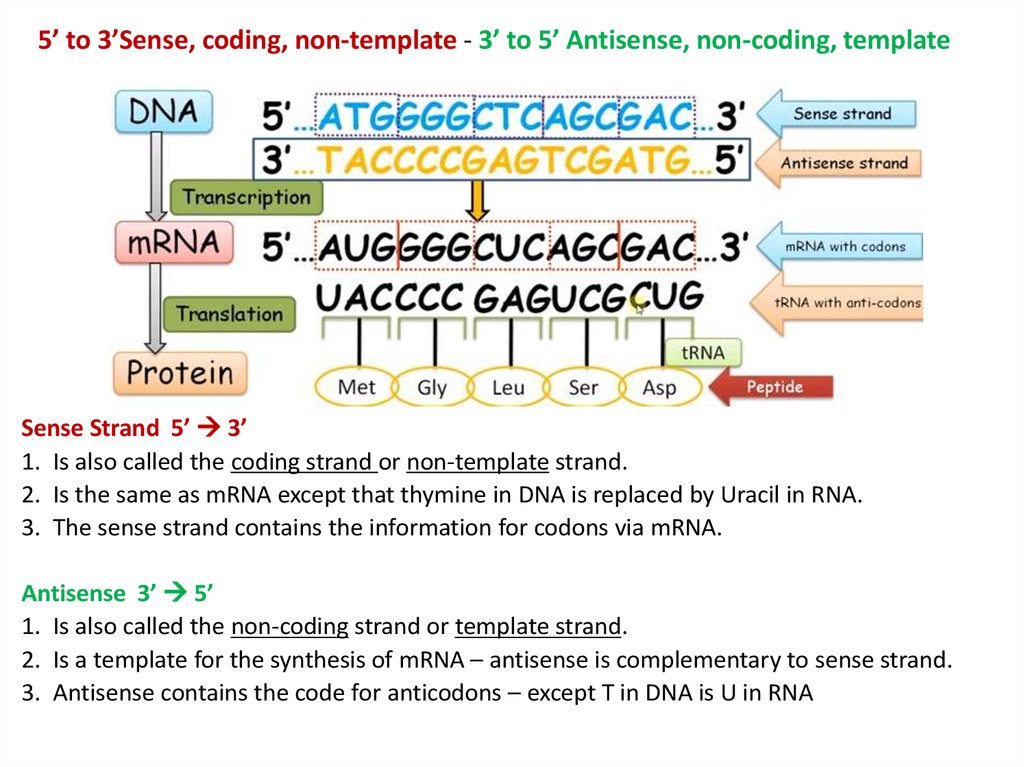
What is transcription vs translation? Transcription is the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template where the code in the DNA is converted into a complementary RNA code. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mRNA template where the code in the mRNA is converted into an amino acid sequence in a protein.
What's the difference between transcription and translation?
Mar 17, 2017 · Since genes are coded for in the DNA and the DNA is transcribed and translated into proteins, the expression of the genes are controlled by which portions of the DNA get copied and made into the proteins. Transcription The first …
Which statement best compares transcription and translation?
Transcription is the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template where the code in the DNA is converted into a complementary RNA code. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mRNA template where the code in the mRNA is converted into an amino acid sequence in a …
Does transcription occur before translation?
Audio translation is much more complex than transcription. In audio translation, someone fluent in both the original and target language must translate what is being said into the target language. Translation is extremely subjective and sensitive to context, as anyone who has laughed at a mistranslated signs like these will know!
What happens in transcription and translation?
Feb 13, 2014 · Here is a more complete definition of translation: Translation. Definitions. Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene sequence. This copy, called a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, leaves the cell nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, where it directs the synthesis of the protein, which it encodes.

What is difference between translation and transcription?
The translation is the process of converting a text file from one language to another language. Transcription is the process of listening to audio, video, live speech, etc., and writing into text form in the exact wording that the original speaker used.Mar 8, 2021
What is transcription and translation?
The process by which DNA is copied to RNA is called transcription, and that by which RNA is used to produce proteins is called translation.
What is called transcription?
Transcription is the process by which the information in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). DNA safely and stably stores genetic material in the nuclei of cells as a reference, or template.
