What is the AP diameter of the pelvis?
The anteroposterior (AP) diameter, from the pubic symphysis to the sacrococcygeal joint, is the largest diameter of the pelvic outlet and typically measures between 9.5 to 12.5 cm. This measurement can vary widely due to the mobility of the coccyx. The transverse diameter, between the ischial tuberosities, is generally between 8 to 11 cm.
What is the pelvic brim?
The pelvic brim is an approximately Mickey Mouse head-shaped line passing through the prominence of the sacrum, the arcuate and pectineal lines, and the upper margin of the pubic symphysis . The pelvic brim is obtusely pointed in front, diverging on either side, and encroached upon behind by the projection forward of the promontory of the sacrum .
What is the average diameter of the pelvic tubes?
It measures 10.5 cm on average; it is the lesser anteroposterior diameter. The diagonal conjugate: Measured between the sacral promontory and the lower edge of the pubic symphysis, measuring an average of 12.5. The anterior-posterior diameter can also be evaluated with external pelvimetry using the various types of pelvic tubes.
What is the shape of the pelvis?
Each has peculiar characteristics regarding the width of the sub-pubic angle, the height of the pelvis, the transverse diameters of the three pelvic planes (inlet, mid pelvis, outlet), and the shape of the circumference of the upper pelvic narrow [1].

What are the diameters of the pelvic outlet?
The diameters of the outlet of the pelvis are two, antero-posterior and transverse. The antero-posterior diameter extends from the tip of the coccyx to the lower part of the pubic symphysis; its measurement is from 90 to 115 mm.
What is the narrowest diameter of the pelvic outlet?
11 cm wideWhich is the narrowest? The narrowest diameter for the fetus to pass through is the pelvic outlet, which is only 11 cm wide in the average female pelvis.
Which pelvis is wider?
female pelvisThe female pelvis is larger and broader than the male pelvis, which is taller (owing to a higher iliac crest), narrower, and more compact. The distance between the ischium bones is small in males.
How wide is the average woman's pelvis?
Average measurement in female about 110 mm. Extends across the greatest width of the superior aperture, from the middle of the brim on one side to the same point on the opposite; about 135 mm.
How wide is the average female pelvis?
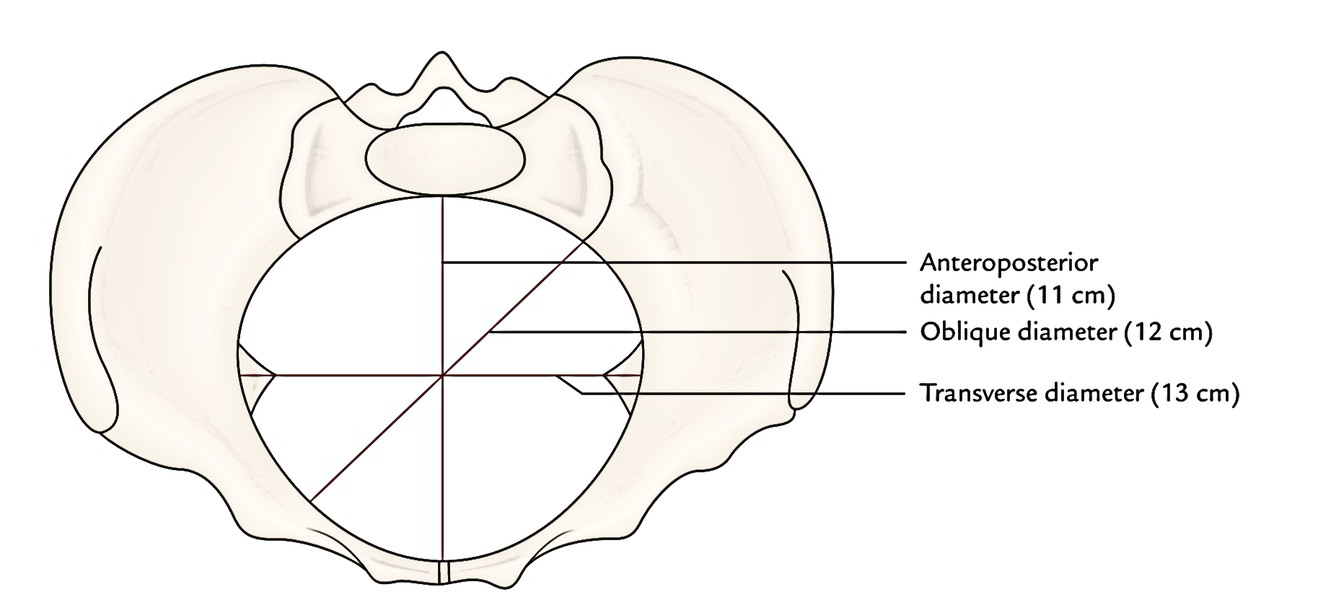
On the other hand, in the normal female pelvis the plane of the superior strait is described as more oval, the transverse diameter averaging 13 cm. and the anteroposterior 11 cm.
