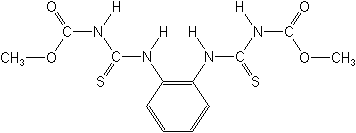
What is thiophanate methyl?
Thiophanate methyl, under the trade names Fungo, Topsin M, Domain, Cavalier, Halt, etc., is a broad-spectrum preventive and curative fungicide for use on turf and as a foliar spray to control powdery and downy mildews, Botrytis diseases, numerous leaf and fruit spots, scabs, and rots.
What are the properties of thiophanate-methyl?
THIOPHANATE-METHYL is incompatible with strong acids and bases, and with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Produces flammable gaseous hydrogen with active metals or nitrides.
How does thiophanate-methyl act as a fungicide?
Thiophanate-methyl acts as a fungicide via its primary metabolite carbendazim . ^ "Thiophanate-methyl" (PDF). Environmental Protection Agency.
What is 1212 thiophanate used for?
12.5.4.12 Methyl Thiophanate The fungicide methyl thiophanate widely used to control some of the most common fungal diseases in crops is metabolized in animals into benzimidazole compounds, including the reproductive toxicant carbendazim.

Is thiophanate methyl safe?
Thiophanate-methyl presents a low acute toxicity profile when administered via the oral or dermal routes; however, it was shown to be harmful if inhaled (harmonised classification according to Regulation (EC) no 1272/20083.
Is thiophanate methyl systemic?
What is Thiophanate-methyl? Thiophanate-Methyl (TM) is a systemic fungicide found in Clearys 3336g. It was first registered to be used as a fungicide by the EPA in 1973.
Is thiophanate methyl a contact fungicide?
Iprodione + Thiophanate-methyl Broad spectrum contact plus systemic fungicide used to control a wide array of foliar blight pathogens.
Is thiophanate methyl poisonous?
TM is not an irritant to the skin and only a slight occular irritant (toxicity category IV) and is a skin sensitizer.
How do you use thiophanate methyl fungicide?
Apply Thiophanate Methyl 70% WP with a sprayer, using a volume sufficient of mixture to ensure complete coverage. Add the required amount of Thiophanate Methyl 70% WP in the spray tank partially filled by shaking the product and then add the rest of the necessary water.
Is thiophanate methyl banned?
PAN-Europe is pleased about the ban, despite its delay, and urges Commission to also ban the last member of this group of pesticides, Thiophanate-methyl, a fungicide producing the same chemical Carbendazim as its major metabolite.
What group is thiophanate methyl?
Mode of Action: THIOPHANATE METHYL 4.5F AG is a tubulin inhibitor fungicide falling into the FRAC Group 1 for Benzimidazoles.
What is anthracnose fungus?
Anthracnose is a term used to loosely describe a group of related fungal diseases that typically cause dark lesions on leaves. In severe cases it may also cause sunken lesions and cankers on twigs and stems.
How long does imidacloprid stay in soil?
Imidacloprid has a photolysis half-life of 39 days at the soil surface, with a range of 26.5-229 days when incorporated into the soil. Persistence in soil allows for continual availability for uptake by plant roots.
What is Captan fungicide?
Captan is a fungicide used on fruits, vegetables, and ornamentals. Acute (short-term) dermal exposure to captan may cause dermatitis and conjunctivitis in humans. Ingestion of large quantities of captan may cause vomiting and diarrhea in humans.
What is chlorothalonil fungicide?
Chlorothalonil is a broad-spectrum organochloride pesticide. It is primarily used as a fungicide, bactericide, and nematicide, and has been reported to be effective on a wide range of vegetables and fruit crops. It is also used as a bactericide, nematocide, and mildew-preventing agent in paints.
What is metalaxyl fungicide?
Metalaxyl is a systemic fungicide used to control plant diseases caused. Use Profile. by the Oomycetes or water-mold fungi. It is used on many food and feed crops, and on non-food, residential and greenhouse crops such as tobacco, ornamental plants, trees, shrubs and vines, and lawns and turf.
Thiophanate-methyl (TM)
Thiophanate-methyl (Benzimidazole) is a broad-spectrum systemic fungicide that is absorbed by the roots and leaves of the treated plants. It has both protective and curative action. It is classified as group I fungicide. Since it targets a broad spectrum of diseases and plants, it has been used widely since 1973.
How Thiophanate-methyl Works - Mode Of Action
Thiophanate-methyl forms a protective barrier on plants and permeates the plant and moves upward in the plant's xylem. It has protective activity which includes new growth and it has a good curative activity.