What is transcription in short?
Transcription Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene sequence. This copy, called a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, leaves the cell nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, where it directs the synthesis of the protein, which it encodes.
What is the purpose of transcription?
The purpose of transcription is to make RNA copies of individual genes that the cell can use in the biochemistry. The purpose of translation is to synthesize proteins, which are used for millions of cellular functions. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mRNA template.
What is translation in biology?
Definition. Uses the genes as templates to produce several functional forms of RNA. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mRNA template. This is the second step of gene expression. Uses rRNA as assembly plant; and tRNA as the translator to produce a protein. Products.
What is the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template?
Transcription is the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template where the code in the DNA is converted into a complementary RNA code. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mRNA template where the code in the mRNA is converted into an amino acid sequence in a protein.
Which antibiotics inhibit transcription?
Antibiotics. Transcription is inhibited by rifampicin and 8-Hydroxyquinoline. Translation is inhibited by anisomycin, cycloheximide, chloramphenicol, tetracyclin, streptomycin, erythromycin and puromycin. Localization. Found in prokaryotes ' cytoplasm and in a eukaryote's nucleus.
Where does transcription occur in prokaryotes?
In prokaryotes both transcription and translation occur in the cytoplasm due to the absence of nucleus. In eukaryote transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation occurs in ribosomes present on the rough endoplasmic membrane in the cytoplasm.
What is the transcription factor?
The transcription factors and RNA polymerase binding to the promoter forms a transcription initiation complex. The promoter consists of a core region like the TATA box where the complex binds. It is in this stage that RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA. Translation initiates with the formation of initiation complex.
What is the initiation of transcription?
Initiation. Occurs when RNA polymerase protein binds to the promoter in DNA and forms a transcription initiation complex. Promoter directs the exact location for the initiation of transcription. Occurs when ribosome subunits, initiation factors and t-RNA bind the mRNA near the AUG start codon. Termination.
What is audio translation?
What is translation? Audio translation is much more complex than transcription. In audio translation, someone fluent in both the original and target language must translate what is being said into the target language. Translation is extremely subjective and sensitive to context, as anyone who has laughed at a mistranslated signs like these will ...
What is a take note?
Take Note is a UK-based transcription service with world-class customer support alongside the highest standards of security and ethics. We deliver a comprehensive range of transcription services including Audio and Video Transcription, Video Captions and On-Site Note Taking.
What is the process of translating a molecule to a sequence of amino acids during protein synthesis?
Translation is the process of translating the sequence of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule to a sequence of amino acids during protein synthesis. The genetic code describes the relationship between the sequence of base pairs in a gene and the corresponding amino acid sequence that it encodes.
What is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene sequence?
Here is a more complete definition of translation: Translation. Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene sequence.
Where does mRNA enter the cell?
This copy, called a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, leaves the cell nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, where it directs the synthesis of the protein, which it encodes. Here is a more complete definition of transcription: Transcription.
What is the talking glossary of genetics?
The Talking Glossary of Genetics Terms website and iPhone app provide an easily transportable and accessible reference for your students. Many times the unfamiliar vocabulary is the major stumbling block to student comprehension. This app/site gives them a handy reference to common terms used in describing the components involved on transcription and translation.#N#Talking Glossary of Genetics Terms#N#Talking Glossary of Genetics Terms iPhone App
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
The 'Central Dogma' of molecular biology is that 'DNA makes RNA makes protein' . This anime shows how molecular machines transcribe the genes in the DNA of every cell into portable RNA messages, how those messenger RNA are modified and exported from the nucleus, and finally how the RNA code is read to build proteins.
What is a clicker case?
This "clicker case" was designed to develop students' ability to read and interpret information stored in DNA. Making use of personal response systems ("clickers") along with a PowerPoint presentation, students follow the story of "Jason," a student intern at the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (CDC). While working with a CDC team in Mexico, Jason is the only person who does not get sick from a new strain of flu. It is up to Jason to use molecular data collected from different local strains of flu to identify which one may be causing the illness. Although designed for an introductory biology course for science or non-science majors, the case could be adapted for upper-level courses by including more complex problems and aspects of gene expression, such as the excision of introns."#N#See: Decoding the Flu
What is the difference between translation and transcription?