Why is female pelvis wider?
The female pelvic bones are typically larger and broader than a male's. This is so a baby can pass through the pubic outlet, the circular hole in the middle of the pelvic bones, during childbirth. The pubic arch, or space under the base of the pelvis, is also wider for this reason.
What is a pelvic brim?
The pelvic brim is the edge of the pelvic inlet. It is an approximately Mickey Mouse head-shaped line passing through the prominence of the sacrum, the arcuate and pectineal lines, and the upper margin of the pubic symphysis. Pelvic brim. Diameters of superior aperture of lesser pelvis -- female.
What are the 4 types of pelvis?
Although pelvises can be classified according to diameter, in obstetric practice they are often divided into 4 main types: gynecoid, android, anthropoid, and platypelloid, based mainly on the shape of the pelvic inlet [5].
What is the average transverse diameter of the pelvic outlet?
pass between the middle of the posterior surface of the symphysis pubis and the junction between 2nd and 3rd sacral vertebrae. Laterally, it passes to the centre of the acetabulum and the upper part of the greater sciatic notch. It is a round plane with diameter of 12.5 cm.
How do you measure Bituberous diameter?
Bituberous diameter: can be measured by pelvimeter....The pelvic capacity is diminished from the inlet to the outlet.Subpubic angle is acute.Convergent side walls.Bituberous diameter is 8 cm or less.
Which plane is contracted when the interspinous diameter is less than 8 cms?
The anteroposterior diameter of the midpelvis, which runs from the inferior aspect of the pubic symphysis to the sacral hollow at the level of the ischial spines, averages 11.5 cm or more. Midpelvic contraction should be suspected whenever the interspinous diameter is less than 10 cm.
What is the average of interspinous diameter?
MeasurementParameterNormal measuresPelvic inletObstetric conjugate10 to 12 cm.Interspinous distance9.5 to 11.5 cm.Pelvic outletSagittal pelvic outlet diameter9.5 to 11.5 cm.Intertuberous diameter10 to 12 cm.1 more row
What is the pelvic brim?
The pelvic brim is the edge of the pelvic inlet. It is an approximately Mickey Mouse head-shaped line passing through the prominence of the sacrum, the arcuate and pectineal lines, and the upper margin of the pubic symphysis .
What is the oblique plane of the pelvis?
The oblique plane passing approximately through the pelvic brim divides the internal part of the pelvis ( pelvic cavity) into the false or greater pelvis and the true or lesser pelvis. The false pelvis, which is above that plane, is sometimes considered to be a part of the abdominal cavity, rather than a part of the pelvic cavity.
Where is the urinary bladder located?
The urinary bladder lies just above the anterior pelvic brim. The sigmoid colon also passes close to the pelvic brim.
How many normal variants of pelvic shape are there?
The four normal variants of pelvic shape according to Caldwell-Malloy classifications[7][13]:
What is the pelvic outlet?
The pelvic outlet also called the inferior pelvic aperture, defines the lower margin of the lesser (true) pelvis. The pelvic cavity (the true pelvis) predominantly contains the urinary bladder, the colon, and the internal reproductive organs. This space is enclosed between the pelvic inlet and the pelvic outlet. The pelvic outlet is the inferior opening of the pelvis that is bounded by coccyx, the ischial tuberosities, and the pubis symphysis.
How does the pelvis form?
By the fifth week, the condensation of mesenchymal tissue in the limb buds form the template for bone models, and the ilium becomes recognizable by about five months prenatally. The pelvis forms via the process of endochondral ossification, where chondrocytes in cartilage stimulate mineralization and blood vessel growth. This ossification stems from three primary ossification centers termed the iliac center, ischial center, and pubic center. The primary ossification centers are well developed by birth, but the ossification process continues postnatally, slowing down after three months of age. Ontogeny of the pelvis is completed in adulthood, typically around 25 years of age. Sexual dimorphism of the pelvis is visually apparent in the ilium, the acetabulum, the iliac height, and the width of the pelvic inlet and outlet. [4][5][6]
What nerves pass through the pelvis?
