Explore
Ascites is the build-up of fluid in the abdomen. This fluid buildup causes swelling that usually develops over a few weeks, although it can also happen in just a few days. Ascites is very...
How long does it take to get ascites?
with ascites admitted to a general hospital do not respond to diuretics (6). It is not surprising, there- fore, that alternative methods for the treatment of ascites are currently being investigated by several groups. Paracentesis, the oldest form of therapy for ascites,
Is there alternative treatment for ascites?
When signs and symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Fatigue
- Easily bleeding or bruising
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Swelling in your legs, feet or ankles (edema)
- Weight loss
- Itchy skin
- Yellow discoloration in the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Fluid accumulation in your abdomen (ascites)
- Spiderlike blood vessels on your skin
What are the early symptoms of ascites?
- It is elicited in minimal ascites (150 ml).
- Use: Diagnosis of small quantity of fluid.
- Procedure: Patient is asked to go on all four (knee chest position) so that fluid collects in dependent mid abdomen. Stethoscope is placed here. ...
How to elicit fluid thrill in ascites?

How does TIPS Help with ascites?
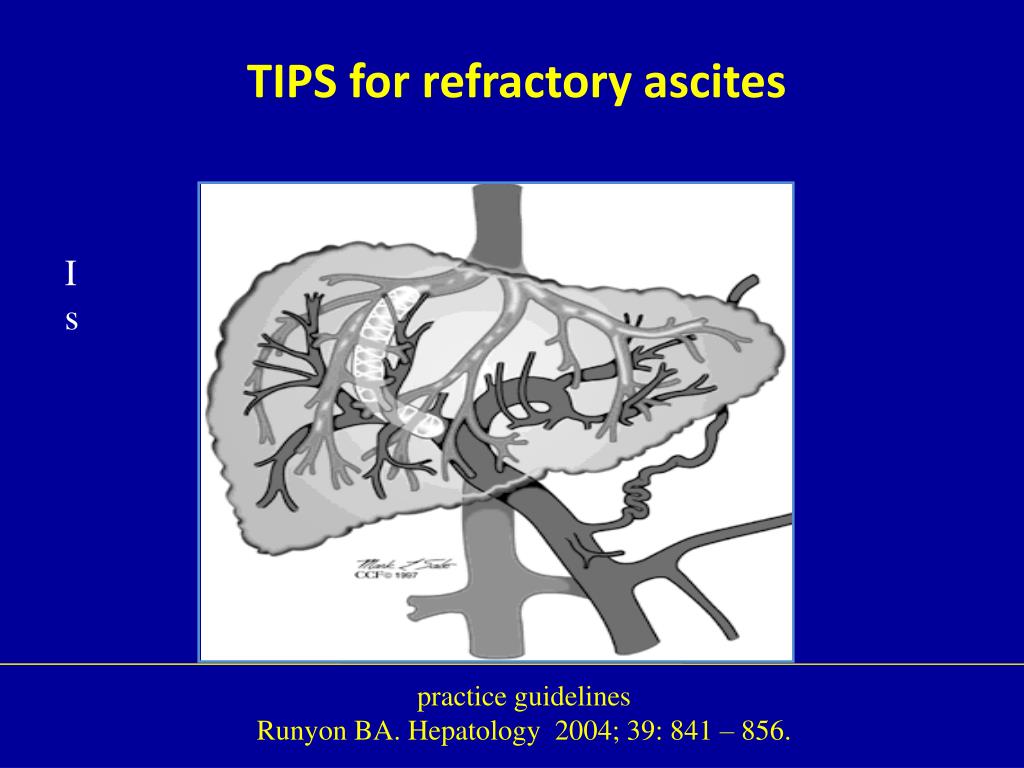
TIPS decrease the effective vascular resistance of the liver by the creation of a tract between the higher-pressure portal vein and the lower-pressure hepatic vein, decreasing the portal venous pressure. This in turn lessens the congestive pressure in veins in the intestine reducing production of ascites.
Does TIPS decrease ascites?
Over 90 percent of people that undergo TIPS to prevent bleeding from varices will have a relief in their symptoms and experience little to no bleeding thereafter. When TIPS is performed for ascites, 60 to 80 percent of people will have relief in their ascites.
