Explore
What drugs can cause Torsades de Pointes? Examples of compounds linked to clinical observations of TdP include amiodarone, most fluoroquinolones, methadone, lithium, chloroquine, erythromycin, azithromycin, pimozide, and phenothiazines. The anti-emetic agent ondansetron may also increase the risk of developing TdP.
What drugs can cause torsades de pointes?
Torsades de pointes (French for “twisting of the points”) is one of several types of life-threatening heart rhythm disturbances. Ventricular fibrillation can lead to cardiac arrest, an event in which the heart suddenly stops. Cardiac arrest is usually fatal.
What does torsades de pointes stand for?
Torsade de Pointes Torsade is defined as the combination of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia plus a prolonged QT-interval. Torsade can be caused by either congenital long-QT syndrome or acquired long-QT syndrome (due to electrolyte abnormalities and/or medications). The vast majority of torsade results from acquired long-QT syndrome, which ...
What causes torsade de pointes?
These include:
- antiarrhythmic drugs, including quinidine, procainamide, and disopyramide
- antipsychotics or tricyclic antidepressants
- methadone, erythromycin, and ketoconazole
- intracranial bleeding, or bleeding inside the skull
- electrolyte disturbances, such as hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalcemia
- acute myocardial infarction, or a blockage in a coronary artery
How to treat torsades de pointes?

What is the cause of torsades de pointes?
People who have Long QT interval (seen on the electrocardiogram), an electrical problem with their heart, tend to get Torsades de Pointes. Genetic abnormalities or sometimes certain medicines can cause Long QT interval.
What does torsades feel like?
You may suddenly feel your heart beating faster than normal, even when you're at rest. In some TdP episodes, you may feel light-headed and faint. In the most serious cases, TdP can cause cardiac arrest or sudden cardiac death. It's also possible have an episode (or more than one) that resolves quickly.
What is the difference between torsades de pointes and ventricular fibrillation?
1. Double peaks. This arrhythmia, which occurs during long episodes of torsades de pointes, has a slower frequency than episodes of ventricular fibrillation that occur duringhypothermia (an experimental condition that was used to permit the study of spontaneous termination of ventricular fibrillation). 2.
What happens to the heart during torsades de pointes?
Torsades de pointes is French for “twisting of points” and refers to when the heart's two lower chambers or ventricles, beat faster than the upper chambers, which are known as the atria. Most cases of torsades de pointes resolve on their own without treatment.
How do you fix torsades?
The torsades rhythm is treated with magnesium sulfate 2 g IV over 1 to 2 minutes, correction of hypokalemia, pacing or isoproterenol to increase heart rate, and correction of the cause.
What meds cause torsades?
Table 2ClassExamplesAntiarrhythmicsDisopyramide, procainamide, quinidine, sotalolMacrolidesAzithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycinFluoroquinolonesCiprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacinAntifungalsFluconazole, ketoconazole, pentamidine, voriconazole5 more rows
How do you manage torsades de pointes?
Pulseless torsades should be defibrillated. Intravenous magnesium is the first-line pharmacologic therapy in Torsades de Pointes. Magnesium has been shown to stabilize the cardiac membrane, though the exact mechanism is unknown. The recommended initial dose of magnesium is a slow 2 g IV push.
Which electrolyte imbalance is associated with torsades de pointes?
Answer. The electrolyte disturbances that have been reported to precipitate torsade include hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia.
Does magnesium shorten QT?
Because magnesium does not affect the QT interval, it is not possible to measure response.
Does a pacemaker prevent torsades?
The pacemaker component of such devices should in theory help prevent torsades by preventing bradycardia. However, the rate of most pacemakers is not likely to provide protection from torsades.
Is torsades de pointes hereditary?
Genetic susceptibility is an important consideration in patients with drug-induced Torsades de Pointes (TdP) because it may be the sentinel event unmasking an underlying congenital long QT syndrome (LQTS). Previous studies have identified congenital LQTS in 5% to 20% of cases with drug-induced TdP.
What is torsades de pointes?
Torsades de pointes (French for “twisting of the points”) is one of several types of life-threatening heart rhythm disturbances. In the case of torsades de pointes (TdP), the heart’s two lower chambers, called the ventricles, beat faster than and out of sync with the upper chambers, called the atria.