How Thiophanate-methyl Works -Various Uses
It is used on vine, tree, and root crops, as well as wheat and canola. Homeowners use it on lawns and ornamentals.
Uses and analysis
It is a widely used fungicide used on tree, vine, and root crops. In Europe it is applied to tomato, wine grapes, beans, wheat, and aubergine.
Fungicidal Action
Thiophanate-methyl acts as a fungicide via its primary metabolite carbendazim .
What is Thiophanate-methyl?
Thiophanate-Methyl (TM) is a systemic fungicide found in Clearys 3336g. It was first registered to be used as a fungicide by the EPA in 1973.
What is fungicide in greenhouses?
A professional broad spectrum fungicide that eradicates pathogens from damaging ornamental plants in commercial greenhouses and nurseries.
What is thiophanate methyl?
Thiophanate methyl, under the trade names Fungo, Topsin M, Domain, Cavalier, Halt, etc., is a broad-spectrum preventive and curative fungicide for use on turf and as a foliar spray to control powdery and downy mildews, Botrytis diseases, numerous leaf and fruit spots, scabs, and rots.
What pesticides are used in MEKC?
Eight widely used fungicides namely carbendazim, imazalil, methylthiophanate, o-phenylphenol, procymidone, prochloraz, triamidefon and thiabendazole were separated with BGE containing borate buffer at pH 9 and 75 mmol/L sodium cholate as surfactant [ 75 ]. The applicability have been shown through spiked food extracts from grape, tomato, lettuce and orange as shown in Figure 11 [ 75 ]. Sample stacking have been developed increasing the sensitivity of the MEKC method and successfully applied for non-spiked apple juice [ 76 ]. The separation electrolyte contained 10 mmol/L phosphate as buffer, 30 mmol/L SDS and isopropanol / isobutylalcohol function as organic modifier enhancing the selectivity of the separation. The sample stacking was achieved by salting the injected sample. Pre-concentration strategies like sweeping, stacking and modified staking with combination of MEKC have been studied for nine multiple pesticides determined from spiked carrot samples because the most problematic task in the CE analysis of food contaminant is the sensitivity of a method [ 14, 77 ]. Atrazine, a triazine type pesticide, have been determined by MEKC from juices with combination of supported liquid membrane and solid-phase extraction used for sample preparation to increase the selectivity and sensitivity of the analytical process [ 78 ].
What is the best method to separate pesticide residues?
Micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC) and capillary electrochromatography (CEC) are powerful techniques for achieving efficient pesticide and pesticide residue separations, although accepted standardized methods are still missing. The N -methylcarbamates, carbendazin, imazalil, methylthiophanate, prochloraz, procimidone, thiabendazole, triadimefon, metribuzin, lenacil, ethofumesate, atrazine, terbuthrin, isoproturon, chlorotoluron, linuron, desethyl atrazine, 2-hydroxyatrazine, desethyl 2-hydroxyatrazine, and 3-chloro-4-methylphenyl urea are only some of the pesticides that have been reported to be separated by means of MEKC and CEC. Online coupling of MEKC with ESI-MS was recently found as achievable using partial filling (PF) or reverse migrating micelles (RMM) techniques. Quantitative migration–toxicity relationship for phenoxy acid herbicides has been obtained with MEKC on using micellar Brij 35 based migration media. Online stacking procedure carried out on injection acts as a preconcentration step and together with SPE for sample preparation shifts the detection limits to the low μg l −1 range, even on use of the classical on-column diode array detection.
What is a group of specific fungicides that includes carbendazim, benomyl,?
Benzimidazoles. Benzimidazoles are a group of specific fungicides, introduced around 1970, that includes carbendazim, benomyl, and thiophanate-methyl as representatives.
Is triforine good for fungus?
Triforine, sold as Funginex or Triforine, is effective against many ascomycetes and imperfect fungi causing powdery mildews, foliar and fruit spots, fruit rots, anthracnose, and some basidiomycetes causing rusts. It is used as a foliar spray.
Is methyl thiophanate toxic to animals?
