How do you treat tinea incognito?
Treatment for tinea incognito is to discontinue the topical corticosteroids. For mild and superficial lesions, they respond well to antifungal creams. Treatment for another week after the resolution of the lesions is important. For more severe forms, oral medications like terbinafine and fluconazole, may be necessary.
How is tinea incognito diagnosed?
How is tinea incognito diagnosed? The diagnosis of tinea is most easily made by taking skin scrapings for microscopy and culture a few days after stopping all creams. If there is little surface scale, the laboratory may report the specimen to be inadequate or negative.
What are tinea infections caused by?
It is caused by a fungal infection—not an actual worm. Fungi on the skin, hair, and nail bed are called dermatophytes. Also referred to by healthcare providers as Tinea infections, infection on the scalp, arms, legs, face, and trunk is characterized by ring-shaped, red, scaly patches with clearing centers.
How do humans get tinea?
Tinea can be spread by skin-to-skin contact or indirectly through towels, clothes or floors. Tinea is also known as ringworm, which is a misleading name as no worm is involved. All fungi need warm, moist environments and tinea is no exception.
What is the first line of treatment for tinea incognito?
Treatment. Most forms of tinea corporis can be treated with once- or twice-daily topical antifungal therapy for 14 to 21 days. Optimal duration of therapy and comparative efficacy of topical agents have not been evaluated extensively.
How long can tinea live on surfaces?
Where does ringworm live? The fungus that causes ringworm can live in humans, dogs, cats, other animals, and soil. The fungus can survive on contaminated objects for long periods of time, sometimes up to 18 months.
What tinea looks like?
Ringworm of the Body (Tinea Corporis) When fungus affects the skin of the body, it often produces itchy, red, raised, scaly patches that may blister and ooze. The patches often have sharply defined edges. They are often redder around the outside with normal skin tone in the center, creating the appearance of a ring.
What happens if tinea is left untreated?
Left untreated, athlete's foot can affect the toenails — which may thicken, become discolored or crumble — and even spread to your hands or groin. Additionally, athlete's foot can make you more vulnerable to bacterial infections, such as cellulitis.
Can tinea be cured?
Fungi can live for a long time on the skin. Because of this, tinea infection is hard to cure and can come back easily. Treatment may need to be repeated.
What does tinea look like on feet?
On the top of the foot, athlete's foot appears as a red scaly patch or patches, ranging in size from 1 to 5 cm. The border of the affected skin may be raised, with bumps, blisters, or scabs.
Can tinea spread to hands?
The infected area on your hand will normally start small and gradually become larger over time. The infection will generally start on the palm of the hand and may or may not spread to your fingers and the back of your hand. The area infected with tinea will be itchy, red, and have a scaly appearance.
What causes tinea on feet?
What causes athlete's foot? Athlete's foot occurs when the tinea fungus grows on the feet. You can catch the fungus through direct contact with an infected person, or by touching surfaces contaminated with the fungus. The fungus thrives in warm, moist environments.
How to treat tinea incognito?
Treatment for tinea incognito is to discontinue the topical corticosteroids. For mild and superficial lesions, they respond well to antifungal creams. Treatment for another week after the resolution of the lesions is important. For more severe forms, oral medications like terbinafine and fluconazole, may be necessary.
What is a ringworm incognito?
Tinea incognito is a localized skin infection caused by fungus, just like tinea corporis (ringworm) and tinea capitis (scalp ringworm). It is a skin infectious process that looks very different from other fungal infections, both the shape and the degree of involvement.
Can a skin scraping test diagnose a fungal infection?
Most often, patients will try to use the topical medication again to attempt the early response and the cycle continues. Diagnose can be made by a skin scraping microscopic test.
Can ringworm be small?
These skin findings comprise of the ringworm we typically see on the body. Lesions can be large or small. At this stage of the disease, if a topical corticosteroid is applied to the lesion, the local inflammation from the fungal infection will be decreased, so to alter the clinical presentation of the typical infection.
Do corticosteroids help fungi?
The clinical cycle is closely related to the use of topical corticosteroids. With initial use, the inflammation caused by the fungi is diminished and lesions appear to be getting better. However, fungi will thrive in the later course of treatment with corticosteroids because of suppressed immune response and result in the clinical picture ...
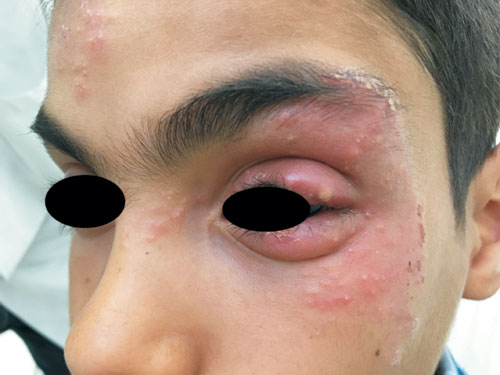
What is tinea incognito?
