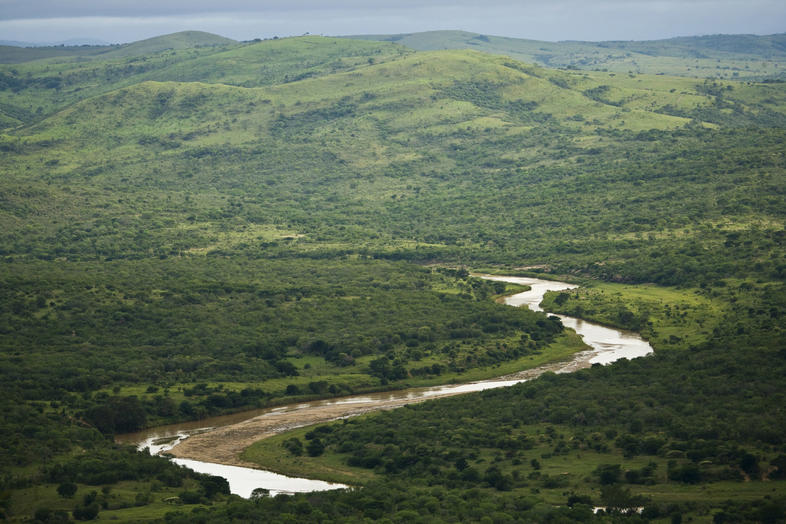

Floodplain
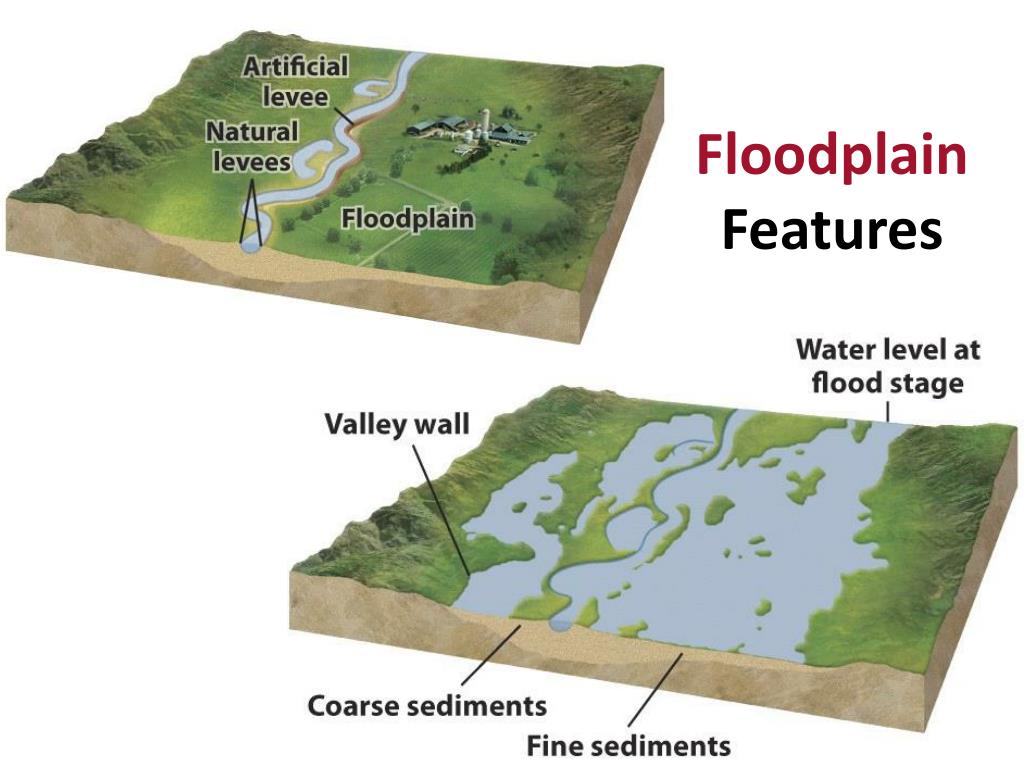
A floodplain or flood plain is an area of land adjacent to a stream or river that stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls and experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.
Why are floodplains good?