The only thing they have in common is that they are used in the documentation and at times recording of words so that they can be understood by another person not necessarily the originator of the words or the one who translated or transcribed the words.
What is transcription in medical?
This is the process of taking information in the same language and using it again in a clearer manner so that the information is understood better by the targeted person or persons. Doing this helps to make a technical topic much easier to grasp by non-technical persons, or even professionals in that field who were not part of authoring the information. A common area where this is applied is in the medical field. Medical notes transcription is common for the purpose of accurate charging for given services. Transcription involves: 1 Reading the material to be transcribed 2 Listening to a recorded voice 3 Writing the information in the same language.
What is the difference between transcription and translation?
The key difference between transcription and translation is that transcription refers to the process of producing a mRNA molecule for the DNA of a gene while translation refers to the process of synthesizing an amino acid sequence from the transcribed mRNA molecule.
What is transcription in biology?
What is Transcription? Transcription is the first step of the gene expression. It is the process of producing a mRNA molecule from a DNA template. Transcription occurs inside the nucleus of eukaryotes. It is an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. RNA polymerase is the enzyme which catalyzes this process.
How does gene expression occur?
Hence, gene expression is the process of synthesizing a protein molecule (gene product) from the genetic information hidden in the gene. Gene expression occurs via two major steps such as transcription and translation.
Where does transcription occur in eukaryotes?
This is the major difference between transcription and translation. Furthermore, transcription occurs inside the nucleus of eukaryotes while transcription occurs in the cytoplasm associated with ribosomes.
What are the steps of gene expression?
Gene expression occurs via two major steps such as transcription and translation . Transcription is the first step, and it is followed by the translation, which is the second major step of gene expression.
How many nucleotides are in a codon?
Structurally, three nucleotides collectively constitute a codon. One codon specifies a specific amino acid out from the total of 20 amino acids. Accordingly, the specified amino acid sequence is synthesized from the mRNA molecule during the translation process.
What is the function of RNA polymerase?
RNA polymerase is the enzyme which catalyzes this process. Among the two strands of DNA in a gene, one serves as the coding sequence while the other is the non-coding sequence. Non-coding sequence serves as the template in transcription since it is complementary to the coding sequence. RNA polymerase enzyme reads the nucleotides ...
How does transcription work?
Through transcription, the sequence of bases of the DNA is transcribed into the reciprocal sequence of bases in a strand of RNA. Through transcription, the information of the DNA molecule is passed onto the new strand of RNA which can then carry the information to where proteins are produced.
Where does translation end?
Translation ends when a stop codon on the mRNA strand reaches the A site in the ribosome. The stop codon doesn’t have a complementary tRNA or anticodon. Instead, a protein called a ‘release factor’ binds to the stop codon and adds a water molecule to the polypeptide chain when it moves into the P site.
What is the link between DNA and proteins?
The RNA molecule is the link between DNA and the production of proteins. During translation, the RNA molecule created in the transcription process delivers information from the DNA to the protein-building machines. DNA and RNA are similar molecules and are both built from smaller molecules called nucleotides.
How do genes make proteins?
Genes provide information for building proteins. They don’t however directly create proteins. The production of proteins is completed through two processes: transcription and translation. Transcription and translation take the information in DNA and use it to produce proteins. Transcription uses a strand of DNA as a template to build ...
What are proteins made of?
Proteins are made from a sequence of amino acids rather than nucleotides. Transcription and translation are the two processes that convert a sequence of nucleotides from DNA into a sequence of amino acids to build the desired protein. These two processes are essential for life. They are found in all organisms – eukaryotic and prokaryotic.
How many nitrogenous bases are there in DNA?
There is a total of four different nitrogenous bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). A strand of DNA is almost always found bonded to another strand of DNA in a double helix. Two strands of DNA are bonded together by their nitrogenous bases.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
There are a couple of key differences between the structure of DNA and RNA molecules. They contain different sugars. DNA has a deoxyribose sugar while RNA has a ribose sugar. While three of their four nitrogenous bases are the same, RNA molecules the have a base called uracil (U) instead of a thymine base.