How many cases of TDP were there between 1978 and 2011?
In a 2013 study, researchers could find only 46 reported cases of TdP between 1978 and 2011. In nearly all of these cases, TdP coincided with a long QT interval. These were perioperative TdP cases, meaning they were present before someone underwent heart surgery. In some cases, heart surgery can lead to arrhythmias.
What antiarrhythmics are associated with TDP?
Some of the antiarrhythmic drugs of concern are: quinidine. procainamide.
What to do if you have TDP?
If you are diagnosed with TdP, your doctor will check your potassium, magnesium, and calcium levels. If they are low, you will be given supplements to get your levels up into the healthy range. You will also undergo EKG monitoring until your heart returns to a normal rhythm .
What is Torsades de Pointes?
Torsades de Pointes is a type of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia characterized by a gradual change in amplitude and twisting of the QRS complexes around an isoelectric line on the electrocardiogram.
How does Torsades de Pointes affect the cellular membrane?
The proposed mechanism for Torsades de Pointes involves inhibition of the delayed rectifier potassium current. This leads to an excess of positive ions within the cellular membrane causing a prolonged repolarization phase. If an ectopic beat is generated during this prolonged repolarization phase, known as an R on T phenomenon, this can result in Torsades de Pointes. Both congenital and drug-induced QT prolongation affect the cellular membrane in similar fashions by blocking the potassium channel. Torsades de Pointes is slightly different from ventricular fibrillation in that it can spontaneously resolve. However, Torsades de Pointes can ultimately progress into venticular fibrillation if left untreated. [9]
Is torsade de pointes hypotensive?
Today one needs to be aware that drug-induced long QT syndrome is common and hence, a thorough medication history must be obtained. Patients with torsade may be hypotensive, have a rapid pulse and have loss of consciousness. Evaluation. An electrocardiogram is paramount in the diagnosis of Torsades de Pointes.
Is Torsades de Pointes asymptomatic?
Around 50% of patients with Torsades de Pointes are asymptomatic. The most common symptoms reported are syncope, palpitations, and dizziness. However, cardiac death is the presenting symptom in up to 10% of patients. Patients with Jervell and Lange Nielsen syndrome may have a history of deafness.
Can you use overdrive pacing for torsades de pointes?
There are limited studies on the success of pacing for treatment of Torsades de Pointes; however, there are numerous case reports that show it is a viable option. Overdrive pacing can be used in the setting of both frequent runs of torsades and Torsades de Pointes that is refractory to magnesium.
Does isoproterenol help with TDP?
Isoproterenol has been shown to help prevent Torsades de Pointes in patients with prolonged QT that is refractory to magnesium. It is a non-selective beta agonist, which increases the heart rate and shortens the QT interval. This lowers the likelihood of an R-on-T phenomenon that can lead to TdP.
What is a torsades de pointes?
Torsades de pointes is a form of tachycardia that shows up as a ribbon-like EKG pattern. Problems that occur with the heart’s rhythm are known as arrhythmias. When the heart beats faster than usual, as in a case of torsades de pointes, it is called tachycardia. Torsades de pointes is French for “twisting of points” and refers to when ...
How to diagnose Torsades de Pointes?
Torsades de pointes can sometimes be diagnosed by assessing a person’s calcium, magnesium, and potassium levels. However, a diagnosis is usually made using an electrocardiogram or EKG.
What medications cause torsades de pointes?
There is also a range of conditions and medications that cause or influence the development of torsades de pointes. These include: 1 antiarrhythmic drugs, including quinidine, procainamide, and disopyramide 2 antipsychotics or tricyclic antidepressants 3 methadone, erythromycin, and ketoconazole 4 intracranial bleeding, or bleeding inside the skull 5 electrolyte disturbances, such as hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalcemia 6 acute myocardial infarction, or a blockage in a coronary artery 7 kidney injury 8 liver failure 9 toxins from heavy metals or insecticides 10 anorexia 11 malnutrition
Can torsades de pointes be treated?
In some cases, torsades de pointes will just be monitored rather than treated. Torsades de pointes can have life-threatening complications, so immediate treatment is vital. Treatment will vary, depending on the individual’s symptoms and the cause of the abnormal heart rhythm. People without syncope, ventricular tachycardia, ...
Is Torsades de Pointes congenital?