Some of the benefits of floodplains to a functioning natural system include:
- Fish and wildlife habitat protection.
- Natural flood and erosion control.
- Surface water quality maintenance.
- Groundwater recharge.
- Biological productivity.
- Higher quality recreational opportunities (fishing, bird watching, boating, etc.)
What is an example of floodplain?
- Overflow of inland or tidal waters; or
- Unusual and rapid accumulation or runoff of surface waters from any source; or
- Mudslides (i.e., mudflows) which are proximately caused by flooding and are akin to a river of liquid and flowing mud on the surfaces of normally dry land areas, as when ...
What are the causes and effects of floods?
- The government should convince communities suffering the consequences of floods every year to relocate permanently.
- The government should provide support to settle in the new location.
- Communities should increase cultivation and vegetation practices to improve food security. ...
What is the meaning of a flood plain?
Flood plains of river are basically land area which is adjacent to the usual course of a river and extends upto the base of valley walls and gets flooded (as the name suggests) during the times of flood or excess discharge of water in the river/stream.
Which are the world's three largest rivers by volume?
List of rivers by dischargeNoContinentRiver1South AmericaAmazon2AfricaCongo (Zaire)3AsiaGanges-Brahmaputra/Meghna4South AmericaOrinoco46 more rows
Which body of water is significantly reduced in size due to water diversion?
The Aral Sea in the Soviet Union, formerly the world's fourth largest lake in area, is disappearing. Between 1960 and 1987, its level dropped nearly 13 meters, and its area decreased by 40 percent. Recession has resulted from reduced inflow caused primarily by withdrawals of water for irrigation.
What happens when deep wells are heavily pumped?
Periods of extended over pumping increase the rate at which water travels through the ground immediately around the well drawing in sediment that adds cloudiness to the water and may eventually clog the cracks that are the arteries in your water delivery system thus severing the well's connection to the aquifer.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of building levees?
Floodwalls and Levees Advantages and DisadvantagesAdvantagesDisadvantagesReduces flood risk to the structure and its contentsRequires interior drainageReduces the physical, financial, and emotional strains that accompany flood eventsMay affect local drainage, possible resulting in water problems for others10 more rows
Is the Black Sea drying up?
By compiling the data gathered over the past 60 years, he noted that the oxygen-rich top layer of the Black Sea had shrunk from 140 metres to 90 metres deep. Impressive figures that correspond to a more than 40 % decrease in the habitable volume.
What percentage of the freshwater consumed in the world is used in agriculture?
70 percentCurrently, agriculture accounts (on average) for 70 percent of all freshwater withdrawals globally (and an even higher share of “consumptive water use” due to the evapotranspiration of crops).
Can you pump a well dry?
Yes, it can. Running the well pump when there isn't water to pump can damage the pump itself which can cause it to burn out prematurely. Well pumps can be quite expensive to replace.
Can you pump water into a well?
Shallow-well pumps These days, the most common pump for a shallow well is a jet pump. Jet pumps are mounted above the well, either in the home or in a well house, and draw the water up from the well through suction (see Single-Drop Jet-Pump System diagram on next page).
How much water can I pump from my well?
The typical 6-inch diameter well will hold approximately 1.5 gallons of water per foot of casing. The height of the water above the pump when it is not operating, multiplied by the gallons of water per foot of casing approximates the amount of available storage within the well casing.
How do you make a levy?
Levees can also be artificially created or reinforced. Artificial levees are usually built by piling soil, sand, or rocks on a cleared, level surface. In places where the flow of a river is strong, levees may also be made of blocks of wood, plastic, or metal.
How does river restoration work?
River restoration refers to a large variety of ecological, physical, spatial and management measures and practices. These are aimed at restoring the natural state and functioning of the river system in support of biodiversity, recreation, flood management and landscape development.
Are flood barriers effective?
The benefits of flood barriers are numerous. They include: Simple but effective protection – requiring minimal setup and little time, flood barriers can be quickly deployed and provide a higher level of protection than traditional barrier methods such as sandbags.
Which human activity has the most negative impact on water quality?
One of the most serious threats to water resources is the degradation of ecosystems, which often takes place through changes to landscapes such as the clearance of forests, the conversion of natural landscapes to farmland, the growth of cities, the building of roads, and surface mining.
