
| Number of Electron Groups | Electron Group Geometry | Number of Lone Pairs |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Electron Groups | Electron Group Geometry | Number of Lone Pairs |
| 4 | tetrahedral | 0 |
| 4 | tetrahedral | 1 |
| 4 | tetrahedral | 2 |
What is the VSEPR model?
Which molecule has two bonded atoms and no lone pair of electrons?
What type of bond involves the exchange of electrons between atoms?
What type of bond does a single valence electron form?
What is the Lewis electron pair theory?
How many valence electrons does ammonia have?
How to find the electron geometry?
See 4 more
About this website
What is the name of the shape with 4 bonds and 2 lone pairs?
When a central atom has two lone electron pairs and four bonding regions, we have an octahedral electron-pair geometry. The two lone pairs are on opposite sides of the octahedron (180° apart), giving a square planar molecular structure that minimizes lone pair-lone pair repulsions.
What is the Vsepr shape for a molecule with four bonding pairs and one lone pair?
For example; four electron pairs are distributed in a tetrahedral shape. If these are all bond pairs the molecular geometry is tetrahedral (e.g. CH4). If there is one lone pair of electrons and three bond pairs the resulting molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal (e.g. NH3).
What is the geometry of a molecule with 4 bonded pairs of electrons and lone pairs of electrons?
tetrahedral# of bonding groups/domains on 'central' atom# of lone pair electrons on 'central' atomMolecular Geometry40tetrahedral31trigonal pyramidal22bent50trigonal bipyramidal9 more rows
What is the electron geometry of a molecule with 4 electron groups and 2 bonding groups around the central atom?
Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion TheoryNumber of electron groupsName of electron group geometry2linear3trigonal-planar4tetrahedral5trigonal-bipyramidal1 more row•Aug 21, 2020
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with 4 outer atoms and 2 lone pairs on the central atom?
# of bonding pair/s of electron on 'central' atom# of lone pair of electrons on 'central' atomElectron-pair Geometry40tetrahedral31tetrahedral22tetrahedral50trigonal bipyramidal9 more rows
How do you determine a VSEPR shape?
VSEPR Rules:Identify the central atom.Count its valence electrons.Add one electron for each bonding atom.Add or subtract electrons for charge (see Top Tip)Divide the total of these by 2 to find the total.number of electron pairs.Use this number to predict the shape.
Do you count lone pairs in VSEPR?
According to this model, valence electrons in the Lewis structure form groups, which may consist of a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond, a lone pair of electrons, or even a single unpaired electron, which in the VSEPR model is counted as a lone pair.
How many lone pairs does a trigonal planar have?
0 lone pairsIs it possible to have lone pairs in a trigonal planar? No, A trigonal planar molecule has 3 bonds and 0 lone pairs, with bond angles of 120 degrees.
Do VSEPR structures show lone pairs?
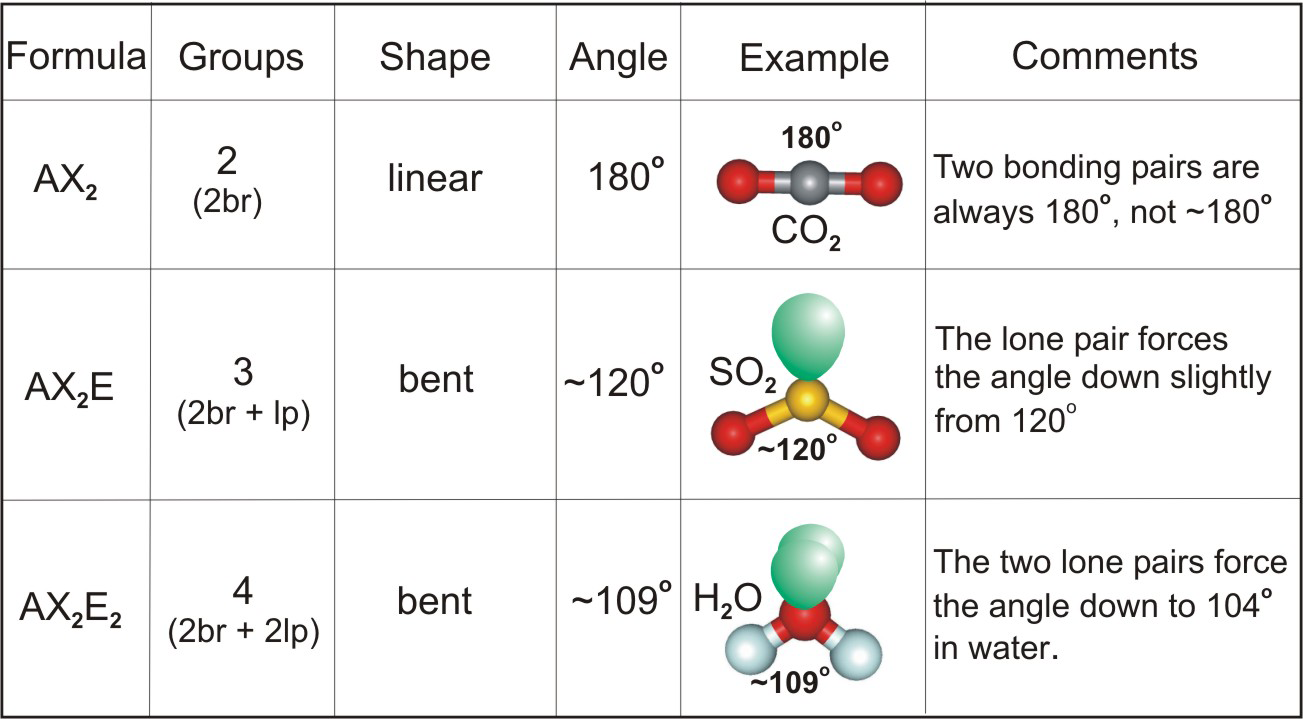
VSEPR only recognizes groups around the central atom. Thus the lone pairs on the oxygen atoms do not influence the molecular geometry. With two bonding pairs on the central atom and no lone pairs, the molecular geometry of CO2 is linear (Figure 9.2. 3).
