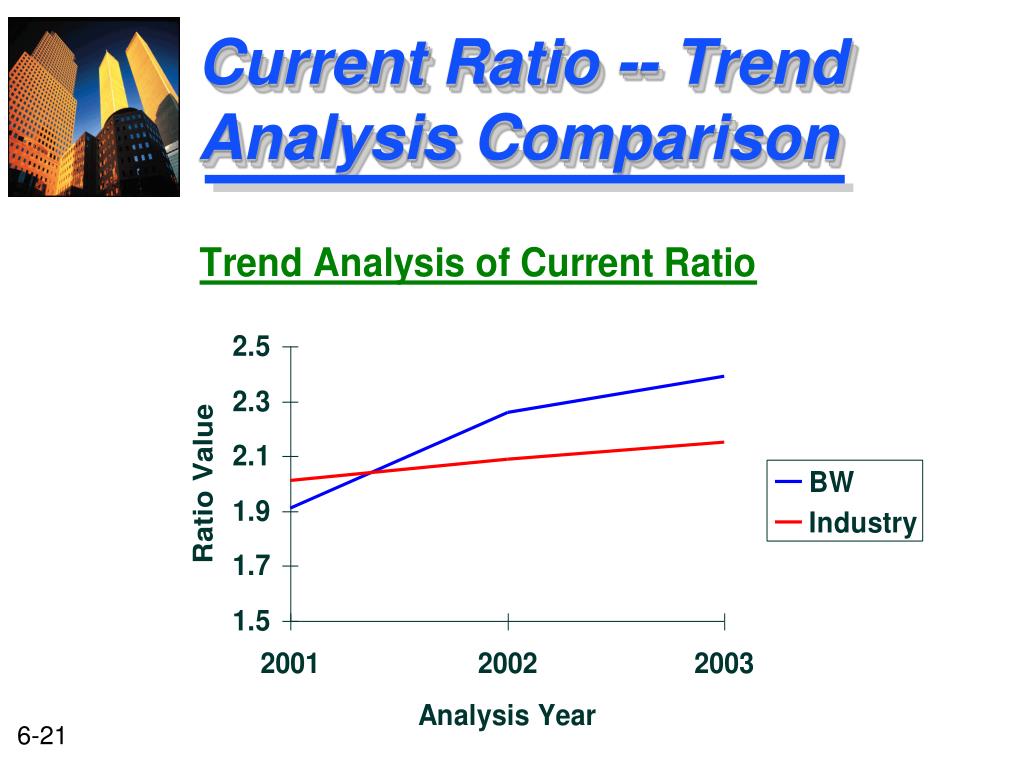
Trends Ratio Analysis
- The ability to appraise performance year over year
- The ability to make timely adjustments and informed management decisions
- Favorable financing options with demonstrated improved performance
- Accurate historical data for the purposes of forecasting
- Historical data that enables best planning practices
What is an example of ratio analysis?
Types of Ratio Analysis
- Liquidity Ratios. This type of ratio helps in measuring the ability of a company to take care of its short-term debt obligations.
- Profitability Ratios. This type of ratio helps in measuring the ability of a company in earning sufficient profits. ...
- Solvency Ratios. ...
- Turnover Ratios. ...
- Earnings Ratios. ...
What are trend analysis methods?
- Timeframe and patterns. Pattern timeframes can play an important role in how a particular pattern is interpreted. ...
- Indicators and studies. ...
- Indicator types. ...
- Indicator characteristics. ...
- Summary. ...
What is the significance of ratio analysis?
Importance and Uses of Ratio Analysis. Ratio Analysis is important for the company in order to analyze its financial position, liquidity, profitability, risk, solvency, efficiency, and operations effectiveness and proper utilization of funds which also indicates the trend or comparison of financial results that can be helpful for decision making for investment by shareholders of the company.
What is a ratio analysis formula?
#9 – Inventory Turnover Ratio analysis
- Formula. Inventory Turnover Formula = Cost of Goods Sold / Inventory. ...
