What is the name of the cluster of galaxies around Virgo?
Virgo Cluster. The Virgo Cluster is a cluster of galaxies whose center is 53.8 ± 0.3 Mly (16.5 ± 0.1 Mpc) away in the constellation Virgo. Comprising approximately 1300 (and possibly up to 2000) member galaxies, the cluster forms the heart of the larger Virgo Supercluster, of which the Local Group (containing the Milky Way galaxy)...
What are the characteristics of the Virgo Cluster?
Characteristics. The Virgo cluster lies within the Virgo Supercluster, and its gravitational effect slows down the nearby galaxies. The large mass of the cluster has the effect of slowing down the recession of the Local Group from the cluster by approximately ten percent.
Where is the Virgo Supercluster?
Map of the Virgo Supercluster centered on the Local Group (image diameter 200 Mly ≈ 60 Mpc ). The Virgo Cluster is visible in the center right of the image, at about 50 Mly from the Local Group. Below is given a table of bright or notable objects in the Virgo Cluster and the subunit of the cluster in which they are located.
How fast is the Virgo Cluster receding away from US?
Hint: Press the Info button in the selection label. 2.0 million light years Use Hubble's Law to calculate the recessional velocity of the Virgo cluster of galaxies. How fast are these galaxies receding away from us? 1240 km/sec Using the formula z=v/c, what is the redshift of the Virgo cluster of galaxies? 0.004
Why is the Virgo Cluster important?
Ever since, the Virgo Cluster has been, and still is, of primary importance for extragalactic astronomy: Large numbers of equidistant galaxies of all types and luminosities can be observed here in great detail, rendering the cluster: (1) an ideal laboratory for the study of the systematic properties of galaxies and (2) ...
What is the Virgo cluster made of?
The cluster is a fairly heterogeneous mixture of spiral and elliptical galaxies. As of 2004, it is believed that the spiral galaxies of the cluster are distributed in an oblong prolate filament, approximately four times as long as it is wide, stretching along the line of sight from the Milky Way.
What shape is the Virgo cluster?
NGC 4473 (middle-right) is an elliptical galaxy with a very oval shape. M87 (bottom-left) is the very large and active galaxy at the centre of the Virgo cluster. M88 (bottom-centre) is another nice spiral galaxy....The Galaxies of the Virgo Cluster.NGC 4459M49NGC 4473M87M88NGC 45264 more rows
What is the mass of the Virgo cluster?
their radial velocity dispersions, we made an estimate for the virial mass of the Virgo cluster. profile of the cluster, we obtain the virial mass estimate of (6.3 ± 0.9) × 1014 M⊙, which is in tight agreement with its mass estimate via the external infall pattern of galaxies.
Where is the Virgo Cluster?
RA 12h 27m 0s | Dec +12° 43′ 0″Virgo Cluster / Coordinates
Where are we in the Virgo Cluster?
The supercluster we live in is known as the Virgo Supercluster. It's an enormous collection of more than a million galaxies, stretching across a region of space 110 million light-years across. Our Sun is just one member of the Milky Way, and the Milky Way is part of a collection of galaxies known as the Local Group.
Is the Earth in the Virgo Cluster?
65.23 million light yearsVirgo Cluster / Distance to Earth
Why is it called the Virgo Supercluster?
The giant, 2000-galaxy, Virgo Cluster is about 65 million light years away. It is the proximity of some 50 nearby small groups of galaxies to the Virgo cluster that suggests that they all form an enormous flattened cluster of clusters; we call it the Local Supercluster.
Is the Virgo Cluster a Local Group?
The Virgo Supercluster (Virgo SC) or the Local Supercluster (LSC or LS) is a mass concentration of galaxies containing the Virgo Cluster and Local Group, which itself contains the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, as well as others.
How fast is the Virgo Cluster moving away from us?
about 1,100 km/secAs the cluster is receding from us at about 1,100 km/sec, this galaxy must move with over 1,600 km/sec through the Virgo Cluster's central region.
What makes up most of the Virgo Supercluster?
The giant Virgo Cluster contains more than a thousand galaxies. The central region seen here includes the cluster's most massive member, M87, below center. At the cluster's center — and the center of subgroup Virgo A — lies the giant elliptical galaxy M87. Bright galaxies like M87 fill the Virgo Cluster.
How many galaxies are in a Virgo Cluster?
2,000 galaxiesMore than 2,000 galaxies reside in the Virgo cluster, scattered in various subclusters whose largest concentration (near the famous system M87 [Virgo A]) is about 5 × 106 light-years in diameter. Of the galaxies in the Virgo cluster, 58 percent are spirals, 27 percent are ellipticals, and the rest are irregulars.