What is the purpose of a river?
Rivers carry water and nutrients to areas all around the earth. They play a very important part in the water cycle, acting as drainage channels for surface water. Rivers drain nearly 75% of the earth's land surface. Rivers provide excellent habitat and food for many of the earth's organisms.
Which is the most important reason for maintaining clean water?
Our cherished way of life depends on clean water: healthy ecosystems provide wildlife habitat and places to fish, paddle, surf, and swim. Our economy depends on clean water: manufacturing, farming, tourism, recreation, energy production, and other economic sectors need clean water to function and flourish.
Why do lakes rivers and streams most likely require more treatment than groundwater?
Surface water typically requires more treatment and filtration than ground water because lakes, rivers, and streams contain more sediment (sand, clay, silt, and other soil particles), germs, chemicals, and toxins than ground water.
The benefits of natural floodplains
Conservation Corps volunteers planted hundreds of young trees Wednesday, May 22, 2019, in a Mississippi floodplain on national refuge land in southeast Minnesota. More frequent, severe flooding due to climate change affects critical bird habitats in the floodplain forests around the Mississippi River.
Flood management vs. floodplains
A home with only its second story visible sits destroyed by Hurricane Katrina on August 30, 2005, in New Orleans, Louisiana. Devastation was widespread throughout the city, with water 12 feet high in some areas. (Photo by Chris Graythen/Getty Images)
An example of successful floodplain management
City workers transport a load of sandbags to be used in re-enforcing a levee gate past the Yazoo & Mississippi Valley Railroad Station May 11, 2011 in Vicksburg, Mississippi. The Mississippi River at Vicksburg was expected to crest at a record 58.5 feet. (Photo by Scott Olson/Getty Images)
Research shows more people are living near floodplains
A map using NASA satellite data shows the number of people exposed to flooding is increasing.
How to know if you are living near a flood-prone area
The Federal Emergency Management Agency has a map to help determine if an area is more likely to flood. The map is used by the National Flood Insurance Program and shows areas that are expected to be covered with water when 11 inches of rain falls in 24 hours.
What living near a floodplain means for you
Most homeowners insurance doesn't cover flood damage. According to FEMA, homes with a low-to-moderate risk are five times more likely to be damaged by a flood than a fire. After you determine your risk, you should contact your insurance company to add flood insurance.
What is a floodplain?
A floodplain is a naturally occurring, low-lying area surrounding a waterway that regularly overflows. Weather patterns and shifting waterways over hundreds or thousands of years create natural floodplains. Water flows through the floodplain, which allows the sediment to settle, forming piles along the sides, known as levees. As a result, the floodplain features a flat area, or streambed, with steep edges on the perimeter, also known as stream banks.
What is the difference between a floodplain and a floodway?
A floodway lies within the floodplain boundary and must be completely clear of buildings and structures to allow the floodwaters to pass during a flood event. Buildings in a floodway could alter the flood watercourse, increasing flood risk to surrounding areas. On the other hand, FEMA allows certain buildings and structures to be erected in specific parts of a floodplain, including the areas designated as the 1% and 2% floodplains.
What is the name of the channel of the watercourse and adjacent land that fills with flowing water during a flood?
The floodway – The channel of the watercourse and adjacent land that fills with flowing water during a flood event.
What is the probability of a flood in a 500 year floodplain?
This is considered a moderate-to-low-risk floodplain zone.
What is the purpose of installing flood vents?
Install flood vents, which allow the waters to flow through the vents and drain out.
Can you get flood insurance if you live in a low risk zone?
Whether you live in a high- or low-risk floodplain zone, purchasing flood insurance is crucial to protect against financial losses resulting from floods, even if not required. Even a couple of inches of water can lead to several thousand or tens of thousands of dollars of damage.
Is a floodplain a landscape?
Depending on the location, a floodplain can be a minor component of a landscape or the primary feature. Some are so small they may not show up on a map, while others are very large, like those that surround the Mississippi River.
What is a Floodplain?
Floodplains are areas that are prone to being inundated by floodwaters during times of heavy rain, snowmelt, or high tides. Most floodplains in Snohomish County consist of low-lying lands along rivers and streams that flood when the waterways rise high enough to spill over their banks.