- Analyst Interpretation. You may note that when we calculate receivables turnover, we took Sales (Credit Sales); however, in inventory turnover ratio, we took Cost of Goods Sold.
- Colgate Case Study. Let us calculate the Inventory Turnover Ratio of Colgate. ...
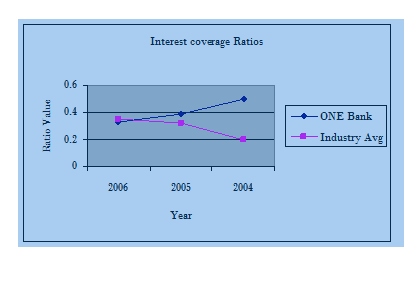
What is meant by trend analysis?
Trend analysis is a technique used in technical analysis that attempts to predict future stock price movements based on recently observed trend data. Trend analysis uses historical data, such as price movements and trade volume, to forecast the long-term direction of market sentiment.
What is trend analysis formula?
The formula for trend analysis (percentage change) can be derived by dividing the difference between the current year amount and the base year amount by the base year amount. Mathematically, it is represented as, Formula – Percentage Change = [(Current Year Amount – Base Year Amount) / Base Year Amount]
Is trend analysis the same as ratio analysis?
Trend analysis often tracks the changes occurring in each line of a financial statement. Sometimes, it may look for percentage changes as well. Ratios, on the other hand, are related to different items put together to judge a relationship among the items.
How do you do trend analysis of financial ratios?
0:303:03Preparing a Trend Analysis of Financial Data - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe index number should be expressed as a percent rounded to the nearest tenth. Where index numberMoreThe index number should be expressed as a percent rounded to the nearest tenth. Where index number the rate equals. The yearly amount portion.
What are the 3 types of trend analysis?
There are three types of trend analysis methods – geographic, temporal and intuitive.
What are the trend ratios?
The comparison of the successive values of each ratio for a single firm over a number of years.
What is an example of trend analysis?
Examples of Trend Analysis Examining sales patterns to see if sales are declining because of specific customers or products or sales regions; Examining expenses report claims for proof of fraudulent claims. Examining expense line items to find out if there are any unusual expenditures in a reporting period.
What are the types of ratio analysis?
A few basic types of ratios used in ratio analysis are profitability ratios, debt or leverage ratios, activity ratios or efficiency ratios, liquidity ratios, solvency ratios, earnings ratios, turnover ratios, and market ratios.
What are the 5 types of ratios?
5 Different Types of Ratios in DetailsProfitability Ratios:Liquidity Ratios:Efficiency Ratios:Debt Ratios:Investor Ratios:A. ... B.More items...•
What are the 4 types of ratios?
Typically, financial ratios are organized into four categories:Profitability ratios.Liquidity ratios.Solvency ratios.Valuation ratios or multiples.
How do you analyze a trend analysis?
Step 1: Determine whether the model fits your data. Examine the trend analysis plot to determine whether your model fits your data. ... Step 2: Compare the fit of your model to other models. ... Step 3: Determine whether the forecasts are accurate.
What are the steps of performing trend analysis?
1 – Choose Which Pattern You Want to Identify. The first and most obvious step in trend analysis is to identify which data trend you want to target. ... 2 – Choose Time Period. ... 3 – Choose Types of Data Needed. ... 4 – Gather Data. ... 5 – Use Charting Tools to Visualize Data.6 – Identify Trends.
What is trend formula in Excel?
The TREND function returns values along a linear trend. It fits a straight line (using the method of least squares) to the array's known_y's and known_x's. TREND returns the y-values along that line for the array of new_x's that you specify.
How is trend analysis done?
Trend analysis involves collecting the information from multiple periods and plotting the collected information on a horizontal line to find actionable patterns from the given information. In Finance, Trend Analysis is used for Technical analysis and Accounting analysis of stocks.
How do you calculate a trend line?
