Full Answer
What initiates the start of translation?
• One codon (AUG) is known as a start codon and initiates the process of translation. It also encodes the amino acid methionine. Key Terms. Codon: A sequence of three adjacent nucleotides that encode a specific amino acid or stop signal during protein synthesis (translation).
What are the steps of initiation of translation?
What are the three major steps of transcription?
- Initiation. Initiation is the beginning of transcription. ...
- Elongation. Elongation is the addition of nucleotides to the mRNA strand. ...
- Termination.
Which step happens first in translation?
What are the 7 steps of translation?
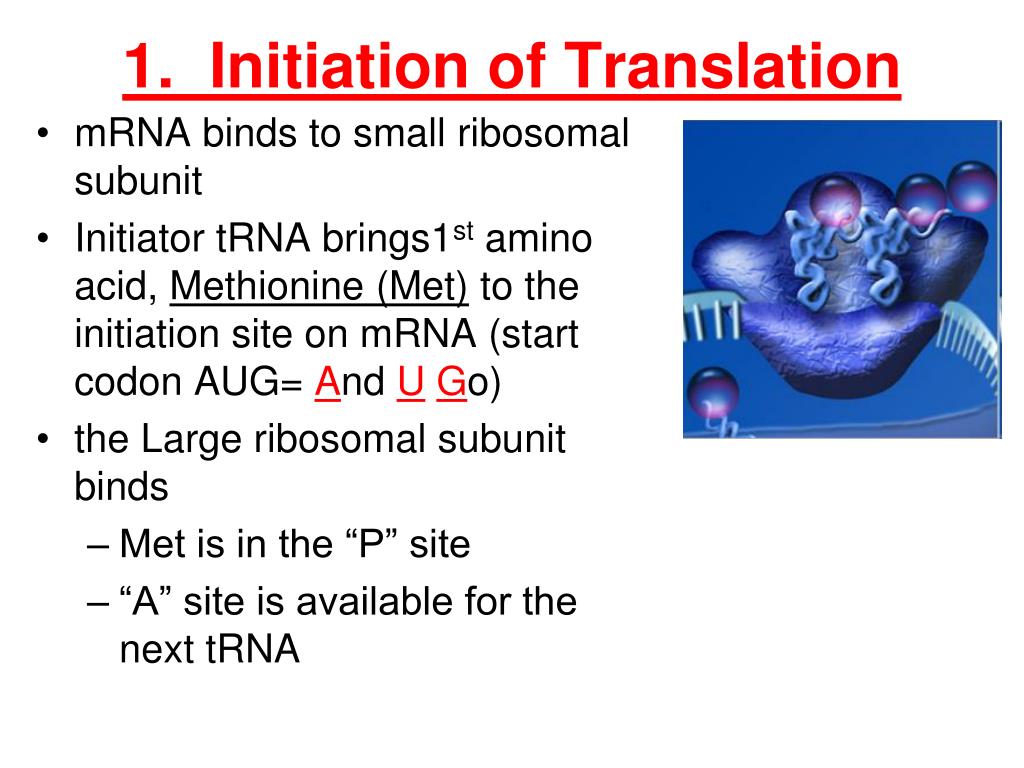
- mRNA binds to the small subunit of the ribosome.
- tRNA with anticodon complementary to the first codon to be translated on the mRNA binds to the ribosome.
- a second tRNA with an anticodon complementary to the second codon on the mRNA then binds.
What are the five steps of translation?
What are the 5 steps in translation?
- Initiation. In this step the small subunit part of the ribosome attaches to the 5′ end of the mRNA strand.
- Elongation.
- Termination.

What is the initiation in translation?
Initiation ("beginning"): in this stage, the ribosome gets together with the mRNA and the first tRNA so translation can begin. Elongation ("middle"): in this stage, amino acids are brought to the ribosome by tRNAs and linked together to form a chain.
What is translation initiation in biology?
Translation initiation, the first stage in protein synthesis, is the process of assembly of large (60S) and small (40S) ribosomal subunits to form an 80S ribosome containing initiator transfer RNA (tRNA) (Met-tRNAiMet) that is base paired to the initiation codon of a messenger RNA in the ribosomal peptidyl (P) site.
What happens in initiation during translation?
Initiation of translation occurs when mRNA, tRNA, and an amino acid meet up inside the ribosome. Once translation has begun, it continues down the line as mRNA shifts along through the ribosome. Each new codon matches with a new tRNA anticodon, bringing in a new amino acid to lengthen the chain.
What is required for translation initiation?
The key components required for translation are mRNA, ribosomes, and transfer RNA (tRNA). During translation, mRNA nucleotide bases are read as codons of three bases. Each codon codes for a particular amino acid.
What is transcription initiation?