Hair involvement is not uncommon. Atypical iatrogenic presentations, particularly following the use of topical steroids, have sometimes been given the appellation “ tinea incognito .” Underlying diseases may predispose individuals to infection, especially immunocompromised patients, or those having a history of diabetes mellitus or other endocrinopathies. Local factors such as sweating, abrasion, and maceration also contribute to the development of infection.
How long does tinea corporis last?
Most forms of tinea corporis can be treated with once- or twice-daily topical antifungal therapy for 14 to 21 days. Optimal duration of therapy and comparative efficacy of topical agents have not been evaluated extensively. Patients with widespread cutaneous lesions or a granulomatous reaction sometimes are treated systemically with terbinafine, griseofulvin, or alternative antifungal agents. Most recommend treatment with oral agents, and in a study using fluconazole 200 mg weekly, 100% of affected individuals were culture negative by the third week. 53 Several studies have documented a slight superiority and less side effects using newer agents, such as terbinafine and fluconazole, compared with griseofulvin. 54,55
What is the best treatment for tinea cruris?
The treatment of tinea cruris consists of the administration of any of several antifungal oral or topical medications. All azoles are effective, whereas nystatin exhibits no activity against tinea. Terbinafine (Lamisil) and ciclopirox (Loprox) are active agents as well. These are applied once or twice a day, and are appropriate therapy when tinea cruris is mild, limited in extent, and shows no signs of fungal folliculitis. When abundant coarse hair or folliculitis is present, or when tinea is extensive, patients respond best to oral medication. Options include the azoles, fluconazole (Diflucan) 100–200 mg weekly for 2–4 weeks, or itraconazole (Sporonox), 100 mg/day or ketoconazole, 200 mg/day until clear. Griseofulvin 500 mg twice daily is effective as well, but nausea and headaches are often limiting side-effects. Oral terbinafine 250 mg daily until clear is effective and well tolerated. All of these medications, except for griseofulvin, also treat Candida in case of a misdiagnosis.
What is ringworm?
Tinea corporis, commonly known as “ringworm,” is a dermatophyte infection of nonhairy (glabrous) surfaces, not otherwise designated as to specific area. It is more prevalent in warm or moist climates. 51 It may be caused by any of the dermatophytes making up the genera Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton. 52 In children the most common cause is T. tonsurans.53 Sites of predilection include the nonhairy areas of the face, trunk, and limbs with exclusion of scalp (tinea capitis), bearded areas (t. barbae), hands (t. manuum), nails (onychomycosis), groin (t. cruris), and feet (t. pedis).
Why is Tinea barbae pustular?
Tinea barbae (infection of the neck and beard area) may be pustular and inflamed because it is often caused by zoophilic organisms such as T. verrucosum. It is more localized than sycosis barbae, which is caused by S. aureus;this difference is helpful in distinguishing the two conditions. View chapterPurchase book.
What causes fungal infections?
Superficial fungal infections may be caused by yeast or dermatophytes. Deep fungal infections of the skin are rare, and occur mainly in severely immunocompromised patients. Dermatophytes are molds that require keratin for nutrition and must live on stratum corneum, hair, or nails to survive. Human infections are caused by Epidermophyton, Microsporum and Trichophyton spp. These infections differ from candidiasis in that they are rarely, if ever, invasive. Transmission is person-to-person, animal-to-person and (rarely) soil-to-person. The organism may persist indefinitely. Most people do not develop clinical fungal infections; those who do may have impaired T-cell responses from an alteration in local defenses (e.g. due to trauma, with vascular compromise) or from primary (hereditary) or secondary (e.g. diabetes, HIV) immunosuppression.
Is oral antifungal effective for dermatophyte infections?
Topical antifungal agents are generally effective for uncomplicated superficial dermatophyte infections. Oral systemic therapy is now widely available and useful for cases in which there is extensive involvement, folliculitis, or in immunocompromised patients.
What is Tinea incognito?
Tinea incognita or Tinea incognito is a fungal infection ( mycosis) of the skin masked and often exacerbated by application of a topical immunosuppressive agent. The usual agent is a topical corticosteroid.
What is the treatment for tinea incognita?
If the tinea incognita is extensive or involves hair bearing areas, treatment with a systemic antifungal may be indicated.
What is the name of the infection that is exacerbated by the application of a topical immunosuppressive
Dermatology. Tinea incognita or Tinea incognito is a fungal infection ( mycosis) of the skin masked and often exacerbated by application of a topical immunosuppressive agent. The usual agent is a topical corticosteroid.
Can topical steroids cause tinea incognita?
In areas where the skin is occluded (groin, buttock crease, armpit ), the immunosuppression by the topical steroid might be significant enough to cause tinea incognita to occur even in the presence of an effective antifungal.
