
Tropism in Plants: Different Types and Examples
- Tropic Movements. When a plant unveils some growth movement in response to a stimulus, which is known as tropism.
- Types of Tropism. Tropic movements are crucial for plant survival and all the metabolic activities are dependant on...
- Things to Remember. Directional response to environmental stimulus in organisms causes their...
What are the different types of tropism?
What Are The 5 Tropisms And The Plant's Response To Each?
- Phototropism. This plant tropism controls the growth of the plant in response to a light source. ...
- Thigmotropism. Tendrils help the plant to climb a support. ...
- Gravitropism. Positive and negative geotropism. ...
- Hydrotropism. Plants need to control their geotropic tendencies first before they can perform hydrotropism. ...
- Thermotropism. ...
What is tropism and its types?
What is Tropism?
- Tropism in Viruses. Viruses and other pathogens may also cause what is known as "host tropism," "tissue tropism," or "cell tropism," which refers to how various viruses/pathogens have evolved to ...
- Different Types of Tropism
- Phototropism. ...
- Gravitropism. ...
- Chemotropism. ...
- Thigmotropism. ...
- Hydrotropism. ...
- Thermotropism. ...
- Magnetotropism. ...
What is tropism explain its types?
tropism, response or orientation of a plant or certain lower animals to a stimulus that acts with greater intensity from one direction than another. It may be achieved by active movement or by structural alteration. Forms of tropism include phototropism (response to light), geotropism (response to gravity), chemotropism (response to particular substances), hydrotropism (response to water ...
What does tropism usually involve?
the turning of an organism in response to a stimulus, either towards or away from the stimulus A tropism is a biological phenomenon, indicating growth or turning movement of a biological organism, usually a plant, in response to an environmental stimulus. In tropisms, this response is dependent on the direction of the stimulus.

What is tropism explain with example?
(a) The growth movement of plant parts in which the direction of the stimulus determines the direction of the response is known as tropisms. Example: Phototropism, where the stems of plants grow upwards in response to sunlight.
What is tropism short answer?
Definition of tropism (Entry 1 of 2) 1a : involuntary orientation by an organism or one of its parts that involves turning or curving by movement or by differential growth and is a positive or negative response to a source of stimulation. b : a reflex reaction involving a tropism.
What is tropism give an example of a type of tropism?
(a) Tropism is the directional movement where the plant parts move in a particular direction with the response to the stimulus. Example- Geotropism: Growth of roots towards gravity. Phototropism: Growth of stems towards the sunlight.
What are the different 4 types of tropism?
Gravitropism. It is a type of tropism where plants show some growth in response to gravity. ... Chemotropism. There are few chemical substances, which are actively responsible for bringing a curvature movement in plant organs. ... Thigmotropism. ... Hydrotropism. ... Thermotropism.
What causes tropism in plants?
Environmental factors, including light, chemical nutrients, water, and gravity are stimuli that can provoke tropisms in a plant. The plant grows in the direction of the stimulus as hormones inside the stem, root, and leaf systems in a plant aid in the elongation and growth process of the plant toward the stimuli.
What is a tropism kid definition?
From Academic Kids In biology, a tropism is a growth or turning movement of an organism in response to an environmental stimulus.
What is tropism in plants simple?
A tropism is a growth toward or away from a stimulus. Common stimuli that influence plant growth include light, gravity, water, and touch. Plant tropisms differ from other stimulus generated movements, such as nastic movements, in that the direction of the response depends on the direction of the stimulus.
What is meant by tropism Class 10?
Definition: 1 Mark. Types point: 2 Marks. 1. A growth movement of a plant in response to an external stimulus in which the direction of stimulus determines the direction of response is called tropism.
What is tropism virus?
Viral tropism is the ability of a given virus to productively infect a particular cell (cellular tropism), tissue (tissue tropism) or host species (host tropism).
How do you use tropism in a sentence?
How to use Tropism in a sentenceThe virus also has gastrointestinal tropism in various bird species. ... Chapters on HIV-1 replication and the factors that determine cell tropism are included. ... The virus first binds to its host cell via specific sialic acid residues, which can control the species tropism of the virus.More items...
