
What are the three key steps of transcription?
Transcription involves four steps:
- Initiation. The DNA molecule unwinds and separates to form a small open complex.
- Elongation. RNA polymerase moves along the template strand, synthesising an mRNA molecule.
- Termination. In prokaryotes there are two ways in which transcription is terminated.
- Processing.
What begins the process of transcription?
Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence near the beginning of a gene (directly or through helper proteins). RNA polymerase uses one of the DNA strands (the template strand) as a template to make a new, complementary RNA molecule. Transcription ends in a process called termination.
What are the three stages of transcription?
What are the 3 Stages of Audio Transcription?
- First Stage of Transcription: Identifying the Need for Transcription Services. Transcribing audio is the best way to take nonvisual information and turn it into something tangible and comprehensible.
- Second Stage of Transcription: Recording an Audio File. ...
- Third Stage of Transcription: Finding a Transcription Service. ...
What happens during the process of transcription?
What are the 7 steps of transcription?
- Initiation. Transcription is catalysed by the enzyme RNA polymerase, which attaches to and moves along the DNA molecule until it recognises a promoter sequence. …
- Elongation. …
- Termination. …
- 5′ Capping. …
- Polyadenylation. …
- Splicing.
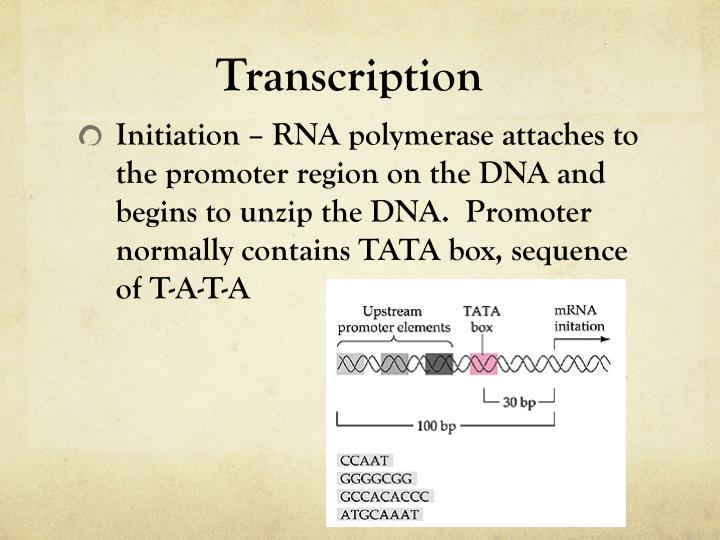
What is transcription simple answer?
Transcription is the process by which the information in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). DNA safely and stably stores genetic material in the nuclei of cells as a reference, or template.
What is transcription short?
Listen to pronunciation. (tran-SKRIP-shun) In biology, the process by which a cell makes an RNA copy of a piece of DNA. This RNA copy, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the genetic information needed to make proteins in a cell.
What is transcription kid definition?
Transcription is the process of copying DNA's instructions for protein building to an RNA molecule. Transcription works like passing a note in class. RNA copies the DNA's message so it can be passed out of a cell's nucleus.
What is transcription in biology for dummies?
Transcription is the first step in gene expression. It involves copying a gene's DNA sequence to make an RNA molecule. Transcription is performed by enzymes called RNA polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an RNA strand (using a DNA strand as a template).
What is transcription and example?
The definition of a transcription is something fully written out, or the process of fully writing something out. An example of a transcription is someone writing out their complete job description and responsibilities. noun.
What is transcription of DNA?
Transcription Transcription, as related to genomics, is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence. This copy, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the gene's protein information encoded in DNA.
What is transcription and translation?
Transcription is the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template where the code in the DNA is converted into a complementary RNA code. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mRNA template where the code in the mRNA is converted into an amino acid sequence in a protein.
How do you explain RNA to a child?
RNA is a copy, or a transcription, of DNA. See, the DNA is very important, since it holds the information needed for making new cells and maintaining life, so it never leaves the nucleus. The RNA is the one that goes out to do work throughout the cell.
How does the process of transcription work?
Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence near the beginning of a gene (directly or through helper proteins). RNA polymerase uses one of the DNA strands (the template strand) as a template to make a new, complementary RNA molecule. Transcription ends in a process called termination.
What is the main function of transcription and translation?
Transcription and translation are the two processes that convert a sequence of nucleotides from DNA into a sequence of amino acids to build the desired protein. These two processes are essential for life. They are found in all organisms – eukaryotic and prokaryotic.