What is Tinea incognita?
Tinea incognita is the name given to a fungal skin infection when the clinical appearance has been altered by inappropriate treatment, usually a topical steroid cream. The result is that the original infection slowly extends.
What is the best treatment for tinea incognita?
Anti- inflammatory creams that can induce tinea incognita include: Topical steroids. Tacrolimus ointment. Pimecrolimus cream. Tinea incognita can also be caused by systemic steroids. Underlying diseases may predispose individuals to infection, especially: Immune suppressive drugs.
What causes tinea corporis?
Tinea incognita is due to dermatophyte fungal infection ( tinea ), most often when it affecting the trunk and/or limbs ( tinea corporis ). Trichophyton rubrum is the most common organism to cause tinea corporis and tinea incognita in New Zealand.
Can tinea incognita be seen on a microscopy?
After stopping a steroid cream, tinea incognita becomes very inflamed and more fungal elements may be seen on microscopy than usual. The responsible organism generally grows promptly in culture. If a skin biopsy is performed, the pathology of tinea incognita reveals the organisms .
Is tinea incognita scaly?
Compared with an untreated tinea corporis, tinea incognita: Has a less raised margin, Is less scaly, More pustular, More extensive, And more irritable. There may also be secondary changes caused by long term use of a topical steroid such as: Atrophy (thin skin, stretch marks ( striae) in the skin folds).
Can you use topical steroids for tinea incognita?
Tinea incognita can be avoided if: Patients do not use topical steroids to treat undiagnosed skin conditions. Medical practitioners consider the diagnosis of dermatophyte infection in any scaly or pustular rash that has a prominent and irregular border, and is unilateral or asymmetrical in distribution.
Abstract
Erythroderma or exfoliative dermatitis is a potentially fatal condition with myriad etiologies. Identifying the cause is essential for proper treatment. Dermatophytosis is an unusual cause of erythroderma. The use of topical steroids can alter the clinical picture of dermatophytosis.
INTRODUCTION
Erythroderma is a potentially life-threatening condition which can often pose a dilemma in determining the etiology and hence treatment. Initial histopathology may not always yield typical features of the underlying disease.
CASE REPORT
A 65-year-old man presented to our outpatient department (OPD) with a history of generalized erythema and scaling. He reported that his complaints had started 2 months back as pruritic lesions over the lower back, for which he had applied an over-the-counter topical medication. There was an initial symptomatic improvement for a few days.
DISCUSSION
Erythroderma, or exfoliative dermatitis, is a disease characterized by erythema and scaling involving >90% of the body surface area. [ 1] The single most common cause of adult erythroderma is a pre-existing dermatosis, the most frequent of which are psoriasis and eczema.
CONCLUSION
Tinea incognito is an uncommon, but important cause of erythroderma, which may pose a diagnostic challenge due to steroid induced alteration of clinical picture.
What is a ringworm nail?
Nail infection (tinea unguium). An infection of the finger or toe nail, this type is characterized by a thickened, deformed nail. This condition more often affects the toenails than the fingernails. It happens more often in adolescents and adults rather than young children. Symptoms of nail ringworm may include:
What is the hardest to treat scalp ringworm?
Your opinion or preference. Treatment for scalp ringworm (tinea capitis) or nail infection (tinea unguium) is hardest to treat and usually includes an oral antifungal medicine for many weeks.
What causes ringworm on the body?
Different fungi, depending on their location on the body, cause ringworm. It is caused by a fungal infection—not an actual worm. Fungi on the skin, hair, and nail bed are called dermatophytes. Also referred to by healthcare providers as Tinea infections, infection on the scalp, arms, legs, face, and trunk is characterized by ring-shaped, red, ...
Why does my scalp itch?
Rash elsewhere on the body. Ringworm of the scalp can also develop into a kerion, a large, tender lesion over the area of the initial ringworm. This is caused by a hypersensitivity to the ringworm and may be associated with a rash elsewhere and tender lymph nodes in the neck.
What are the symptoms of nail ringworm?
Symptoms of nail ringworm may include: Thickening of the ends of the nails. Yellow color to the nails. Body ringworm (tinea corporis). This skin infection is characterized by a ring-like rash anywhere on the body or the face. It happens in all ages, but is seen more often in children.
How to treat ringworm in the foot?
Treatment for ringworm of the body, groin, and foot is usually a topical antifungal agent or an oral antifungal medicine. The length of the treatment depends on the location of the ringworm. Because the fungi can live indefinitely on the skin, recurrences of ringworm are likely. Treatment may need to be repeated.
How do you know if you have ringworm?
The symptoms of body ringworm may include: Red, circular lesion with raised edges. The middle of the lesion may become less red as the lesion grows. Itching of the affected area. The symptoms of ringworm may resemble other skin conditions. Always talk with your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.