The fungicide methyl thiophanate widely used to control some of the most common fungal diseases in crops is metabolized in animals into benzimidazole compounds, including the reproductive toxicant carbendazim. However, standard toxicological tests did not indicate that methyl thiophanate may cause testicular toxicity and/or embryotoxicity, which are typical effects of many benzimidazoles. In the B6C3F1 mouse in spite of the high doses administered, none of the testicular parameters examined (sperm head count, specific enzyme activities, histopathology on days 3–35 post-dosing) showed significant alterations as compared to controls at any time post-dosing. Pregnant CD rat dams administered orally the limit dose of 650 mg/kg BW/day during preimplantation (gestational day or GD 2–5) or peri-implantation (GD 6–9) phases showed maternal toxicity, with only marginal reductions of the growth of embryos and adnexa ( Traina et al., 1998 ). Earlier studies submitted by Atochem North America, Inc. (1985) for methyl thiophanate, show for the rat a teratogenic NOAEL = 2500 ppm (125 mg/kg/day) based on the high dose tested (HDT) with a maternal NOAEL = 250 ppm (12.5 mg/kg/day), LEL = 1200 ppm (60 mg/kg/day) and a fetotoxic NOAEL = 2500 ppm (HDT).
Description
Thiophanate-methyl (Benzimidazole) is a broad-spectrum systemic fungicide that is absorbed by the roots and leaves of the treated plants. It has both protective and curative action. It is classified as group I fungicide. Since it targets a broad spectrum of diseases and plants, it has been used widely since 1973.
Features of Thiophanate Methyl
Thiomyl Systemic Fungicide/ Repackage Of Cleary 3336 Wp/ Treats Bulbs After Digging For Over-Wintering
Mode Of Action
Thiophanate-methyl forms a protective barrier on plants and permeates the plant and moves upward in the plant’s xylem. It has protective activity which includes new growth and it has a good curative activity.
How long does it take for thiophanate methyl to degrade?
Thiophanate-methyl degraded by 90% during a 6-18 week period in soils of various textures, suggesting that biodegradation may be a moderate environmental fate process in soil. If released into water, thiophanate methyl is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc.
What is a NIOSH approved respirator?
RECOMMENDED RESPIRATOR: Where the neat test chemical is weighed and diluted, wear a NIOSH-approved half face respirator equipped with an organic vapor/acid gas cartridge (specific for organic vapors, HCl, acid gas and SO2) with a dust/mist filter. (NTP, 1992)
How long does thiophanate methyl stay in the atmosphere?
Vapor-phase thiophanate methyl will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 5 hours. Particulate-phase thiophanate methyl will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition.
What are the symptoms of exposure to a compound?
SYMPTOMS: Symptoms of exposure to this compound may include irritation, itching, redness, swelling, and dryness of the skin; congestion; and, sometimes, dermatitis. ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: This compound may irritate the skin. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx. (NTP, 1992)
How does thiophanate methyl release to the environment?
Thiophanate methyl's production may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams; its use as a fungicide will result in its direct release to the environment. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 7.13X10-8 mm Hg at 25 °C indicates thiophanate methyl will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the atmosphere. Vapor-phase thiophanate methyl will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 5 hours. Particulate-phase thiophanate methyl will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Thiophanate-methyl is stable to sunlight, suggesting that the compound is not expected to be susceptible to direct photolysis in sunlight. If released to soil, thiophanate methyl is expected to have moderate mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 330. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon an estimated Henry's Law constant of 1.2X10-9 atm-cu m/mole. Thiophanate methyl will not volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Thiophanate-methyl degraded by 90% during a 6-18 week period in soils of various textures, suggesting that biodegradation may be a moderate environmental fate process in soil. If released into water, thiophanate methyl is expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Thiophanate-methyl was degraded in aqueous solution by irradiation with UV and sunlight to methyl benzimidazole-2-yl carbamate. Biodegradation data in aquatic media were not available. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's estimated Henry's Law constant. An estimated BCF of 4 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process since this compound is stable in neutral, aqueous solution; however it may be reactive under basic conditions. Occupational exposure to thiophanate methyl may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where thiophanate methyl is produced or used. Use data indicate that the general public may be exposed to thiophanate methyl via inhalation and dermal contact with consumer products containing this compound. (SRC)
What is the USEPA code for thiophanate methyl?
For thiophanate methyl (USEPA/OPP Pesticide Code: 102001) ACTIVE products with label matches. /SRP: Registered for use in the U.S. but approved pesticide uses may change periodically and so federal, state and local authorities must be consulted for currently approved uses./
How to treat a contaminated eye?
Perform CPR if necessary. Immediately flush contaminated eyes with gently flowing water. Do not induce vomiting. If vomiting occurs, lean patient forward or place on the left side (head-down position, if possible) to maintain an open airway and prevent aspiration. Keep patient quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Obtain medical attention. /Poisons A and B/