Is the Earth in the Virgo Cluster?
65.23 million light yearsVirgo Cluster / Distance to Earth
What would the Great Attractor be?
The Great Attractor is thought to be at the gravitational center of the Laniakea supercluster—of which the Milky Way is but one galaxy of 100,000 others. One theory is that it's a confluence of dark energy. Another is that it might be caused by over-density, an area of dense mass with an intense gravitational pull.
How far is the edge of the universe?
that the "edge" of the Universe is four billion light-years away
Will the expansion of the universe move them farther and farther apart?
the exp ansion of the Universe will move them farther and farther apart
What are the names of the spirals in the Milky Way?
A. Its notable spirals include the Milky Way, M31, and M33.
Which type of galaxies are the dustiest?
Type Sc are the dustiest of the galaxies. M-31 in Andromeda is a slightly bigger version of our own Milky Way. While our two companions, the Magellanic Clouds, are irregulars, Andromeda's two companions, M-32 and M-110, are dwarf ellipticals. The latest evidence from 2MASS suggests our own Milky Way is type SBb.
When are distant galaxies seen in the past?
A. Distant galaxies are seen in the past, when Cepheid variables behaved differently than they do today.
Which is older, elliptical or spiral?
A. Ellipticals are all older and more massive than spirals.
Is a spiral the same age?
Both types are about the same age, but spirals vary less in mass.
What is the resultant plot of rotation speed vs. distance from the center?
The resultant plot of rotation speed vs. distance from the center. This allows us to calculate the total mass that lies within any given distance from the Galactic Center.
What does it mean when a star is pulled in a super fast orbit?
The largest stars are being pulled in a super fast orbit, which suggests a rather large mass at the center.
What is the relationship between the distance of a galaxy and its velocity of recession away from us?
Hubble's law relates the distance of a galaxy to its velocity of recession away from us. Distance is directly proportional to veloci ty.
Which type of galaxies are brighter?
The luminosities of active galaxies are much brighter and their emission is mostly nonstellar.
What does it mean when you look at the galaxy?
Looking towards the galaxy we see more stars than perpendicular to it. This suggests a disk shape.
Where do disk stars orbit?
Disk stars orbit in the galaxy along the plane around the Galactic center, while halo stars orbit with random orientations and eccentricities.
What is the magnitude of a Cepheid star?
A Cepheid variable star in the Virgo Cluster has an absolute magnitude of -5 and is observed to have an apparent magnitude of 26.3. Use these figures to calculate the distance to the Virgo Cluster.
Which galaxy is the home of the first black hole?
Of course giant elliptical galaxy M87 dominates the Virgo cluster. It's the home of a super massive black hole, the first black hole ever imaged by planet Earth's Event Horizon Telescope. Specific copyrights apply.
What is the name of the galaxy in Markarian's chain?
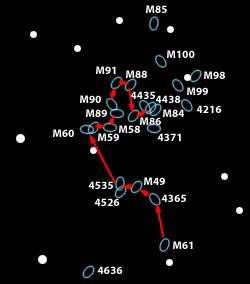
M84 and M86 are recognized as part of Markarian's Chain, a visually striking line-up of galaxies vertically on the right side of this frame. Near the middle of the chain lies an intriguing interacting pair of galaxies, NGC 4438 and NGC 4435, known to some as Markarian's Eyes. Of course giant elliptical galaxy M87 dominates the Virgo cluster.
What is the Virgo cluster?
The cluster is an aggregate of at least three separate subclumps: Virgo A, centered on M87, a second centered on the galaxy M86, and Virgo B, centered on M49, with some authors including a Virgo C subcluster, centered on the galaxy M60 as well as a LVC (Low Velocity Cloud) subclump, centered on the large spiral galaxy NGC 4216.
How does a Virgo cluster affect its gravitational force?
The Virgo cluster lies within the Virgo Supercluster, and its gravitational effect slows down the nearby galaxies. The large mass of the cluster has the effect ...
What is column 9 in Virgo Cluster?
Column 9: Subcluster where the galaxy is located. Virgo A, N Cloud, or LVC . Virgo A or own subgroup. Fainter galaxies within the cluster are usually known by their numbers in the Virgo Cluster Catalog, particularly members of the numerous dwarf galaxy population.
What is the largest galaxy in the constellation Virgo?