To calculate the trend line for the graph of a linear relationship, find the slope-intercept form of the line, y = mx + b, where x is the independent variable, y is the dependent variable, m is the slope of the line, and b is the y-intercept.
How does excel calculate trend analysis?
Add a trendlineSelect a chart.Select the + to the top right of the chart.Select Trendline. Note: Excel displays the Trendline option only if you select a chart that has more than one data series without selecting a data series.In the Add Trendline dialog box, select any data series options you want, and click OK.
Why do companies use ratios?
Ratios also help companies compare themselves to businesses with different operations. For example, a small business is simply unable to have the sales or other operating capabilities of a much larger organization. Ratios, however, strip away these differences and provide indicators that show how well the small business operates compared to the large competitor. The small business can also turn this into a trend and ratio analysis report. This provides information on how the small business can improve itself to be like a much larger operation.
When to use ratios?
Trend and ratio analysis typically occur at month end, year-end, or at any point when a business decides a review is necessary to assess financial information.
What is financial analysis?
Financial analysis often looks at previous information and compares it to current data. This process — called trend analysis — helps a company understand what it does well and what it does not.
Do accountants use ratios?
Ratios take a bit more time to compute. Many financial statements used in trend analysis do not have automatic ratios computed by accounting software. Accountants, therefore, need to use a series of mathematical formulas to create the indicators or percentages indicative from ratios. The ratios can, however, draw a connection between trend and ratio analysis. For example, an accountant can keep a record for each ratio computed for a period of time; this then creates a trend for financial comparison.
What Does Ratio Analysis Tell You?
Investors and analysts employ ratio analysis to evaluate the financial health of companies by scrutinizing past and current financial statements. Comparative data can demonstrate how a company is performing over time and can be used to estimate likely future performance. This data can also compare a company's financial standing with industry averages while measuring how a company stacks up against others within the same sector.
What are the most commonly used ratios in fundamental analysis?
These are the most commonly used ratios in fundamental analysis. They include dividend yield, P/E ratio, earnings per share (EPS), and dividend payout ratio. Investors use these metrics to predict earnings and future performance.
What is solvency ratio?
Also called financial leverage ratios, solvency ratios compare a company's debt levels with its assets, equity, and earnings, to evaluate the likelihood of a company staying afloat over the long haul, by paying off its long-term debt as well as the interest on its debt.
What is the purpose of liquidity ratio?
1. Liquidity Ratios. Liquidity ratios measure a company's ability to pay off its short-term debts as they become due, using the company's current or quick assets. Liquidity ratios include the current ratio, quick ratio, and working capital ratio. 2.
What are some examples of profitability ratios?
These ratios convey how well a company can generate profits from its operations. Profit margin, return on assets, return on equity, return on capital employed, and gross margin ratios are all examples of profitability ratios .
What is ratio in business?
Ratios are comparison points for companies. They evaluate stocks within an industry. Likewise, they measure a company today against its historical numbers. In most cases, it is also important to understand the variables driving ratios as management has the flexibility to, at times, alter its strategy to make its stock and company ratios more attractive. Generally, ratios are typically not used in isolation but rather in combination with other ratios. Having a good idea of the ratios in each of the four previously mentioned categories will give you a comprehensive view of the company from different angles and help you spot potential red flags.
Why is it important to understand the variables driving ratios?
In most cases, it is also important to understand the variables driving ratios as management has the flexibility to, at times, alter its strategy to make its stock and company ratios more attractive. Generally, ratios are typically not used in isolation but rather in combination with other ratios.
What is trend analysis?
Trend analysis is an analysis of the trend of the company by comparing its financial statements to analyze the trend of market or analysis of the future on the basis of results of past performance and it’s an attempt to make the best decisions on the basis of results of the analysis done.
What is trend analysis in accounting?
The trend analysis in accounting can be used by management or the analyst to forecast future financial statements. Following blindly can turn out to be dangerous if a proper analysis of the past event is not done.
What is the Importance of Trend Analysis?