The lumbosacral trunk (L4-S3), the sacral plexus, and coccygeal plexus all pass through the pelvic cavity. Numerous branching nerves innervate pelvic and perineal muscles. Additionally, there are parasympathetic and sympathetic innervations within the pelvis. Divisions of the pelvic splanchnic (parasympathetic), sacral splanchnic (sympathetic), and the inferior hypogastric plexuses also have branches that supply the viscera of the pelvis. While many nerves originate below the level of the pelvic brim, very few of these nerves pass through the pelvic outlet but, instead, exit through the many foramina within the pelvis or terminate within the true pelvis.
Can a fetus fit through the pelvic outlet?
Fetal macrosomia, which correlates with maternal diabetes, may increase the risk that the fetus cannot fit through the pelvic outlet during vaginal delivery. Patients with gestational diabetes or maternal diabetes should be monitored carefully for fetal macrosomia and evaluated for risk of fetal demise during vaginal delivery. Shoulder dystocia results from the impaction of the fetal shoulders against the pelvic outlet. Following the delivery of the head, the anterior shoulder may become trapped behind the pubic symphysis. Complications may include fetal brachial plexus injuries, fetal hypoxia, fetal rib or clavicle fractures, umbilical cord compression, perineal lacerations, and postpartum hemorrhage. Several maneuvers and surgical interventions may be employed as needed to complete the delivery. The Gaskin maneuver, with the mother on all fours, widens the pelvic outlet and has been shown to allow successful delivery in up to 80% of cases. [18][19][20][21]
Can pelvic outlet be measured?
In contrast to the pelvis inlet, the pelvic outlet can be estimated via a physical exam. The pelvic outlet is a principal component of pelvimetry. These measurements are useful when assessing the risk of labor arrest, cephalo-pelvic disproportion, or a fetus’s ability to navigate through the birth canal. However, pelvimetry has limited use as the female pelvic joints and ligaments slacken during labor. Clinical evidence indicates that pelvimetry does not change the management of pregnant patients, as all pregnant individuals should be allowed the trial of labor regardless of pelvimetry results. [16][17]
Which part of the pelvic brim is the largest diameter?
The largest diameter of the presenting part has passed through the pelvic brim. Pelvic brim widest from side to side. At the level of the ischial spines 0 = engagement.
How many joints are there in the symphysis pubis?
one symphysis pubis, two sacroilliac joints and one sacrococcygeal joint.
What is the graphical record of the progression of labour?
provides graphical record of the progression of labour, particularly the dilatation of the cervix. progress can be assessed from the visual patterns of cervical dilatation and descent of the presenting part in conjunction with the record of the maternal and fetal wellbeing.
What is the process of permanent and pregressive shortening of the muscles of the uterus?
the process of permanent and pregressive shortening of the muscles of the uterus which accompanies contractions during labour- to dilate the cervix, to expel the fetus and to expel the uterus, membranes and to control bleeding.
How much dilation is in a cervix?
the extent to which the cervix has opened in preparation as a result of uterine contractions, full dilatation is 10cm.
What is the ischial tuberosity?
ischial tuberosity. is a large prominence when the body rests when sitting. ischial spines. lies above the ischial tuberosity, inward projections, situation of fetal head is estimated in terms of centimeters above or below. what are the joints of the pelvis.
What is the pelvic cavity?
The Pelvic Cavity. It is a segment, the boundaries of which are: the roof is the plane of pelvic brim, the floor is the plane of least pelvic dimension, anteriorly the shorter symphysis pubis, posteriorly the longer sacrum. The Pelvic Outlet. Anatomical outlet. It is lozenge-shaped bounded by;
What is the difference between a false pelvis and a true pelvis?
False pelvis: above the pelvic brim and has no obstetric importance. True pelvis: below the pelvic brim and related to the child -birth. THE TRUE PELVIS. It is composed of inlet, cavity , and outlet. The Pelvic Inlet (Brim)
What is the diameter of a sacrocotyloid?
from the left sacroiliac joint to the right iliopectineal eminence. Sacro-cotyloid diameters = 9-9.5 cm. from the promontory of the sacrum to the right and left iliopectineal eminence, so the right diameter ends at the right eminence and vice versa. The Pelvic Cavity. It is a segment, the boundaries of which are:
Where is the upper border of symphysis pubis?
from the tip of the sacral promontory to the most bulging point on the back of symphysis pubis which is about 1 cm below its upper border.