What is a tip procedure?
A TIPS procedure involves creating a pathway through the liver that connects the portal vein (the vein that carries blood from the digestive organs to the liver) to a hepatic vein (one of three veins that carry blood from the liver to the heart).
How long do you live after a TIPS procedure?
According to an older randomized trial, 88% of people with cirrhosis and variceal bleeding who received TIPS survived for 2 years, and 61% survived for at least 5 years. A more recent analysis of TIPS procedures in one hospital found that 78.2% of patients survived longer than 90 days after the procedure.
Is a TIPS procedure safe?
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is a safe and effective procedure for the treatment of complications of liver cirrhosis, such as refractory ascites, hepatic hydrothorax and refractory variceal bleeding. The aim of this paper is to describe a rare case of liver failure after a TIPS procedure.
When is TIPS indicated?
When is TIPS procedure indicated? TIPS is indicated to treat patients with portal hypertension (variceal bleeding, portal hypertension gastropathy and severe ascites) and in some cases in Budd-Chiari Syndrome.
How long does a TIPS procedure take?
The blood will flow directly from your portal system into your vena cava (the large vein that drains blood from your body and empties into your heart). This will ease the portal hypertension. The procedure usually takes about 2 to 3 hours, but it can take longer.
How successful is TIPS surgery?
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is an interventional radiology technique that has shown a 90% success rate to decompress the portal circulation.
Why is TIPS performed?
Why perform it? The TIPS procedure is usually performed in patients with liver cirrhosis. If you have this condition, your normal blood flow through the liver is blocked by scar tissue within the liver, which increases the pressure in your portal vein.
What is the mortality rate with a TIPS procedure?
Complications of the TIPS procedure included a 30% incidence of new or worsened encephalopathy and a 15% incidence of other severe complications (intraperitoneal hemorrhage, severe accelerated liver failure). The procedure-related death rate was 5%.
What is the most common complication following TIPS?
ENCEPHALOPATHY. The development of encephalopathy after TIPS is probably the most frequent complication related to the procedure, its incidence ranging between 5 and 35%.
Is there a better alternative to TIPS surgery?
Background: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPSS) is an effective treatment for portal hypertension and its associated complications. EUS-guided creation of an intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (IPSS) may become a useful alternative to conventional TIPSS.
What is a TIPS procedure?
A transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is a minimally invasive procedure that doctors use to treat portal vein hypertension and other complications of advanced liver disease. As well as being less invasive than traditional bypass surgery, the TIPS procedure carries fewer risks. While a TIPS procedure can help reduce the risk ...
How long do people with cirrhosis live after TIPS?
According to an older randomized trial, 88% of people with cirrhosis and variceal bleeding who received TIPS survived for 2 years, and 61% survived for at least 5 years. A more recent analysis of TIPS procedures in one hospital found that 78.2% of patients survived longer than 90 days after the procedure.
How to relieve blood pressure in portal vein?
A doctor may use a TIPS procedure to relieve blood pressure in the portal vein by rerouting the blood flow from the other digestive organs past the liver. The liver plays a vital role in circulation. In addition to the arteries, the liver has two types of veins with different functions. The portal vein carries nutrient-rich blood from ...
Can a TIPS procedure correct liver damage?
While a TIPS procedure can help reduce the risk of further complications, it cannot correct existing liver damage, and some people may require additional treatments. In this article, we discuss the uses of a TIPS procedure, its effect on life expectancy, how the procedure works, and what to expect during recovery.
Can ascites cause a hernia?
Without treatment, ascites can lead to abdominal pain, hernias, and bacterial infections. Hepatorenal syndrome is a type of progressive kidney failure that occurs in people who have severe liver damage. Hepatorenal syndrome is a serious condition with a poor outlook.
How to prevent ascites?
Stopping all alcohol intake, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising, not smoking, and limiting salt intake can help prevent cirrhosis or cancer that may lead to ascites. Ascites can’t be cured but lifestyle changes and treatments may decrease complications.
What is ascites in a patient?
What is ascites? Ascites is a condition in which fluid collects in spaces within your abdomen. If severe, ascites may be painful. The problem may keep you from moving around comfortably. Ascites can set the stage for an infection in your abdomen.