1. What is Tropism?
Tropism is the natural ability of an organism to transform or change in response to a stimulus. Natural responses are genetically programmed rather...
2. What are the Types of Tropism?
There are different types of tropism, they are:Phototropism is nothing but the growth and development of plants in response to light.Gravitropism i...
3. What is Gravitropism?
In response to gravity, certain plants show some growth and development, this type of tropism in plants with respect to gravity is called Gravitrop...
4. Explain Hydrotropism and Thermotropism.
Hydrotropism: In relation to the stimulus of water, the movement or the growth of a plant is called hydrotropic movement. This is also called hydro...
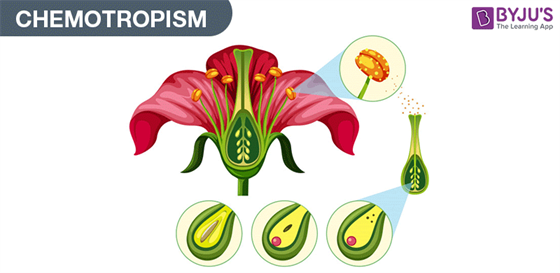
5. Explain Chemotropism and Thigmotropism?
Chemotropism: The chemical substances in a plant are responsible for bringing a curvature movement in plant organs. When plants start to grow in re...
6. What is Meant by Tropism? Define Tropism.
Tropism is a biological process in which a biological organism, normally a plant, grows or turns in response to an environmental stimulus. This res...
7. Name any Two Types of Tropism.
Phototropism (response to light), geotropism (response to gravity), chemotropism (response to specific substances), hydrotropism (response to water...
What is tropism in biology?
Define Tropism. Ans. Tropism is a biological process in which a biological organism, normally a plant, grows or turns in response to an environmental stimulus. This response is influenced by the stimulus's direction in tropisms (as opposed to nastic movements which are non-directional responses).
What is tropism in animals?
Chemotropism: Chemotropism, or the inclination to transform or shift towards or away from a particular chemical element, is a common tropism in the animal kingdom. Chemo Tropisms are used by certain single-celled species for a variety of purposes. For example, one chemical may indicate the presence of a partner, while another may indicate the presence of a dangerous or unpleasant environment. These simple organisms would simply shift towards or away from stimuli in the direction that their forefathers found to be most evolutionary rewarding. Certain chemicals also attract animals in higher species, but they may not always travel towards it. To put it another way, although they have tropism, they do not always show taxis. Sharks, for example, have a positive chemotropism for blood, which means they gravitate toward it. A shark, on the other hand, would often examine or test a meal before devouring it, demonstrating that other processes can override a tropism.
What is the term for a virus that preferentially targets a particular host?
Tropism meaning in viruses- Viruses and other pathogens may also cause what is known as "host tropism," "tissue tropism," or "cell tropism," which refers to how various viruses/pathogens have evolved to preferentially target particular host organisms, tissues, or cell types inside those species. Tropisms are named for the stimulus they are reacting to (for example, a phototropism is a reaction to sunlight) and may be positive (towards the stimulus) or negative (against the stimulus) (away from the stimulus).
What is the term for the movement of an animal after a stimulus?
Innate responses, unlike acquired abilities, are genetically programmed. Tropism causes organisms to spontaneously gravitate toward a stimulus. Individual tropisms are also called after the stimulus that triggers the movement, which can be any signal from the setting. The animal would shift toward stimulation in an optimistic tropism.
What is the movement or development of an organism in response to a chemical stimulus?
Chemotropism is the movement or development of an organism in response to a chemical stimulus.
What is the term for how viruses have evolved to preferentially target particular host organisms, tissues, or cell types?
Viruses and other pathogens may also cause what is known as "host tropism, " "tissue tropism," or "cell tropism," which refers to how various viruses/pathogens have evolved to preferentially target particular host organisms, tissues, or cell types inside those species. Q2. Name any Two Types of Tropism.
When roots come into contact with a hard surface, such as rock, they sometimes transform?
Thigmotropism: When roots come into contact with a hard surface, such as rock, they sometimes transform. This tropism is triggered by the stimulus of touch
What are the different types of tropisms?