What is the shape of the inlet?
Inlet is triangular or heart-shaped with anterior narrow apex.
Which muscle is located at the ischial spine?
The levator ani muscles are situated at this level and its ischio-coccygeous part is attached to the ischial spines.
Where is the apex of the posterior sagittal plane?
Posterior sagittal plane: its apex at the tip of the coccyx.
Which pelvis shape is most favorable for a vaginal birth?
The gynecoid pelvis is the most common pelvis shape in females and is favorable for a vaginal birth. Other pelvis types, such as the android and platypelloid shapes, may lead to a more difficult vaginal birth or the recommendation of a C-section. But pelvis shape alone doesn’t determine how you give birth.
Which pelvis is narrower, gynecoid or Android?
Android. This type of pelvis bears more resemblance to the male pelvis. It’s narrower than the gynecoid pelvis and is shaped more like a heart or a wedge.
Why is it so hard to give birth with a platypelloid pelvis?
Platypelloid. The shape of the platypelloid pelvis can make a vaginal birth difficult because the baby may have trouble passing through the pelvic inlet. Many pregnant women with a platypelloid pelvis need to have a C-section.
What is the pelvic inlet?
During vaginal childbirth, the baby passes through the birth canal, which runs through your pelvic cavity. The pelvic inlet is at beginning of the birth canal. The four different pelvis shapes are: Gynecoid. This is the most common type of pelvis in females and is generally considered to be the typical female pelvis.
What to do if you are pregnant and have concerns about pelvis shape?
If you’re pregnant or planning to become pregnant and have concerns about how your pelvis shape might affect childbirth, speak with your doctor. They can examine your pelvis to help get an idea of how it’s structured.
Why is labor so difficult with an Android pelvis?
The narrower shape of the android pelvis can make labor difficult because the baby might move more slowly through the birth canal. Some pregnant women with an android pelvis may require a C-section. Anthropoid. The elongated shape of the anthropoid pelvis makes it roomier from front to back than the android pelvis.
What are some examples of health conditions that can affect your pelvis?
Several health conditions can affect your pelvis and the surrounding muscles. Some examples include: Pelvic floor dysfunction. This is when the muscles of your pelvic floor have trouble coordinating to help you go to the bathroom. It can lead to incontinence and pain in your pelvis or lower back.
What is the rim of the pelvic inlet?
The bony upper edge of the true (lesser) pelvis, which is the rim of the pelvic inlet (superior pelvic aperture). The pelvic brim comprises the pubic crest and pectineal line of each pubis, the arcuate line of each ilium, the inner edge of the alae of the sacrum, and the sacral promontory.
Where does the ureter cross the pelvic brimnear?
It crosses the pelvic brimnear the bifurcation of the common iliac artery, where it becomes the "pelvic" ureter.
What is the surgical goal of ovarian vein isolation?
The surgical goal is to isolate the ovarian vein significantly above the pelvic brimand before the vein becomes substantially dilated.
Where are proximal and distal ureteral stones located?
Proximal and distal ureteral stones were defined as those above and below the pelvic brim, respectively, as suggested by Hollenback and colleagues,[sup.10] while mid-ureteral stones were located over the sacral bone.
Where is the cervix located?
The cervix was located in pelvic brimand thick contracted uterus was in abdominal cavity.
Which crest is bounded anteriorly by the pubic symphysis?
the upper opening of the true pelvis, bounded anteriorly by the pubic symphysis and the pubic crest on either side, laterally by the iliopectineal lines, and posteriorly by the promontory of the sacrum.
What degree is the inlet view?
The inlet view is taken with the patient supine and the X-ray beam directed 60[degrees] caudally (i.e., perpendicular to the pelvic brim).

Overview
Structure
The pelvic brim is an approximately Mickey Mouse head-shaped line passing through the prominence of the sacrum, the arcuate and pectineal lines, and the upper margin of the pubic symphysis.
The pelvic brim is obtusely pointed in front, diverging on either side, and encroached upon behind by the projection forward of the promontory of the sacrum.
Clinical significance
The pelvic brim may be a site of compression of structures that pass through the pelvic inlet. This can include the femoral nerves, which may occur during abdominal surgery.
See also
• Linea terminalis
• Pelvis justo major
• Pelvic inlet
Additional images
• Pelvis
External links
• Anatomy photo:44:os-0504 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center