vagal tone of a well trained athlete?
Well-trained athletes may have very high Vagal tone which lowers the automaticity in the sinoatrial node to the point where cells in the AV-junction establishes an escape rhythm. This is asymptomatic and benign.
What happens when cells in bundle of His are not reached by the atrial impulse?
In such scenarios, cells in the bundle of His (which possess automaticity) will not be reached by the atrial impulse and hence start discharging action potentials and an escape rhythm. This will also manifest as a junctional escape rhythm on the ECG.
How many beats per minute is a junctional rhythm?
Junctional escape rhythm is a regular rhythm with a frequency of around 40–60 beats per minute.
What is the intrinsic rate of AV junction?
In general, the AV junction's intrinsic rate is 40-60 bpm so an accelerated junctional rhythm is from 60-100bpm and then becomes junctional tachycardia at a rate of >100 bpm.
Is amiodarone used for tachycardia?
Amiodarone to control the rhythm, electrical cardioversion is not used. Junctional tachycardia is a form of supraventricular tachycardia characterized by involvement of the AV node. It can be contrasted to atrial tachycardia.
Can junctional tachycardia coexist with atrioventricular tachycardia?
It can coexist with other superventricular tachycardias due to the disassociation between the SA node and the AV node. Forms of junctional tachycardia include junctional ectopic tachycardia (JET) and atrioventricular nodal re-entrant tachycardia (AVNRT) which can be distinguished by performing electrophysiological studies.
What is junctional rhythm?
A junctional rhythm is an abnormal heart rhythm that originates from the AV node or His bundle. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of junctional rhythm and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in educating patients about their prognosis.
Where does the heartbeat originate?
A junctional rhythm is where the heartbeat originates from the AV node or His bundle , which lies within the tissue at the junction of the atria and the ventricle. Generally, in sinus rhythm, a heartbeat is originated at the SA node.
Can junctional rhythm cause shortness of breath?
Patients with junctional rhythm may present with a varied array of symptoms or may be asymptomatic. Symptoms mostly depend on the underlying cause of the junctional rhythm, for instance, a patient presenting with heart failure exacerbation may present with shortness of breath, wheezing, and lower extremity edema.
Which artery supplies blood to the AV node?
The blood supply to the AV node is from the AV nodal branch of the right coronary artery (90%) or the left circumflex artery (10%) depending on right or left dominant blood supply to the heart. The first septal perforator of the left anterior descending artery also supplies blood to the AV node.
Does the heart beat with pacemaker sites?
Pathophysiology. A heart has numerous pacemaker sites within its conduction system, which are independently able to keep the heart beating. And the rate of a heartbeat depends upon the pace maker site, and as we go down its conduction system, the rate of spontaneous depolarization at pacemaker sites decreases.
Can Digoxin cause junctional rhythm?
Digoxin toxicity can also lead to an accelerated junctional rhythm. Epidemiology. Junctional rhythm is typical among individuals who have a sinus node dysfunction (SND), and 1 in every 600 cardiac patients above the age of 65 within the United States has SND.
What is the heart rate of junctional tachycardia?
With accelerated, it's between 60 and 100. With junctional tachycardia, the heart rate will be over 100. In this case, we have approximately 115 beats per minute, so that fits the bill for junctional tachycardia.
How many beats per minute is junctional rhythm?
The inherent rate of a junctional rhythm is a little slower, so it's between 40 and 60 beats per minute. And the key characteristic of a junctional rhythm is that the P wave is messed up. It's either absent, it's inverted, it happens after the QRS complex instead of before, or we have a very short PR interval.
What is the second backup of the heart?
As we explained in our article on the natural pacemakers of the heart, a junctional rhythm is the secondary backup for the heart. When the sinus node fails to kick off an electrical impulse to make the heart beat, the atrial foci are the first backup, and if that fails, the junctional foci are the next backup.
How many beats per minute is 1500?
If we use the small box method to calculate this heart rate shown above, we can see that there are 18 small boxes between the R waves. 1500 divided by 18 is 83. This means 83 beats per minute. We know it's not a regular junctional rhythm because that inherent rate is supposed to be between 40-60 BPM, and this rate is higher at 83. Accelerated junctional rhythms have an expected rate of 60-100 BPM.
Is the ventricular rhythm regular?
There are equal distances between the R waves, meaning the ventricular rhythm is regular. The P waves, though they look strange, are also regular; they have an equal distance between them. So the atrial rhythm is also regular.
Can digoxin be used for junctional dysrhythmias?
Again, remember that you would NOT use digoxin in patients with junctional dysrhythmias as it is contraindicated.
What is the heart rate of a ventricular rhythm?
With idioventricular rhythms, the heart rate is expected to be under 40 beats per minute. It is possible to have an accelerated ventricular rhythm, which would mean a heart rate over 40.
How slow is ventricular rhythm?
The inherent rate of a ventricular rhythm is very slow, between 20-40 beats per minute. The defining characteristics of ventricular rhythms are the lack of P waves and the wide QRS complexes. The QRS complex will be over 0.12 seconds in duration (over three small boxes wide).
What to do if you have ventricular tachycardia?
If the patient does not have a pulse, then they should be treated immediately with defibrillation.
Why can't the atrial rhythm be assessed?
The regularity of the atrial rhythm can't be assessed because of the lack of P waves, but the regularity of the ventricular rhythm can be assessed due to the presence of QRS complexes. In this strip shown above, there are equal distances between the QRS complexes so the ventricular rhythm is regular.
What is the rhythm you never want to see on your patient?
Asystole is the rhythm you never want to see on your patient, but you do want to see on your exam, because it is the easiest one to pick out. It looks the closest to a flat line.
What happens when the sinus node fails to kick off an electrical impulse to make the heart beat?
When the sinus node fails to kick off an electrical impulse to make the heart beat, the atrial foci are the first backup, and if that fails, the junctional foci are the next backup, and if that fails, the ventricular foci will take over and create a ventricular rhythm.
Can you see ventricular fibrillation on an EKG?
When you see ventricular fibrillation on an EKG strip, it's difficult to assess the heart rate. There are no P-waves to assess. The QRS complexes are replaced with "v-fib waves" instead. If you see an ekg strip with little bumps as shown above, then that is V-fib.

Overview
A heart rhythm disorder with heartbeats faster than usual, greater than 100 beats per minute.
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
- When the heart beats too fast, it may not pump enough blood to the rest of the body. So the organs and tissues may not get enough oxygen. Signs and symptoms that occur during an episode of ventricular tachycardia are due to a lack of oxygen and may include: 1. Chest pain (angina) 2. Dizziness 3. Pounding heartbeat (palpitations) 4. Lightheadedness 5. Shortness of br…
Prevention
- Ventricular tachycardia is caused by faulty heart signaling that triggers a fast heart rate in the lower heart chambers (ventricles). The fast heart rate doesn't allow the ventricles to fill and squeeze (contract) to pump enough blood to the body. Many things can cause or contribute to problems with heart signaling and lead to ventricular tachycardia. These include: 1. Prior heart a…