Causes. Torsades de pointes is more common in women than men, but anyone can develop the condition. It is usually a complication of LQTS, which can be drug-induced or congenital, meaning the person is born with it.
Can torsades de pointes cause syncope?
low blood pressure. In more serious cases, torsades de pointes can cause lack of consciousness, known as syncope, or even a cardiac arrest, which can lead to death. It is crucial to accurately diagnose torsades de pointes and distinguish it from other forms of ventricular tachycardia.
Can you develop torsades de pointes without warning?
A person can develop torsades de pointes without any warning. Symptoms may vary depending on the individual and the length of the episode.
How to treat torsades de pointes?
The most effective treatment to terminate torsades is an electrical cardioversion - a procedure in which an electrical current is applied across the heart to temporarily stop and then resynchronise the heart's cells. Treatment to prevent recurrent torsades includes infusion of magnesium sulphate, correction of electrolyte imbalances such as low blood potassium levels ( hypokalaemia ), and withdrawal of any medications that prolong the QT interval. Treatments used to prevent torsades in specific circumstances include beta blockers or mexiletine in long QT syndrome. Occasionally a pacemaker may be used to accelerate the heart's own sinus rhythm, and those at risk of further torsades may be offered an implantable defibrillator to automatically detect and defibrillate further episodes of the arrhythmia.
Why do Torsades occur?
Torsades occurs as both an inherited (linked to at least 17 genes) and as an acquired form caused most often by drugs and/or electrolyte disorders that cause excessive lengthening of the QT interval.
What is a TDP?
Torsades de pointes, torsade de pointes or torsades des pointes ( TdP) ( / tɔːˌsɑːd də ˈpwæ̃t /, French: [tɔʁsad də pwɛ̃t̪], translated as "twisting of peaks") is a specific type of abnormal heart rhythm that can lead to sudden cardiac death. It is a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia that exhibits distinct characteristics on ...
What drugs can cause torsades de pointes?
Certain drugs and combinations of drugs resulting in drug interactions are common contributors to torsades de pointes risk. QT-prolonging medications such as clarithromycin, levofloxacin, or haloperidol, when taken concurrently with cytochrome P450 inhibitors, such as fluoxetine, cimetidine, or particular foods including grapefruit, ...
How to prevent torsades?
Treatment to prevent recurrent torsades includes infusion of magnesium sulphate, correction of electrolyte imbalances such as low blood potassium levels ( hypokalaemia ), and withdrawal of any medications that prolong the QT interval.
When was the Torsade first described?
The phenomenon was originally described in a French medical journal by Dessertenne in 1966 , when he observed this cardiac rhythm disorder in an 80-year-old female patient with complete intermittent atrioventricular block. In coining the term, he referred his colleagues to the "Dictionnaire Le Robert", a bilingual French English dictionary, of which his wife had just given him a copy. Here, "torsade" is defined as:
Is "torsade de pointes" plural or singular?
The singular and plural forms ( torsade de pointes, torsades de pointes and torsades des pointes) have all often been used. The question of whether each one is grammatically "correct" and the others "incorrect" has repeatedly arisen. This is seen among major medical dictionaries, where one enters only the plural form, another enters the plural form as the headword but lists the singular as a variant, and yet another enters the singular form as the headword and gives a usage comment saying that the plural is not preferred. One group of physicians has suggested that it would make the most sense to use the singular form to refer to the arrhythmia entity (where an arrhythmia may involve one or multiple episodes), and that one might best reserve the plural form for describing repeated twisting during a single episode. Other authors have suggested all three words should be plural. Regarding the natural language variation, they concluded, in good nature, "Wasn't it the French who coined the term vive la difference ?"
What is Torsades de Pointes?
Torsades de pointes (“twisting of the points”) is a life-threatening heart rhythm disturbance.
How to diagnose Torsades de Pointes?
Torsades de pointes can be diagnosed by assessing an individual’s calcium, magnesium, and potassium levels, but the best way to diagnose this condition is through an electrocardiogram (EKG).
What is a TDP?
Torsades de pointes (TdP) is a rare form of tachycardia arrhythmia where the heart’s two lower chambers beat faster than, and out of sync with, the two upper chambers. Typically, TdP resolves without intervention or treatment. However, left untreated, it can potentially develop into a serious heart condition called ventricular fibrillation, ...