How many VSEPR shapes are there?
The 6 basic molecular shapes are linear, trigonal planar, angular (bent), tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal, and trigonal bipyramidal.
How do you find the number of VSEPR electron groups?
0:435:38Electron Groups - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo each one of these represents a single electron group so if we have a single bond in a double bondMoreSo each one of these represents a single electron group so if we have a single bond in a double bond that represents two electron groups if we have a single double.
What is VSEPR theory with example?
VSEPR theory is used to predict the arrangement of electron pairs around central atoms in molecules, especially simple and symmetric molecules. A central atom is defined in this theory as an atom which is bonded to two or more other atoms, while a terminal atom is bonded to only one other atom.
What is the shape of SF4 molecule?
trigonal bipyramidal shapeSF4 molecular geometry is see-saw with one pair of valence electrons. The nature of the molecule is polar. These atoms form a trigonal bipyramidal shape.
What is the shape of a 4 plus?
A structure with a steric number of 5 and a lone pair represents a seesaw shape. Thus, the correct option is b. seesaw.
How many lone pairs are in a tetrahedral?
0 lone pairsThis group consist of tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal, and bent geometries. The tetrahedral geometry exists when there are 4 bonds and 0 lone pairs. This is one of the most important and common geometries, as many molecules will adopt this.
How many VSEPR shapes are there?
The 6 basic molecular shapes are linear, trigonal planar, angular (bent), tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal, and trigonal bipyramidal.
1. What is the VSEP Number?
The VSEP number or the Valence Shell Electron Pair number is used to describe the shape of the molecules. For example, the shape of a molecule will...
2. What is VSEPR Theory?
The VSEPR Theory (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory) is based on the fact that there is a repulsion between the pairs of valence electro...
3. How can we use the VSEPR Theory to Predict the Shapes of Molecules?
According to the VSEPR Theory the shape of a molecule with only two atoms is linear. In molecules with three or more atoms, one of the atoms is cal...
4. What are the advantages of the VSEPR theory?
Advantages of the VSEPR theory are given below:The VSEPR theory can be used to predict the 3-D shape of molecules and ions very effectively. The VS...
VSEPR Theory, Chart & Examples - Video & Lesson Transcript - Study.com
What is VSEPR theory? Learn the postulates of VSEPR theory and the application of VSEPR theory in predicting the shapes of molecules. Also, see the...
VSEPR and Molecular Shapes Tables - gccaz.edu
CHM151LL: VSEPR and Molecular Geometry Tables © GCC, 2006 page 2 of 6 4 Molecular Geometries Where Central Atom Has No Lone Pairs # of Outer
VSEPR Theory and the Basic Molecular Shapes | Chemistry | JoVE
Valence shell electron-pair repulsion or VSEPR theory serves as a tool to predict molecular structure. It assumes that the negatively charged electron groups, which may be electrons involved in a single bond, multiple bonds, or lone pairs, repel one another and try to stay at the maximum possible distance from each other to minimize repulsions.
