What is transduction in psychology?
What is Transduction in Psychology? The transformation of something from one form, place, or notion to another is known as transduction. Transduction psychology definitionis a term used to describe reasoning from specific situations to generic cases.
How does the signal transduction pathway of touch and vision work?
The signal transduction pathway of touch and vision works in the same way that many nerve signals do. Instead of creating a second messenger or processing a signal internally, the stimulation of the receptor protein causes an influx of ions into the cell. This causes the cell membrane to depolarize.
What is signal transduction?
Signal transduction is the process of transferring a signal throughout an organism, especially across or through a cell. Signal transduction relies on proteins known as receptors, which wait for a chemical, physical, or electrical signal.
What is the signal transduction pathway in the liver?
One pathway stimulates a cellular process in the muscle cells which increases the number of glucose transporters in their cell membrane. The other signal transduction pathway in the liver turns off a key enzyme which is required to produce glucose. 1. Which of the following is NOT an example of signal transduction?

Where does transduction occur for vision?
the retinaLight is tranduced in rods and cones; visual information is processed in the retina before entering the brain.
How does transduction occur in the photoreceptors of the eye?
In a photoreceptor cell, the light-absorbing pigment signals through an intracellular biochemical pathway to transduce light into electrical activity across the cell membrane. Interestingly, in ipRGCs this phototransduction cascade is more similar to those in invertebrate photoreceptors than to those in rods and cones.
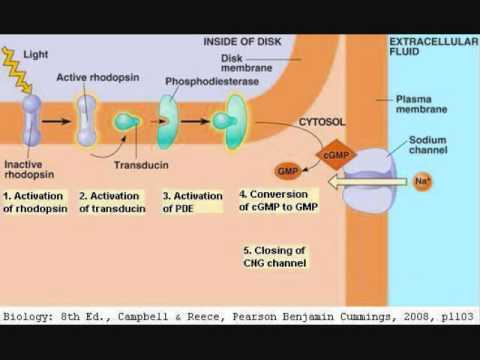
What are the steps for transduction for vision?
This feature is available to authenticated users only.Phototransduction. ... The G-protein Cascade of Phototransduction. ... Step 1: Activation of Rhodopsin. ... Step 2: Activation of the G-protein. ... Step 3: Activation of the PDE. ... Step 4: Hydrolysis of Cyclic GMP. ... Step 5: Closure of Ion Channels. ... Predicted Kinetics and Amplification.More items...
What part of the eye is responsible for transduction of light?
The retinaThe retina is composed of specialized cells, the rods and cones, which convert light energy into neural activity. This conversion is made possible by light-sensitive pigments located on the discs in the outer segments of the rods and cones.
What is the first step in visual transduction?
The first stage in transducing light into a form the brain can comprehend is the 'capturing' of light energy into a chemical format. This is achieved by the presence of various light 'pigment' molecules within the outer segments of these receptors.
What is the first step in the visual transduction process of the retina?
Photo-transduction occurs in a three-stage process. First, a pigment, rhodopsin, absorbs a photon and is isomerized. Second, the isomerization triggers a biochemical cascade. Finally, the sodium currents are altered, modulating the ionic current within the receptor.
What is the blind spot in the eye and how does it impact the transduction of light energy?
The eye's retina receives and reacts to incoming light and sends signals to the brain, allowing you to see. One part of the retina, however, doesn't give you visual information—this is your eye's “blind spot.”
Where does transduction occur in touch?
13:5115:15Sensory Transduction: How Our Senses Work - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThere are two different signal transduction pathways activation of ionotropic receptors leads toMoreThere are two different signal transduction pathways activation of ionotropic receptors leads to cation channel opening and increases ion levels in the cell. Causing.
How does light transduction result in a nerve impulse?
The light is mapped as an image along the surface of the retina by activating a series of light-sensitive cells known as rods and cones. These photoreceptor cells convert the light into electrical impulses which are transmitted to the brain via nerve fibers.
Which layer of the eye converts light to nerve impulses?