What causes ascites in the liver?
The most common cause of ascites is cirrhosis of the liver. Drinking too much alcohol is one of the most common causes of cirrhosis of the liver. Different types of cancer can also cause this condition. Ascites caused by cancer most often occur with advanced or recurrent cancer. Ascites may also be caused by other problems such as heart conditions, ...
What is ascites in the body?
Ascites is a condition in which fluid collects in spaces within your abdomen. As fluid collects in the abdomen, it can affect your lungs, kidneys, and other organs. Ascites causes abdominal pain, swelling, nausea, vomiting, and other difficulties. Stopping all alcohol intake, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising, not smoking, ...
What is the best way to see the inside of your abdomen?
Imaging. Your healthcare provider may request images of the inside of your abdomen using ultrasound, MRI, or a CT scan. An MRI creates images using a magnetic field and radiofrequency energy. A CT scan creates computerized images using X-rays.
How do you know if you have ascites?
These are symptoms of ascites: Swelling in the abdomen. Weight gain. Sense of fullness. Bloating. Sense of heaviness. Nausea or indigestion. Vomiting. Swelling in the lower legs.
Can ascites cause kidney failure?
Ascites can make eating, drinking, and moving around difficult. It can also make it hard to breathe. Ascites can lead to abdominal infections, which may cause kidney failure. It can also cause umbilical or inguinal hernias.
Is TIPS good for long term survival?
In summary, compared with other treatment options, TIPS seems to provide a high rate of response and rather good long-term survival. In addition, TIPS is the only treatment option which also treats the refractory ascites, the source of the hepatic hydrothorax.
Is refractory ascites a complication of cirrhosis?
Refractory ascites is a frequent complication of advanced cirrhosis and is associated with hepatorenal syndrome and hepatic hydrothorax. Large volume paracentesis and pleurodesis are regarded as first-line treatments in patients who do not respond adequately to diuretics. These treatments, however, do not prevent recurrence and carry the risk ...
Does LVP cause ascites?
Large volume paracentesis (LVP) relieves symptoms rapidly and has few technical complications. 7 However, it does not correct the underlying problem leading to ascites formation and, therefore, ascites reappears in almost all patients requiring serial use of paracenteses. LVP has haemodynamic side effects.
How to treat ascites?
Ascites is treated by decreasing dietary sodium and taking diuretic medications. In addition, more severe cases may need a paracentesis, placement of a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, and ultimately a liver transplant.
What is an ascites?
Ascites refers to the buildup of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity. Based on the severity of fluid accumulation, ascites can be categorized as mild, moderate, and large. There are two different types of ascites: uncomplicated and refractory ascites.
What are the complications of ascites?
Other complications that ascites can include hepatorenal syndrome, malnutrition, pleural effusion, and gastrointestinal bleeding.
What causes ascites in the liver?
The most common cause of ascites is cirrhosis, which is a late stage of liver disease characterized by permanent scarring and fibrosis of the liver, often as a consequence of chronic alcoholism or hepatitis. Normally, the liver receives blood from the spleen and gastrointestinal organs via the portal vein. When fibrosis becomes extensive, it is ...
Is ascites a kidney failure?
Often, refractory ascites can be associated with kidney failure.
Is ascites life threatening?
Is ascites life-threatening? Ascites can lead to the development of life-threatening complications , such as spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, which is a bacterial infection of the ascitic fluid. If not caught and treated promptly, bacteria can enter the bloodstream and lead to sepsis.
Can ascites be reversed?
With treatment, ascites can be temporarily reversed. But over time, more invasive treatments will be needed to temporarily reverse ascites. Eventually, most people with ascites will need a liver transplant.
What is a TIPS shunt?
Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) is a shunt or a bypass use to connect two veins within the liver with the use of x-ray by interventional radiology. This tract is what we call a Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosytemic Shunt or simply abbreviated as TIPS. See the “yellow” tract on the picture to your left.
How to prepare for TIPS?
Prior to the TIPS procedure itself, you will be prepared by the nurses by having an intravenous or IV inserted. The specific area of your body where the catheter will be inserted will be shaved, sterilized and covered with a surgical drape preparing you for the start of the procedure.
How is a stent placed?