The various forms of tropism include a response to light, gravity, substances, water, mechanical stimulation, wound lesion, and electric current. The various types of tropisms are normally named for the stimulus involved. For instance, chemotropism is a reaction to chemical substances and phototropism is a reaction to sunlight.
What is a positive tropism?
Positive tropism is a movement or growth of an organism, typically a plant, towards a stimulus.
What is the difference between chemotropism and chemotaxis?
Positive chemotropism is characterized by growing towards a chemical stimulus whereas negative chemotropism is growing away from the chemical stimulus. Chemotropism is quite different from Chemotaxis being that chemotaxis is related to locomotion (movement) whereas chemotropism is related to growth.
What is the term for a type of tropism that involves movement or growth in response to gravity?
Geotropism is a type of tropism that involves movement or growth in response to gravity. This occurs typically in plants and fungi. According to Charles Darwin, roots show positive geotropism whereas stems show negative geotropism. Apogeotropismis negative geotropism.
What is the difference between nastic movement and tropism?
In nastic movement, the organism responds to a stimulus but not in the direction of the stimulus. Nastic movements are non-directional responses to stimulus whereas in tropisms the response to the stimulus is solely dependent on the direction of the stimulus.
How does tropism work?
The organism responds either by movement (curving or turning) or by differential growth to the stimulus that acts with greater intensity from one direction than another. In tropisms, the organism’s response is dependent on the direction of the stimulus. Nevertheless, tropism could be a positive or negative response and may be achieved by structural alteration or by active movement. An organism will move towards the stimulus in a positive reaction whereas an organism will move away from the stimulus in a negative reaction.
What is the term for an involuntary response of an organism or one of its parts to a source of?
Tropism is an involuntary response of an organism or one of its parts to a source of environmental stimulation. Types include phototropism, tissue tropism
What is tropism in biology?
(Entry 1 of 2) 1 a : involuntary orientation by an organism or one of its parts that involves turning or curving by movement or by differential growth and is a positive or negative response to a source of stimulation. b : a reflex reaction involving a tropism.
What is tropism in medical terms?
Medical Definition of tropism. : involuntary orientation by an organism or one of its parts that involves turning or curving by movement or by differential growth and is a positive or negative response to a source of stimulation also : a reflex reaction involving a tropism. Other Words from tropism.
Tropic Movements
When a plant unveils some growth movement in response to a stimulus, which is known as tropism. Tropism is specific to the direction of the stimulus, and in response to a stimulus, plants can either display a negative or positive movement.
Types of Tropism
There are 6 basic types of tropic movements observed in plants as identified by their response to an external stimulus:
Things to Remember
Directional response to environmental stimulus in organisms causes their growth or movement. This is called
Sample Questions
Ans: Directional movement of living organisms in response to a stimulus is termed tropism. In rooted organisms like plants, tropism occurs as a structural alteration at the organ level which is seen as growth.
What is tropism in plants?
Simply put, tropisms are plant apparatus in their fight against environmental changes. They enable the plants to adapt to their environment and grow depending on the stimulus they experience. Stimuli, like the sun's light, earth gravity, and various physical stimuli, all affect the growth of the plant, and their direction generally dictates the direction of the plant's response. If a plant grows in the direction of the stimuli (gravity, for example), that is known as a positive tropism, and negative tropism is the growth opposite from the stimuli.
What is the difference between positive and negative tropism?
Positive tropism is growth in the direction of the stimuli, while negative tropism is the growth opposite from the stimuli. Plants are like humans and animals, at least in the sense that they constantly adapt to their environment to preserve their well-being.
Do plants need to control their geotropic tendencies?
Plants need to control their geotropic tendencies first before they can perform hydrotropism. We all know that water is essential for a plant's well-being, and hydrotropism regulates the growth of the plant to a water source. Plants need to control their geotropic tendencies first before they can perform hydrotropism.
When the movement is towards the stimulus, it is called a positive or negative tropism?
When the movement is towards the stimulus, it is called positive trop ism. Likewise, when the movement is away from the stimulus, it is called negative tropism. While there are several forms of tropism, we'll just focus on three key types: phototropism, geotropism and thigmatropism.