VSEPR Theory: Predicting Shapes, Postulates and Limitations - Collegedunia
Steps to Use The VSEPR theory To Predict the Shape of Molecules [Click Here for Sample Questions] Step 1: First, draw the lewis electron dot arrangement for a given ion or molecule. Step 2: The least electronegative atom is taken as the central atom in the structure. Step 3: Count the total number of bonded pairs and valence shell electrons by analyzing the atoms bonded with the central atom.
VSEPR Theory Notes:Meaning, Postulates,Limitations & VSEPR Number
Read more about Chemical Equations, here.. Actual Shape. The actual shape depends on the number of bond pairs and lone pairs around the central atom. When we name the shape of a molecule according to the VSEPR theory we do not take the lone pair into consideration but the lone pair still exerts a repulsion and affects the shape of the molecule.
Which pair of electrons have more repulsion?
The lone pair of electrons are situated more closer to the central atom than the bonding electron. Hence, they have more repulsion and thus, occupy more space than bond pairs. Comment on Adhiraj Das's post “The lone pair of electron...”. Button opens signup modal.
What is the angle between hydrogen atoms?
So the angle between the hydrogen atoms will always be ~109.5 degrees (104.45, to be presice, due to reasons he stated) and the structure will always be bent/angular, you'll just be looking at if from a different angle depending on where the lone pairs were placed.
How many electron clouds does water have?
In compounds such as Methane, seen drawn at. 2:57. , all of the 4 bonding electron clouds are a 109.5 degrees from each other. Since water also has 4 electron clouds, it will take the same shape, except with unbonding electron clouds taking the place of two of those bonding electron clouds.
Is a tetrahedron a triangular?
Direct link to Sherrie Hall's post “A tetrahedron is a triang...”. more. A tetrahedron is a triangular pyramid but a triangular pyramid is not necessarily a tetrahedron (the regular polygon), so you're right but by using both terms it gives you just that little bit more precision in describing the shapes.
What is the bond angle between a lone pair and a bonding pair?
Justification: greater lone pair - bonding pair repulsion increases bond angle between the lone pair and the bonding pairs to >109.5° therefore the bond angle between the bonding pairs decreases to less than 109.5° and the molecule is said to be trigonal pyramidal
What is the shape of a molecule?
The shape of a molecule, its geometry, is a description of the way the atoms in the molecule occupy space. A diatomic molecule, a molecule composed of only 2 atoms, must always be linear in shape as the centres of the 2 atoms will always be in a straight line. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion ...
How to use Lewis structure?
How to use the table: 1. Draw the Lewis structure ( electron dot diagram) for your molecule and determine which atom is the central atom. 2. Count the total number of number of electron pairs around the central atom (the steric number) Identify the appropriate section of the table.
How to find the steric number of a lone pair?
number of bonding pairs + number of lone pairs = total number of electron pairs = steric number. If the central atom obeys the octet rule there will be 4 pairs of electrons, that is, 4 × 2 electrons = 8 electrons, and the steric number will be 4: number of bonding pairs + number of lone pairs = 4. 3.
What do the dots in a Lewis structure represent?
Remember that the pairs of dots in a Lewis structure (electron dot diagram) represent pairs of valence electrons (an 'electron cloud'). These electron pairs can be either: lone pairs (non-bonding pairs) of electrons. (those electron pairs not used in the formation of covalent bonds) bonding pairs of electrons.
Why do electron pairs in the valence shell of an atom orient themselves?
1. Electron pairs in the valence shell of an atom orient themselves so that their total energy is minimized.
What is the bond angle between two lone pairs?
Justification: greater repulsion between the 2 lone pairs of electrons increases the bond angle between them to >109.5° therefore the bond angle between the bonding pairs decreases to less than 109.5° and the molecule is said to be bent.
What is the VSEPR theory?
VSEPR theory doesn’t distinguish between single and multiple bond. Lone pair on central atom is considered as electron cloud and repels the bond pair of electrons causing the bond angle to decrease. The degree of repulsion. The geometry based on the total number of electron groups surrounding central atom is called electronic geometry.
What determines the shape of a polyatomic molecule?
In a polyatomic molecule, central atom solely determines the shape. The total number of bond pair and lone pair determines the geometry of the molecule. Shape is determined based on the number of lone pair on central atom . The complete form of VSEPR is Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory. There are three postulates of VSEPR theory.
What is the geometry of a central atom?
The geometry based on the total number of electron groups surrounding central atom is called electronic geometry. 3D molecular shape changes from electronic geometry when there is (are) lone pair of electrons on the central atom. Bond angle is determined by connecting the two adjacent atoms with a central atom.
How are electrons arranged in a polyatomic molecule?