The stent will be placed under the fluoroscopy extending from the portal vein into the hepatic vein. Once the stent is properly placed, the balloon is inflated, expanding the stent into place. The skin will then be covered with a bandage leaving you with no need for sutures.
Can you drink liquids after a TIPS procedure?
However, you may be allowed to drink clear liquids to help you on the day of the TIPS procedure. It is well advised to take your morning medication as instructed by your physician and to stay in the hospital for 24 hrs for observation after the procedure.
Can TIPS cause confusion?
When TIPS is performed, the TIPS will allow toxin-containing blood with ammonia to bypass your liver. This may affects your brain in a way that may cause confusion or even comma. Different treatments can be use to treat this condition.
How to treat ascites?
Treatments for Ascites. Key treatments for ascites include salt -restricted diets and bed rest. In addition to those two treatments, diuretics or drugs are also utilized for excreting more water from the kidneys. The process of therapeutic paracentesis is used to remove the fluid by inserting a thin needle or tube to remove excess fluid from ...
What are some home remedies for ascites?
17 Effective Treatments & Remedies for Ascites. The home remedies for ascites may include garlic, dandelion, gram, bitter gourd, fenugreek, radish, melon, onion, and adequate sleep. Ascites is a condition where there is fluid buildup in the abdomen or peritoneal cavity. This may lead to inflammation in the arms, legs, and spleen.
What is the procedure used to remove fluid from the abdomen?
The process of therapeutic paracentesis is used to remove the fluid by inserting a thin needle or tube to remove excess fluid from the abdomen. Large-volume paracentesis (LVP) is the treatment used for draining large amounts of fluid from the patient’s body. A short hospital stay is required for such treatments.
What is the best medicine for ascites?
Dandelion, the herbal diuretic, is used for curing ascites, as it may not only drain the excess fluid but may also provide potassium to the body. Drink dandelion tea twice daily to get relief. [2]
Is salt bad for ascites?
Salt is also very harmful to patients suffering from ascites. Word of Caution: A doctor should be visited if there is any doubt that you might be suffering from ascites as a proper diagnosis is a must. At times, it’s necessary to consult your doctor, even before trying any of these home remedies and foods.
Is melon good for ascites?
You should eat melon daily in a significant portion to stay healthy and fight ascites. It also helps in digestion and restoring the fluid balance, as well as other parts of homeostasis.
Can ascites cause spleen inflammation?
This may lead to inflammation in the arms, legs, and spleen. When the fluid moves around to the lungs, it can make breathing difficult. Ascites is technically known as peritoneal fluid excess, peritoneal cavity fluid, and hydroperitoneum. [1]
What Is TIPS?
TIPS is a connection created between a vein in the liver (hepatic vein) and a branch of the portal vein to reduce pressure in the portal vein. A portal vein transports blood to the liver from the spleen, stomach, pancreas, and intestines.
Purpose of a TIPS Procedure
There are several conditions that a person might have that would indicate a need for the TIPS procedure:
How to Prepare
Typically, patients have a TIPS procedure done in a hospital setting, in interventional radiology by a radiologist who uses imaging to diagnose and treat diseases. When entering the procedure area, the team will ask the patient to move over to the bed for the procedure, lying on their back and exposing their neck.
What to Expect on the Day of the Procedure
In the preoperative area on the day of the procedure, a nurse will assess your vital signs, weight, pregnancy status (if applicable), and blood sugar levels (if applicable). Patients will remove their clothes and jewelry, and change into a surgical gown that allows the radiologist to easily access the procedure site.
Recovery
Patients undergoing TIPS should expect to wake up from general anesthesia in a recovery room and then be transferred to a hospital room to stay overnight to monitor for bleeding or other complications. The minimally invasive approach reduces the time it takes to recover from the procedure.
Summary
The TIPS procedure can help reduce high blood pressure in the portal veins, which filter blood from the intestines through the liver, and its complications, especially bleeding when these veins burst from the increased pressure. It's typically used to help with liver conditions like hepatitis and cirrhosis.
A Word From Verywell
The TIPS procedure can be successful in treating serious symptoms resulting from portal hypertension in patients with severe liver disease. All procedures carry risks, but this procedure has reduced risks compared with undergoing liver surgery.