What is produced in transcription?
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA).
What is a transcription and translation?
Transcription is the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template where the code in the DNA is converted into a complementary RNA code. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mRNA template where the code in the mRNA is converted into an amino acid sequence in a protein.
What does transcription mean in writing?
Transcription is the process in which speech or audio is converted into a written document. Closed captions are time-coded to the video, while a transcript is just the text with no time information.
Transcribing yourself or outsourcing?
If you have to make transcripts for an investigation or for another project, you have 2 choices. You either do it yourself (which takes a lot of time) or you outsource it and have it done by a professional agency (which of course costs money).
Summary – What is a transcription in a nutshell
Transcription is a crucial part of qualitative research. Make sure you choose the right transcription type for your project. As a guideline, we recommend using verbatim in a sentence if the intonation of the speakers is important. Edited transcription, however, focuses on the content of the interview and is easier to read.
Transcription Definition
Transcription refers to the first step of gene expression where an RNA polymer is created from a DNA template. This reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called RNA polymerases and the RNA polymer is antiparallel and complementary to the DNA template.
Function of Transcription
Life on earth is said to have begun from self-replicating RNA since it is the only class of molecules capable of both catalysis and carrying genetic information. With evolution, proteins took over catalysis because they are capable of a greater variety of sequences and structures.
Mechanism of Transcription
Transcription creates a single stranded RNA molecule from double stranded DNA. Therefore, only the information in one of the strands is transferred into the nucleotide sequence of RNA. One strand of DNA is called the coding strand and the other is the template strand.
Types of RNA Transcripts
Traditionally, three types of RNA transcripts were known – messenger RNA (mRNA), tRNA and rRNA – and all three are intimately associated with protein synthesis . While mRNA determines amino acid sequence, tRNA and rRNA are crucial for the mechanism of translating the mRNA code.
Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Transcription
The obvious difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription is the presence of a nuclear membrane in eukaryotes. Eukaryotic RNA transcripts need to be exported from the nucleus, whereas prokaryotes conduct coupled transcription and translation in the cytoplasm.
Quiz
1. Which of these properties makes DNA a more stable genetic material?
What is Transcription?
It is one of the first processes in gene expression. The genetic information flows from DNA to protein and this flow of information takes place in a sequential process of transcription and translation. Only one strand of DNA is copied during the process of transcription known as the template strand and the RNA formed is called the mRNA.
RNA Polymerase
The RNA polymerase is the main enzyme involved in transcription. It uses single-strand DNA to synthesize a complementary RNA strand. The DNA-dependent RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and catalyses the polymerization in the 5’ to 3’ direction on the template strand.
RNA Processing
The transcribed RNA is known as the pre-mRNA. It is processed further to convert it into mature RNA. RNA processing include:
Frequently Asked Questions
Transcription is the process in which a DNA sequence is transcribed into an RNA molecule with the help of enzyme RNA polymerase. One of the DNA strands acts as a template to make a complementary RNA strand.
Key points
Transcription is the first step in gene expression. It involves copying a gene's DNA sequence to make an RNA molecule.
Introduction
Have you ever had to transcribe something? Maybe someone left a message on your voicemail, and you had to write it down on paper. Or maybe you took notes in class, then rewrote them neatly to help you review.
Overview of transcription
Transcription is the first step in gene expression, in which information from a gene is used to construct a functional product such as a protein. The goal of transcription is to make a RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence.
RNA polymerase
The main enzyme involved in transcription is RNA polymerase, which uses a single-stranded DNA template to synthesize a complementary strand of RNA. Specifically, RNA polymerase builds an RNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction, adding each new nucleotide to the 3' end of the strand.
Stages of transcription
Transcription of a gene takes place in three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. Here, we will briefly see how these steps happen in bacteria. You can learn more about the details of each stage (and about how eukaryotic transcription is different) in the stages of transcription article.
Eukaryotic RNA modifications
In bacteria, RNA transcripts can act as messenger RNAs ( mRNAs) right away. In eukaryotes, the transcript of a protein-coding gene is called a pre-mRNA and must go through extra processing before it can direct translation.
Transcription happens for individual genes
Not all genes are transcribed all the time. Instead, transcription is controlled individually for each gene (or, in bacteria, for small groups of genes that are transcribed together). Cells carefully regulate transcription, transcribing just the genes whose products are needed at a particular moment.