Electrons are arranged in polyatomic molecule I such a way that the repulsion between atoms is minimized. Any Bond pair or lone pair is considered as one density area surrounding area of electron density. VSEPR theory doesn’t distinguish between single and multiple bond. Lone pair on central atom is considered as electron cloud and repels ...
How many electron density groups does H2O have?
Take the water molecule. H2O has two bond pairs and two lone pairs, total four electron density groups. The shape of the molecule is bent although the geometry is tetrahedral. The bond angle is 104.5 0 which is less than ideal for tetrahedral geometry (109.5 0) due to presence of two lone lone pairs.
What is VSEPR Theory?
The chemical formula of a compound such as {eq}H_ {2}O {/eq} or {eq}CH_ {4} {/eq} tells the ratio of elements in the compound, but does not provide information about its 3-dimensional shape. In chemistry, it is important to also examine the shape of a molecule in order to determine its behavior.
How is the shape of a molecule determined?
The shape of a molecule is determined by the number of valence shell electron pairs. These pairs can be bonded or unbonded.
What is valence shell electron pair repulsion?
As you just learned, valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) is used to predict the geometrical shape of a molecule using the molecule's Lewis electron dot configuration. It depends on groupings of electrons around the central atom in the molecule and whether the groupings are shared electrons or lone pairs of electrons, as shown in this abbreviated VSEPR chart:
How many domains are there in water?
In a molecule of water, there are 4 bonding domains around the central atom (two single bonds to oxygen and two lone pairs). Each of these domains repels each other. Notice how the two lone pairs cause the bonded hydrogens to become closer together. Remember, lone pairs have the greatest repulsion. This causes water to have a bent or angular shape. The hydrogen atoms will be less than 109 degrees apart from each other.
What is the bonding domain?
The bonding domain (also referred to as electron domain) is defined as the number of bonds around the central atom plus the number of lone pairs around the central atom. Again, double and triple bonds count as one domain.
How many electron domains are there in ammonia?
This is the geometry of ammonia. The central atom is nitrogen. Around the central atom are four electron domains. Three of the domains are bonded pairs (single hydrogen bonds to the central atom) and the fourth domain is a lone pair. According to VSEPR Theory, a molecule with these attributes will have a trigonal pyramidal geometry.
Why do valence electrons move?
VSEPR Theory states that valence electron pairs will position themselves as far apart as possible in order to minimize repulsions. When the valence electrons move, the 3-dimensional shape of the atom is affected. Imagine tying two balloons together. As more balloons are added, they naturally move away from each other changing its overall shape. The same is true in a molecule.
What is the VSEPR theory?from en.wikipedia.org
VSEPR theory is used to predict the arrangement of electron pairs around central atoms in molecules, especially simple and symmetric molecules . A central atom is defined in this theory as an atom which is bonded to two or more other atoms, while a terminal atom is bonded to only one other atom. For example in the molecule methyl isocyanate (H 3 C-N=C=O), the two carbons and one nitrogen are central atoms, and the three hydrogens and one oxygen are terminal atoms. The geometry of the central atoms and their non-bonding electron pairs in turn determine the geometry of the larger whole molecule.
What is the VSEPR model?from toppr.com
It is basically a model to predict the geometry of molecules. Specifically, VSEPR models look at the bonding and molecular geometry of organic molecules and polyatomic ions.
How many valence electrons does the central atom of the atom have?from chem.libretexts.org
A The central atom, O, has six valence electrons, and each H atom contributes one valence electron. Subtracting one electron for the positive charge gives a total of eight valence electrons, so the Lewis electron structure is. B There are four electron groups around oxygen, three bonding pairs and one lone pair.
What is the molecular geometry of a trigonal bipyramid?from chem.libretexts.org
There are four different molecular geometries that are possible in this category, depending upon the number of bonded groups and lone pairs of electrons: When all electron groups are bonds (m=5 or AX 5 ), the molecular geometry is a trigonal bipyramid with bond angles of 120° and 90° between adjacent ligands.
How many valence electrons does oxygen have?from chem.libretexts.org
Oxygen has six valence electrons and each hydrogen has one valence electron, producing the Lewis electron structure. 2. There are four groups around the central oxygen atom, two bonding pairs and two lone pairs. Repulsions are minimized by directing the bonding pairs and the lone pairs to the corners of a tetrahedron.
How many electron groups are there in the central atom?from chem.libretexts.org
There are three electron groups around the central atom: two double bonds and one lone pair. We initially place the groups in a trigonal planar arrangement to minimize repulsions (Table 3.2.1. 1 ). 3. With two bonding pairs and one lone pair, the structure is designated as AX 2 E.
What is electron pair geometry?from toppr.com
Electron Pair Geometry: This is the 3-D arrangement of electron pairs around the central atom of a polyatomic ion or molecule.