What causes TDP in the heart?
TdP can also be triggered by certain medications, including antidepressants and anti-arrhythmia drugs. Additional risk factors for Torsades de pointes: Low potassium in the body. Low magnesium in the body.
What are the risk factors for Torsades de Pointes?
Additional risk factors for Torsades de pointes: Low potassium in the body. Low magnesium in the body. Low calcium in the body. Anorexia (eating disorder). Presence of liver disease. Bleeding inside the cranium (skull). Blockage in a coronary artery. Toxins from heavy metals or insecticides.
What is the best treatment for TDP?
For a congenital form of TdP, your doctor may prescribe beta blockers, along with inserting a pacemaker or (in rare cases) an implantable cardioverter defibrillator.
Can Torsades de Pointes cause syncope?
In some serious cases, Torsades de pointes can precipitate unconsciousness ( passing out), a condition known as syncope.
What is Torsades de Pointes (TdP)?
Disclaimer: This material should be used to supplement your understanding of the cardiovascular system. Any use of the information given in this post series is at your own risk and should be verified prior to making it a part of your nursing practice. There may be affiliate links associated with some products but we promise that we will never recommend anything that we don’t use ourselves.
How is Torsades unique?
Torsades is unique in that each waveform is a different height and it usually grows taller and shorter in a roller coaster like pattern.
What causes torsades in the heart?
The cause of torsades is a long QT interval (an abnormally long repolarization of the heart) that turns into a continuous circular electrical route in the ventricles. Ventricular depolarization and repolarization occurs from the beginning of the Q wave to the end of the T wave and is called the QT interval.
What do you need to know about torsades?
There are 4 things you need to know about torsades: How to recognize this arrhythmia on an ECG. Why or how does this arrhythmia happen. What intervention you need to do when a patient is in torsades. When to avoid certain medications.
Who is Susan Dupont?
Written by: ME! Susan DuPont of BossRN.com who is a full-time nurse in a level I trauma Emergency Room. In her spare time, she loves the outdoors, fishing, and hunting.
Can a patient with long QT go into Torsades?
Patients who have long Q T syndrome (constant long QT intervals) can go into Torsades with just a loud noise, exercise or intense emotional distress. Some medications can cause a patient without a long QT to have a long QT interval.

Overview
Torsades de pointes, torsade de pointes or torsades des pointes (TdP) (/tɔːˌsɑːd də ˈpwæ̃t/, French: [tɔʁsad də pwɛ̃t̪], translated as "twisting of peaks") is a specific type of abnormal heart rhythm that can lead to sudden cardiac death. It is a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia that exhibits distinct characteristics on the electrocardiogram (ECG). It was described by French physician François De…
Signs and symptoms
Most episodes will revert spontaneously to a normal sinus rhythm. Symptoms and consequences include palpitations, dizziness, lightheadedness (during shorter episodes), fainting (during longer episodes), and sudden cardiac death.
Causes
Torsades occurs as both an inherited (linked to at least 17 genes) and as an acquired form caused most often by drugs and/or electrolyte disorders that cause excessive lengthening of the QT interval.
Common causes for torsades de pointes include drug-induced QT prolongation and less often diarrhea, low serum magnesium, and low serum potassium or congenital long QT syndrome. It ca…
Risk factors
The following is a partial list of factors associated with an increased tendency towards developing torsades de pointes:
• Medications
• Hypokalemia (low serum potassium)
• Hypomagnesemia (low serum magnesium)
Pathophysiology
Action potential of cardiac muscles can be broken down into five phases:
• Phase 0: Sodium channels open, resulting in the entrance of Na into the cells; this results in the depolarization of the cardiac muscles.
• Phase 1: Sodium channels close; this stops depolarization. Potassium channels open, leading to an outward current of K out of the cells.
Diagnosis
The ECG tracing in torsades demonstrates a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia with a characteristic illusion of a twisting of the QRS complex around the isoelectric baseline (peaks, which are at first pointing up, appear to be pointing down for subsequent "beats" when looking at ECG traces of the "heartbeat"). It is hemodynamically unstable and causes a sudden drop in arterial blood pressure, leading to dizziness and fainting. Depending on their cause, most individ…
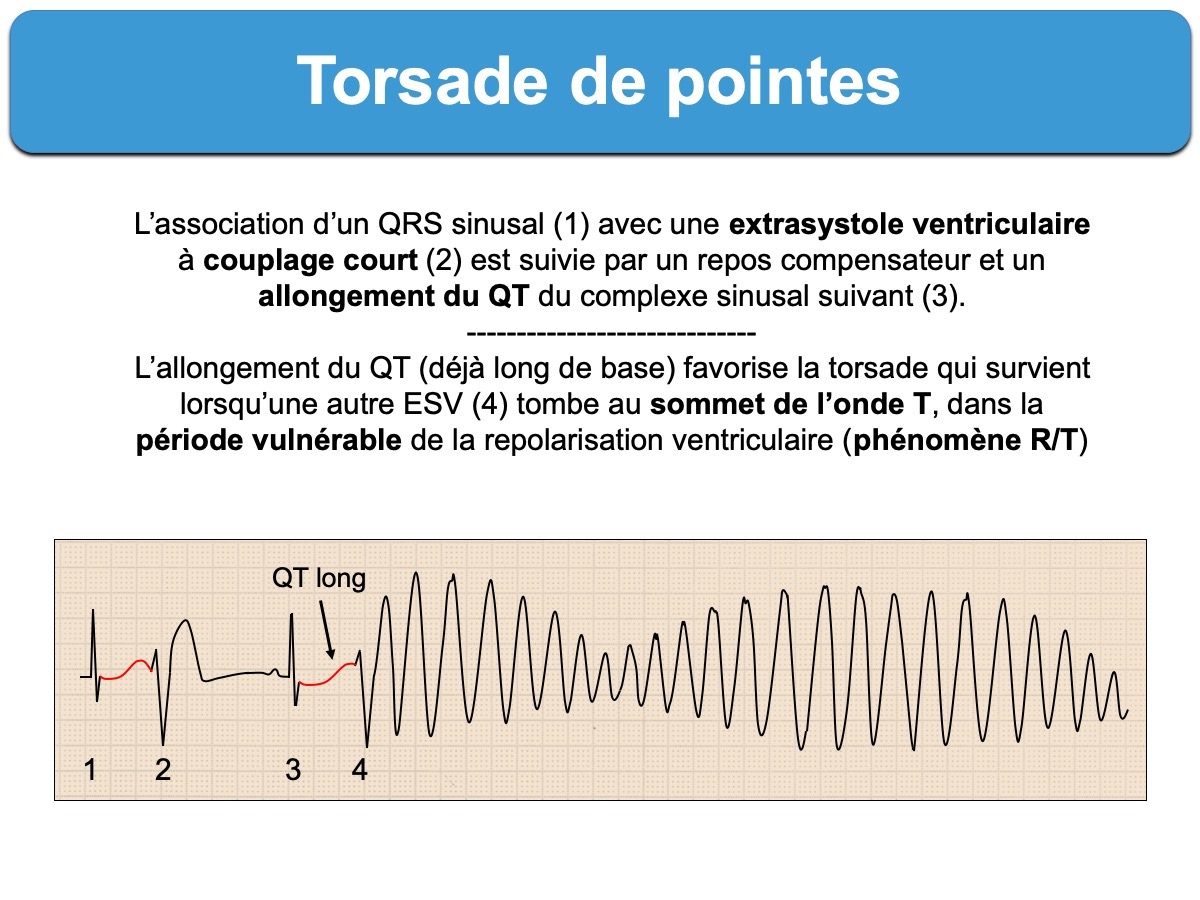
R-on-T phenomenon
The R-on-T phenomenon is the superimposition of a premature ventricular contraction on the T wave of a preceding heart beat. Studies suggest that R-on-T phenomenon is likely to start a sustained ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. It's considered a cardiac arrhythmia in which the ventricles of the heart become again excited during the repolarization of the previous heart action. Because part of the heart muscle cannot be excited at this early point in time, a pre…
Treatment
The treatment of torsades de pointes aims to restore a normal rhythm and to prevent the arrhythmia recurring. While torsades may spontaneously revert to a normal sinus rhythm, sustained torsades requires emergency treatment to prevent cardiac arrest. The most effective treatment to terminate torsades is an electrical cardioversion - a procedure in which an electrical current is applied across the heart to temporarily stop and then resynchronise the heart's cells. T…