Messier 87 is the largest galaxy (lower left). The Virgo Cluster is a large cluster of galaxies whose center is 53.8 ± 0.3 Mly (16.5 ± 0.1 Mpc) away in the constellation Virgo. Comprising approximately 1300 (and possibly up to 2000) member galaxies, the cluster forms the heart of the larger Virgo Supercluster, of which the Local Group ...
How many galaxies are in the Virgo Cluster?
Although some of the cluster's most prominent members can be seen with smaller instruments, a 6-inch telescope will reveal about 160 of the cluster's galaxies on a clear night.
What is the intracluster medium of Virgo?
As with many other rich galaxy clusters, Virgo's intracluster medium is filled with a hot, rarefied plasma at temperatures of 30 million kelvins that emits X-Rays. Within the intracluster medium (ICM) are found a large number of intergalactic stars (up to 10% of the stars in the cluster), including some planetary nebulae. It is theorized that these were expelled from their home galaxies by interactions with other galaxies. The ICM also contains some globular clusters, possibly stripped off dwarf galaxies, and even at least one star formation region.
What are the three subgroups of Virgo?
The three subgroups are in the process of merging to form a larger single cluster and are surrounded by other smaller galaxy clouds, mostly composed of spiral galaxies, known as N Cloud, S Cloud, and Virgo E that are in the process of infalling to merge with them, plus other farther isolated galaxies and galaxy groups (like the galaxy cloud Coma I) that are also attracted by the gravity of Virgo to merge with it in the future. This strongly suggests the Virgo cluster is a dynamically young cluster that is still forming.
What percent of Virgo clusters are spirals?
Of the galaxies in the Virgo cluster, 58 percent are spirals, 27 percent are ellipticals, and the rest are irregulars. Although spirals are more numerous, the four brightest galaxies are giant ellipticals, among them M87.
How many galaxies are in the Virgo cluster?
The Virgo cluster is located at a distance of about 5 × 10 7 light-years in the direction of the constellation Virgo. More than 2,000 galaxies reside in the Virgo cluster, scattered in various subclusters whose largest concentration (near the famous system M87 [ Virgo A ]) is about 5 × 10 6 light-years in diameter.
How fast do galaxies move?
Light-year, in astronomy, the distance traveled by light moving in a vacuum in the course of one year, at its accepted velocity of 299,792,458 metres per second (186,282 miles per second).
Do Virgo galaxies have globular clusters?
Inspection of other elliptical galaxies in Virgo shows that they too have globular clusters whose apparent magnitudes are similar to those in M87, though their stellar population is substantially smaller. It appears…. Galaxies tend to cluster together, sometimes in small groups and sometimes in enormous complexes.
What is the disk around a black hole?
The accretion disk surrounding the massive black hole in active galaxies consists of hot gas at many different temperatures. The dusty infalling gas that ultimately powers the system is thought to form a rather fat, donut shaped disk which effectively absorbs much of the high energy radiation reaching it, re-emitting it in the form of cooler, infrared radiation.
Which nucleus is located directly along the axis of a high-speed jet of particles emitted?
Particularly intense active galactic nucleus in which the observer's line of sight happen to lie directly along the axis of a high-speed jet of particles emitted from the active region.
What is a luminescent galaxies?
Luminous galaxies with nonstellar emission; previously normal systems currently characterized by widespread episodes of star formation, most likely a result of interactions with a neighbour.
What are the most common types of galaxies?
Most galaxies are not large spirals - the most common galaxy types are dwarf ellipticals and dwarf irregulars.
How does the energy in the galactic nucleus work?
The leading theory for the energy source in active galactic nuclei holds that these objects are powered by material accreting onto a super massive black hole. As matter spirals toward the hole, it heats up, producing large amounts of energy. At the same time, high-speed jets of gas can be ejected perpendicular to the accretion disk, forming jets and lobes in many active objects. The jets transport magnetic fields generated in the disk out to the radio lobes, where they play a crucial role in producing the observed radiation.
What is the relation used to determine the absolute luminosity of a spiral galaxy?
A relation used to determine the absolute luminosity of a spiral galaxy. The rotational velocity, measured from the broadening of spectral lines, is related to the total mass, hence the total luminosity.
What are the characteristics of spiral galaxies?
Spiral galaxies of both types are also characterized by their size and the corresponding tight or looseness of their spiral arms.
What is the angle between the solar system and the galactic plane?
The angle between the plane of the solar system and the galactic plane is large but less than a right angle. The current Main Window view shows a gamma ray view of our galaxy. Locate our galaxy's "hot spot" in order to determine the location of the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way.
How long has the most distant galaxies been seen?
The most distant galaxies seen so far have lookback times of about 13 billion years. This means:
