What forms the tonsillar bed?
Following structures form the tonsillar bed ( from inside outwards): Pharyngobasilar fascia. Superior Constrictor muscle. Buccopharyngeal fascia.
Where is tonsil bed?
The tonsils are collections of lymphoid tissue located in the oral cavity; adenoids contain similar tissue and are in the nasopharynx behind the palate.
What is the tonsillar fossa?
The tonsillar fossa or sinus is a triangular space between the anterior pillar in front, the posterior pillar behind, and the dorsal surface of the posterior one third of the tongue inferiorly (Figure 2). Because the tonsils are positioned in it, its borders also limit the tonsil [7].
What are the 4 types of tonsils?
What are tonsils? Tonsils are fleshy masses of lymphatic tissue found in the throat, or pharynx. There are four different types of tonsils: palatine, pharyngeal (commonly referred to as the adenoid), lingual and tubal. Together these four types of tonsils make up what is called Waldeyer's ring.
When should tonsils be removed?
A health care provider might recommend removing the tonsils if a child gets a lot of tonsil infections (called tonsillitis). Experts define "a lot" as when a doctor diagnoses a child with at least 7 infections a year, more than 5 infections a year for 2 years in a row, or three infections a year for 3 years.
Why do tonsils get removed?
A tonsillectomy was once a common procedure to treat infection and inflammation of the tonsils (tonsillitis). Today, a tonsillectomy is usually performed for sleep-disordered breathing but may still be a treatment when tonsillitis occurs frequently or doesn't respond to other treatments.
What does tonsillar mean in medical terms?
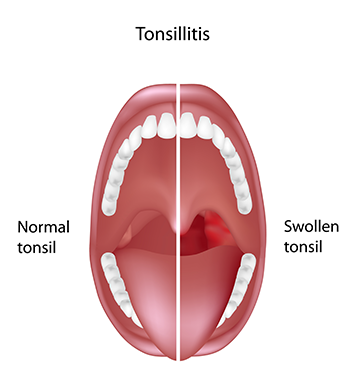
Inflamed tonsils Tonsils are fleshy pads located at each side of the back of the throat. Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils, two oval-shaped pads of tissue at the back of the throat — one tonsil on each side.
What is the function of tonsillar tissues?
Tonsils are lymphoid tissue aggregates situated near the entrance of the digestive and respiratory tracts and play a key role in our immune system. They act as a front-line defense forming the initial immunological response to inhaled or ingested pathogens.
Where are your tonsillar lymph nodes?
Tonsillar: Located just below the angle of the mandible. Drainage: The tonsilar and posterior pharyngeal regions. Sub-Mandibular: Along the underside of the jaw on either side.
Can you live without tonsils?
For some, the tonsils harbor bacteria that foster chronic infection. “The good news is, having your tonsils removed has proven to significantly reduce the rate of infection for chronic sufferers. And you don't need your tonsils, so there are no long-term consequences for having them removed,” Dr. Ingley says.
Which tonsils are usually removed?
There are several types of tonsils. The palatine tonsils are removed in a tonsillectomy. Palatine tonsils are collections of lymph tissue on the right and left side of the upper throat (also called the oropharynx).
What do normal tonsils look like?
What do my tonsils look like? If you still have your tonsils, you can see them when you open your mouth wide and look in the mirror. They're oval-shaped, pinkish mounds of tissue located on each side of your throat.
How tonsil stones are removed?
If your tonsil stones are small, you can try to remove them at home. The best way to do this is to gently scrape them off with a toothbrush or cotton swab. Using a water pick or gargling can also help dislodge the stones.
What do tonsil stones look like?
Tonsil stones look like small white or pale yellow bumps on your tonsils. Usually they're gravel size or slightly larger. They can smell foul and cause bad breath. Other typical symptoms include: sore throat, the sensation of something being stuck in the back of your throat, and problems swallowing.
Where are the 3 tonsils located?
Tonsils are a pair of oval-shaped tissues that sit at the very back of the mouth on either side of the throat.
What are the 3 tonsils and where are they located?
There are three sets of tonsils in the back of the mouth: the adenoids, the palantine, and the lingual tonsils. 1 These tonsils are made up of lymphatic tissue and are typically small in size.
What is the Waldeyer's tonsilar ring?
FMA. 9609. Anatomical terminology. The tonsils are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. These organs play an important role in the immune system.
What is the best treatment for tonsillitis?
The most common way to treat tonsillitis is with anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, or if bacterial in origin, antibiotics, e.g. amoxicillin and azithromycin. Surgical removal ( tonsillectomy) may be advised if the tonsils obstruct the airway or interfere with swallowing, or in patients with severe or recurrent tonsillitis. However, different mechanisms of pathogenesis for these two subtypes of tonsillar hypertrophy have been described, and may have different responses to identical therapeutic efforts. In older patients, asymmetric tonsils (also known as asymmetric tonsil hypertrophy) may be an indicator of virally infected tonsils, or tumors such as lymphoma or squamous cell carcinoma .
How big is a palatine tonsil?
In adults, each palatine tonsil normally measures up to 2.5 cm in length, 2.0 cm in width and 1.2 cm in thickness. The adenoid grows until the age of 5, starts to shrink at the age of 7 and becomes very small in adulthood.
How many tonsils are there in the human body?
Humans are born with four types of tonsils: the pharyngeal tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils.
What is the substance that accumulates on the palatine tonsil?
A tonsillolith (also known as a “tonsil stone”) is material that accumulates on the palatine tonsil. This can reach the size of a peppercorn and is white or cream in color. The main substance is mostly calcium, but it has a strong unpleasant odor because of hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan and other chemicals.
Where are the palatine tonsils located?
When used unqualified, the term most commonly refers specifically to the palatine tonsils, which are two lymphoid organs situated at either side of the back of the human throat. The palatine tonsils and the adenoid tonsil are organs consisting of lymphoepithelial tissue located near the oropharynx and nasopharynx (parts of the throat).
What is the function of tonsils?
The tonsils are immunocompetent organs which serve as the immune system's first line of defense against ingested or inhaled foreign pathogens, and as such frequently engorge with blood to assist in immune responses to common illnesses such as the common cold.
The Basics
Lateral or tonsillar lymph node (located in the jugulodigastric area) enlargement will appear as these lumps in the neck. In this case it is not prudent to treat it like it is an infection and treat with antibiotics.
Children And Adolescents
Though there is still a small chance of malignancy, in children it is less likely. In children it is commonly caused by an infection or a subclinical viral infection. Once the infection is treated, the lymph node enlargement will subside. It is not instantaneous and may take some time after treatment has begun. The swelling can be from a cyst also.
Other Lumps In The Neck
Anterior neck lumps, submental triangle lumps, swelling around the hyoid bone, and thyroid gland. With a lump on the thyroid glad, it will elevate with swallowing. Other areas of swelling are the submandibular region and parotid region. Treatment and diagnosis needs to be made by a medical professional.
How does tonsil cancer form?
Tonsil cancer forms when healthy cells in the tonsils develop changes in their DNA. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. The changes tell the cells to grow out of control and to continue living when healthy cells would normally die. The accumulating cells form a tumor that can grow beyond the tonsils ...
What is the name of the two pads in the back of your mouth?
Tonsils . Your tonsils are two oval-shaped pads in the back of your mouth. Your tonsils are part of your body's germ-fighting immune system. Tonsil cancer is an abnormal growth of cells that forms in a tons il.
What is HPV and throat cancer?
Close. HPV and throat cancer. HPV and throat cancer. Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common sexually transmitted infection that increases the risk of certain types of throat cancer. HPV has been linked to cancer that affects the soft palate, tonsils, back of the tongue, ...
How to reduce the risk of tonsil cancer?
To reduce your risk of tonsil cancer: Don't use tobacco. If you don't use tobacco, don't start. If you currently use tobacco of any kind, talk with your doctor about strategies to help you quit. Limit alcohol if you choose to drink. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
How do you know if you have tonsil cancer?
Signs and symptoms of tonsil cancer include: Difficulty swallowing. A sensation that something is caught in the back of your throat. Swelling and pain in the neck. Earache. Jaw stiffness.
What does a dentist check for?
Get regular dental care. During your appointment, your dentist will check your mouth for signs of cancer and precancerous changes.
Can tonsil cancer be transmitted?
This common sexually transmitted infection is detected in most tonsil cancers in the United States. Tonsil cancer caused by HPV tends to occur at a younger age and is more likely to respond well to available treatments.

Overview
The tonsils are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. These organs play an important role in the immune system.
When used unqualified, the term most commonly refers specifically to the palatine tonsils, which are two lymphoid organs situated at either side of the back of the human throat. The palatine to…
Structure
Humans are born with four types of tonsils: the pharyngeal tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils.
The palatine tonsils tend to reach their largest size in puberty, and they gradually undergo atrophy thereafter. However, they are largest relative to the diameter of the throat in young children. In adults, each palatine tonsil normally measures up to 2.5 cm in length, 2.0 cm in width and 1.2 c…
Function
The tonsils are immunocompetent organs which serve as the immune system's first line of defense against ingested or inhaled foreign pathogens, and as such frequently engorge with blood to assist in immune responses to common illnesses such as the common cold. The tonsils have on their surface specialized antigen capture cells called Microfold cell (M cells) that allow for the uptake of antigens produced by pathogens. These M cells then alert the B cells and T cells in th…
Clinical significance
The palatine tonsils can become enlarged (adenotonsillar hyperplasia) or inflamed (tonsillitis). The most common way to treat tonsillitis is with anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, or if bacterial in origin, antibiotics, e.g. amoxicillin and azithromycin. Surgical removal (tonsillectomy) may be advised if the tonsils obstruct the airway or interfere with swallowing, or in patients with severe or recurrent tonsillitis. However, different mechanisms of pathogenesis for these two sub…
Additional images
• Illustration of frontal view of tonsils
External links
• Media related to Tonsils at Wikimedia Commons