The optic nerve sends visual information from the retina to the brain. The retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. The retina instantly converts light, or an image, into electrical impulses. The retina then sends these impulses, or nerve signals, to the brain.
What is the function of phototransduction?
In most sensorysystems, activationof a receptorby the appropriate stimulus causes the cell membrane to depolarize, ultimately stimulating an action potentialand transmitterrelease onto the neurons it contacts. In the retina, however, photoreceptors do not exhibit action potentials; rather, light activation causes ...
What is phototransduction in neuroscience?
Phototransduction - Neuroscience - NC BI Bookshelf. In most sensory systems, activation of a receptor by the appropriate stimulus causes the cell membrane to depolarize, ultimately stimulating an action potential and transmitter release onto the neurons it contacts. In the retina, however, photoreceptors do not exhibit action potentials; rather, ...
What is the protein that absorbs light?
The photopigment contains a light-absorbing chromophore (retinal, an aldehyde of vitamin A) coupled to one of several possible proteins called opsinsthat tune the molecule's absorption of light to a particular region of the spectrum.
What is the potential of a receptor in the dark?
In the dark, the receptoris in a depolarized state, with a membrane potential of roughly -40 mV (including those portions of the cell that release transmitters). Progressive increases in the intensity of illumination cause the potential across the receptor membrane to become more negative, a response that saturates when ...
What is signal transduction?
Signal Transduction Definition. Signal transduction is the process of transferring a signal throughout an organism, especially across or through a cell. Signal transduction relies on proteins known as receptors, which wait for a chemical, physical, or electrical signal. Chemical signals are called ligands, and can be produced by organisms ...
What happens to the signal during transduction?
Then, the receptor protein embedded in the cellular membrane must accept the signal. Upon receiving the signal, this protein goes through a conformational change. This changes its shape and thus, how it interacts with the molecules around it.
How does touch and vision work?
Touch and Vision. The signal transduction pathway of touch and vision works in the same way that many nerve signals do. Instead of creating a second messenger or processing a signal internally, the stimulation of the receptor protein causes an influx of ions into the cell. This causes the cell membrane to depolarize.
How does a signal get received?
A signal is received by a receptor protein, and the protein transfers the signal through the cell membrane and into the cell. The kinds of receptors and the second messengers they create can be very different. This is based on the action which the signal must stimulate.
Which pathway in the liver turns off a key enzyme required to produce glucose?
The other signal transduction pathway in the liver turns off a key enzyme which is required to produce glucose.
What is the process of chemical signaling?
Regardless of which type of signal, it must be transferred throughout the body and across cell membranes. This process is known as signal transduction. A generalized image of signal transduction can be seen below.
When only one receptor protein is stimulated, only a small section of the membrane depolarizes?
But when you receive a strong signal, such as pressing your finger against a surface or seeing a bright light, the entire membrane of many cells is depolarized at the same time.
Signal Transduction Definition
Signal Transduction Pathway
- During signal transduction, a signal may have many components. There is the primary messenger, which may be a chemical signal, electrical pulse, or even physical stimulation. Then, the receptor protein embedded in the cellular membrane must accept the signal. Upon receiving the signal, this protein goes through a conformational change. This changes its shape and thus, how it interact…
Examples of Signal Transduction
- Touch and Vision
The signal transduction pathway of touch and vision works in the same way that many nerve signals do. Instead of creating a second messenger or processing a signal internally, the stimulation of the receptor protein causes an influx of ions into the cell. This causes the cell me… - Hormones
Unlike touch and vision, hormones are signals that your body creates to regulate itself. Hormones can cause the body to do many different things, and they themselves are often triggered by a separate signal transduction pathway. Typically, a hormone is release from an endocrine gland, …
Quiz
- 1. Which of the following is NOT an example of signal transduction? A. A molecule found in blood binds to a protein in a shark’s olfactory cells. A signal is sent to the brain. B. Cow’s milk contains growth hormones. Upon receiving these hormones, a baby cow’s cells grow and divide. C.A cell uses the energy for a molecule of glucose to drive other reactions. 2. Why is it necessary that dif…