What is VSEPR in biology?from sigmaaldrich.com
VSEPR is a molecular geometry model that helps predict the general shape of a molecule but doesn’t provide information about the length or type of bonds. VSEPR theory is not effective in molecules where the central atom is a transition metal and thus has a high atomic mass that offsets or weakens the pull of bonded valence electrons.
What does VSEPR Stand for?from sigmaaldrich.com
VSEPR is an acronym that stands for valence shell electron pair repulsion. The model was proposed by Nevil Sidgwick and Herbert Powell in 1940. Ronald Gillespie and Ronald Nyholm then developed the model into their theory published in 1957; they are considered the developers of the VSEPR theory. The approach was commonly referred to as VSEPR from 1963 to the present.
What is molecular geometry?from sigmaaldrich.com
Molecular geometry describes the three-dimensional structure of a molecule. Chemists are able to predict the arrangement of atoms and chemical bonds using the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory or VSEPR. This theory revolves around the idea that electrons repel each other and therefore will bond accordingly.
Why Do Most Atoms Form Chemical Bonds?from biologyjunction.com
Most elements contain atoms that form chemical bonds. This is because those atoms become more stable when they are bonded together. Neighbouring atoms are attracted to each other by electrical forces which make them stick together. Atoms that are strongly attractive rarely spend much time on their own – other atoms will usually bond to them quite quickly. The arrangement of electrons around a central atom is what determines the strength in which it seeks out other atoms to bond with.
What is the orbital of an atom?from biologyjunction.com
The orbital is a region in which the probability of finding an electron is relatively higher than usual. Atoms have a nucleus and within this nucleus they have their own electrons rotating around. When orbitals are overlapped to create molecules via bonding, these types of orbitals are named molecular orbitals. Molecular orbital theory and valence bond theory both explain the properties of molecular and atomic orbitals. Orbitals can hold two electrons within them maximum. The main difference between molecular orbital calculation and atomic orbital calculation is that electrons within a molecular orbital are influenced by two or more nuclei. This depends on the number of atoms in the molecule. Atomic orbitals are different as they are only influenced by one positive nucleus.
How many valence electrons does the central atom of the atom have?from chem.libretexts.org
A The central atom, O, has six valence electrons, and each H atom contributes one valence electron. Subtracting one electron for the positive charge gives a total of eight valence electrons, so the Lewis electron structure is. B There are four electron groups around oxygen, three bonding pairs and one lone pair.
How many electrons does iodine have?from chem.libretexts.org
Each iodine atom contributes seven electrons and the negative charge one, so the Lewis electron structure is. 2. There are five electron groups about the central atom in I 3−, two bonding pairs and three lone pairs. To minimize repulsions, the groups are directed to the corners of a trigonal bipyramid.
What is the VSEPR model?
The VSEPR model is a straightforward yet useful way to understand and explain the shapes and structure of molecules. To reduce the electrostatic repulsion between electron pair is what the theory is based on. Before starting to use the VSEPR model, the Lewis dot picture is considered to determine the electron domain.
Which molecule has two bonded atoms and no lone pair of electrons?
CO 2. A molecule which has two bonded atoms and no lone pair of electrons (around the central atom): This is an example of AX 2. In this molecule, Carbon is contributing 4 electrons for bond formation, and each oxygen atom is donating a pair of electrons.
What type of bond involves the exchange of electrons between atoms?
Electron sharing involves the “sharing” of one or more electrons between the atoms involved in the bond formation, whereas electron exchange is the exchange of electrons between atoms and not the sharing. Co-ordinate bond is a type of covalent bond where the electrons being shared are contributed from one atom only.
What type of bond does a single valence electron form?
According to this theory, the valence electrons in an atom can form a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond, a lone pair of electrons, or even a single unpaired electron and is counted as a lone pair. The arrangement of electron groups where the electron repulsion is minimized is the most stable arrangement.
What is the Lewis electron pair theory?
However, this theory provides no information on how the atoms are arranged. The VSEPR model helps to understand the different shapes and arrangement of molecules. But this model does not say anything regarding the multiple bonds present or the bond length. It is just a representative model.
How many valence electrons does ammonia have?
In this molecule, ammonia has four valence electrons, and all four are involved in bond formation whereas hydrogen contributes its one electron in bond formation. The molecular geometry observed, in this case, is tetrahedral.
How to find the electron geometry?
Follow the below steps, 1) Find out the sum of the total number of lone pairs and the number of binding domains. 2) The sum called the steric number determines the electronic shape of the molecule. For example, a steric number of two gives a linear electronic structure.
.PNG)