It is most helpful for the traders because moving with trends, and not going against them, will make a profit to an investor. The trend is the best friend of the traders is a well-known quote in the market.
What is sideways trend?
A sideways/horizontal trend means assets prices or share prices – as with the broader economy level – are not moving in any direction; they are moving sideways, up for some time, then down for some time. The direction of the trend cannot be decided. It is the trend where investors are worried about their investment, and the government is trying to push the economy in the uptrend. Generally, the sideways or horizontal trend is considered risky because when sentiments will be turned against cannot be predicted; hence investors try to keep away in such a situation.
Why is the sideways trend considered risky?
Generally, the sideways or horizontal trend is considered risky because when sentiments will be turned against cannot be predicted; hence investors try to keep away in such a situation.
What is an uptrend in the stock market?
An uptrend or bull market is when financial markets and assets – as with the broader economy level – move in the upward directions and keep increasing prices of the stock or the assets or even the size of the economy over the period. It is a time of booming where jobs get created, the economy moves into a positive market, and sentiments in the markets are favorable, and the investment cycle has started.
Why is trend the best friend of the traders?
It is most helpful for the traders because moving with trends, and not going against them, will make a profit to an investor. The trend is the best friend of the traders is a well-known quote in the market. A trend is nothing but the general direction the market is heading during a specific period.
Trend Analysis Explained
Cameron Williams has nearly a decade of experience working in the financial industry. A former investment advisor, Cameron now writes about investing, banking, insurance, and general personal finance. He studied economics at Utah State University and holds FINRA securities licenses including Series 6, Series 63, and Series 65.
Definition and Example of Trend Analysis
Trend analysis is the analysis of trends in price movements of a security— it’s an essential piece of technical analysis. Trends are made up of peaks and troughs of a stock chart that you can analyze and determine market trends accordingly.
How Does Trend Analysis Work?
When investors and traders analyze trends of the price of a security, they generally do so following short-term, intermediate, and long-term time frames. For individual investors, a good rule of thumb for trend timeframes is:
Types of Trend Analysis
There are many different price and chart indicators used to determine the trend of a stock price. Some of the most common types of indicators used include:
What It Means for Individual Investors
While most technical analysis strategies, like trend analysis, are used by short-term day traders and swing traders, long-term investors can use trend analysis to maximize their profit on entry and exit transactions.
What is trend analysis?
Trend analysis is a technique used in technical analysis that attempts to predict future stock price movements based on recently observed trend data.
Why is trend analysis important?
Trend analysis is helpful because moving with trends, and not against them, will lead to profit for an investor. It is based on the idea that what has happened in the past gives traders an idea of what will happen in the future. There are three main types of trends: short-, intermediate- and long-term.
What Is a Trend?
A trend is the overall direction of a market during a specified period of time. Trends can be both upward and downward, relating to bullish and bearish markets, respectively. While there is no specified minimum amount of time required for a direction to be considered a trend, the longer the direction is maintained, the more notable the trend. Trends are identified by drawing lines, known as trendlines, that connect price action making higher highs and higher lows for an uptrend, or lower lows and lower highs for a downtrend.
What Are Examples of Trend Trading Strategies?
Typically, these include moving averages, momentum indicators, and trendlines, and chart patterns.
What Are Some Criticisms of Trend Analysis?
Critics of trend analysis, and technical trading in general, argue that markets are efficient, and already price in all available information. That means that history does not necessarily need to repeat itself and that the past does not predict the future. Adherents of fundamental analysis, for example, analyze the financial condition of companies using financial statements and economic models to predict future prices. For these types of investors, day-to-day stock movements follow a random walk that cannot be interpreted as patterns or trends.
What are the three types of trends?
There are three main types of trends: short-, intermediate- and long-term. A trend is the general direction the market is taking during a specified period of time. Trends can be both upward and downward, relating to bullish and bearish markets, respectively.
What is trend following?
Trend following is a trading system based on using trend analysis and following the recommendation produced to determine which investments to make.