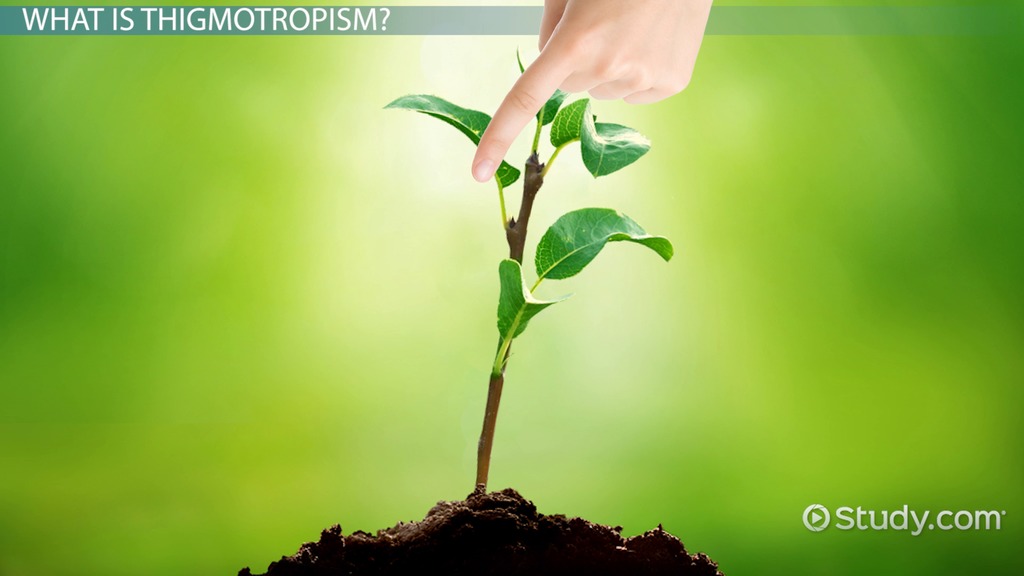
What is thrigmotropism in plants?
Thigmotropism is plant response to touch. The most common example is the curling response of vines when in contact with an object. The response is controlled by specialized epidermal cells, which mediate the differential growth on each side of the stem. Elongation of cells on one side of the stem cause bending of the stem in the opposite direction.
What is the response of an entire plant organ, such as a flower or leaf, to the sun's position?
Heliotropism is the response of an entire plant organ, such as a flower or leaf, to the sun's position in the sky. Plants orient leaves at different angles in relation to the sun to regulate temperature, evapotranspiration, and rate of photosynthesis in leaves.
Which term describes the phenomenon of plants following the Sun across the sky as they move from east to west?
Heliotropism (phenomenon of fancy moving plants following the sun across the sky as they move from east to west direction)
How do plants respond to environmental stimuli?
Plants respond positively to some stimuli by moving toward them , and negatively to other stimuli by moving away from them. There are several different examples of tropisms in plants. Gravitropism, or the response to gravity, causes roots to move towards gravity, or down into the soil, to reach water and minerals. It also causes stems to move away from gravity, so that leaves and stems will be in a position to intercept light.
What Is Tropism?
- A tropism is the innate ability of an organism to turn or move in response to a stimulus. As opposed to a learned ability, innate reactions are genetically programmed. Organisms with a tropism will naturally turn toward a stimulus. A stimulus can be any signal from the environment, …
Tropism Examples
Tropism Types
Tropism in Microbiology
Tropism in Plants
Tropism in Animals
- Plant exhibit thigmotropism, a response to touch. The roots of plants may turn when they touch a hard surface, like a rock.
- Some animals may be drawn to certain magnetic poles and use magnetic fields as a source of direction. Many animals and plants exhibit magnetotropism.
- Chemotropism is seen in fishes where they are both drawn to and avoid a variety of different …
- Plant exhibit thigmotropism, a response to touch. The roots of plants may turn when they touch a hard surface, like a rock.
- Some animals may be drawn to certain magnetic poles and use magnetic fields as a source of direction. Many animals and plants exhibit magnetotropism.
- Chemotropism is seen in fishes where they are both drawn to and avoid a variety of different chemicals.
- Salmon show chemotrophic ability when they are able to travel far in the ocean and still return to the same stream in which they were spawned. Salmon are drawn to the unique chemical signatures tha...