Transcription initiation involves the interaction of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase with promoters. In bacteria, this is a highly regulated process. Many regulators interact directly with the bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, whereas other regulators interact directly with promoters.
What happens in initiation of transcription?
Transcription initiation is the phase during which the first nucleotides in the RNA chain are synthesized. It is a multistep process that starts when the RNAP holoenzyme binds to the DNA template and ends when the core polymerase escapes from the promoter after the synthesis of approximately the first nine nucleotides.
What is the first step when initiating translation?
Translation is generally divided into three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination (Figure 7.8). In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes the first step of the initiation stage is the binding of a specific initiator methionyl tRNA and the mRNA to the small ribosomal subunit.
What is the first step during the initiation of translation?
What is the first step during the initiation of translation? -once mRNA is bound to the small subunit, an initiator aminoacetyl tRNA binds to the start codon on the mRNA, then the large subunit binds to the small subunit to complete the initiation complex!
What process is important for the initiation of translation quizlet?
What process is important for the initiation of translation? A ribozyme is a catalytic protein that assists in the processing of tRNA.
How is translation initiation regulated?
Initiation of translation is regulated by the accessibility of ribosomes to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence. This stretch of four to nine purine residues are located upstream the initiation codon and hybridize to a pyrimidine-rich sequence near the 3' end of the 16S RNA within the 30S bacterial ribosomal subunit.
What is the initiation factors during transcription?
Transcription initiation factors (TFII) are proteins which enable RNA polymerase II to bind to the DNA template in order to start the transcription process. TFIIA is one of several TFs which are required for transcription.
Where does transcription initiation occur?
the promoterInitiation is the beginning of transcription. It occurs when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a region of a gene called the promoter.
What is the process of translation?
Translation, the process of mRNA-encoded protein synthesis, requires a complex apparatus, composed of the ribosome, tRNAs and additional protein factors, including aminoacyl tRNA synthetases. The ribosome provides the platform for proper assembly of mRNA, tRNAs and protein factors and carries the peptidyl-transferase activity.
What is the process of mRNA synthesis?
Translation, the process of mRNA-encoded protein synthesis, requires a complex apparatus, composed of the ribosome, tRNAs and additional protein factors, including aminoacyl tRNA synthetases. The ribosome provides the platform for proper assembly of mRNA, tRNAs and protein factors and carries the pe …. Translation, the process of mRNA-encoded ...
What are the stages of translation?
Translation: Beginning, middle, and end 1 Initiation ("beginning"): in this stage, the ribosome gets together with the mRNA and the first tRNA so translation can begin. 2 Elongation ("middle"): in this stage, amino acids are brought to the ribosome by tRNAs and linked together to form a chain. 3 Termination ("end"): in the last stage, the finished polypeptide is released to go and do its job in the cell.
What is the initiation complex of tRNA?
Together, they form the initiation complex, the molecular setup needed to start making a new protein.
What is the G/A sequence of bacterial translation?
Bacterial translation initiation: On a bacterial mRNA, a G/A-rich sequence called the Shine-Dalgarno sequence is found slightly upstream (5' of) the start codon (AUG). The small ribosomal subunit recognizes and binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence.
How are codons read in translation?
In translation, the codons of an mRNA are read in order (from the 5' end to the 3' end) by molecules called transfer RNAs, or tRNAs. Each tRNA has an anticodon, a set of three nucleotides that binds to a matching mRNA codon through base pairing. The other end of the tRNA carries the amino acid that's specified by the codon.
What is the initiation phase of translation?
The initiation phase of translation is an important control point for protein synthesis. In eukaryotes, initiation can be inhibited at two different steps - firstly, it can inhibit binding of 40S subunit to the 5’cap, and secondly, it can inhibit binding of 40S subunit to specific tRNA. Many growth factors, hormones, and other factors increase the translational activity of the cell. Again, in mRNA without 5-’cap, initiation is regulated by ferritin (an iron-binding protein).
What are the phases of translation?
Translation occurs in three phases - Initiation, Elongation, and Termination.
Components of Translation
The key components required for translation are mRNA, ribosomes, and transfer RNA (tRNA).
Initiation
For translation to begin, the start codon (5’AUG) must be recognised. This codon is specific to the amino acid methionine, which is nearly always the first amino acid in a polypeptide chain. At the 5’ cap of mRNA, the small 40s subunit of the ribosome binds. Subsequently, the larger 60s subunit binds to complete the initiation complex.
Elongation
The ribosome has two tRNA binding sites; the P site which holds the p eptide chain and the A site which a ccepts the tRNA.
Termination
One of the three stop codons enters the A site. No tRNA molecules bind to these codons, so the peptide and tRNA in the P site become hydrolysed releasing the polypeptide into the cytoplasm. The small and large subunits of the ribosome dissociate, ready for the next round of translation.