What are the benefits of floodplains?
They provide a wide range of benefits to our local communities, including: Natural flood and erosion control—reducing flood velocities, peak flows and erosion potential; providing flood storage and conveyance.
What happens if a well is flooded?
Flood waters may carry silt, raw sewage, oil or chemical waste. If your well has been flooded, you should assume that the well is contaminated. If you are on a public water system, monitor local news to find out if your water is safe to drink.
When was Living with the River published?
Living with the River (PDF): a 2007 publication by the Washington State Department of Ecology
Is it safe to drive through flood waters?
Hazards. Flood waters can be deceiving in terms of their depth and how quickly they move. It is not safe to walk or drive through flood waters since as little as six inches of water can cause you to lose your balance, and two feet of water can sweep your car away.
Why are floodplains important?
The wide variety of plants and animals supported directly or indirectly by floodplains constitutes an extremely valuable, renewable resource important for our economic welfare, aesthetic enjoyment, and physical well-being.
What are the physical characteristics of floodplains?
Likewise, the physical characteristics of the floodplain shape flood flows and can provide flood loss reduction benefits to include the following: Excess water storage: Except in narrow, steep valleys and areas of coastal bluffs, floodplains provide a broad area which allows floodwaters to spread out and temporarily store excess water.
How do floodplains help with flood loss?
Floodplains provide numerous flood loss reduction benefits as a result of their unique natural functions. Rivers and streams shape floodplain topography and influence riparian habitats and riverine ecosystems. Likewise, the physical characteristics of the floodplain shape flood flows and can provide flood loss reduction benefits to include ...
What are the benefits of natural floodplains?
Benefits of Natural Floodplains. Natural floodplains provide flood risk reduction benefits by slowing runoff and storing flood water. They also provide other benefits of considerable economic, social, and environmental value that are often overlooked when local land-use decisions are made. Floodplains frequently contain wetlands ...
How much water does a floodplain hold?
One acre of floodplain flooded one foot deep holds approximately 330,000 gallons of water. Flow rate and erosion reduction: In their natural vegetated state, floodplains slow the rate at which the incoming overland flow reaches the main water body in the area. Vegetation also reduces shoreline erosion.
What is flow regulation during non-flood periods?
Flow regulation during non-flood periods: During non-flood periods, groundwater discharge acts to naturally regulate the flow in a river or the level of a lake or pond. In other words, during periods of abundant water, the water can enter the groundwater system whenever there is available capacity rather than contribute to seasonal flood peaks. During low flow periods, the water flows from the higher groundwater system into lower surface waters, so that the frequency and duration of extremely low flows is reduced.
What is slowing runoff?
Slowing runoff: A natural floodplain has surface conditions favoring local ponding and flood detention, plus subsurface conditions favoring infiltration and storage. Slowing runoff across the floodplain allows additional time for the runoff to infiltrate and recharge available groundwater aquifers when there is unused storage capacity. The slowing of runoff provides the additional benefit of natural purification of water as local runoff or overbank floodwater infiltrates and percolates through the floodplain alluvium.
What Are Floodplains?
These events highlight the importance of floodplains, land around bodies of water that takes on excess water in times of flood and when managed wisely, can help to reduce the risk of damage when storms or snowmelt overwhelm the banks. In other words, when Mother Nature gets dramatic, floodplains go to work.
What are the deposits of soil during floods?
River channels naturally meander through the floodplain landscape and over time deposits soil-forming material especially during floods. These deposits provide fertile soil for agricultural production. Photo of Willamette River courtesy of Aaron Hockley.
What is flood storage?
Flood storage. Floodplains take on and store excess water in times of flood, releasing it slowly overland and into groundwater. The flood storage capacity of floodplains means that there is less likelihood that floodwater will end up in your basement.
Why are floodplains important?
These events highlight the importance of floodplains, land around bodies of water that takes on excess water in times of flood and when managed wisely, can help to reduce the risk of damage when storms or snowmelt overwhelm the banks. In other words, when Mother Nature gets dramatic, floodplains go to work.
How much did the Willamette Valley flood cost?
Closer to home, the Willamette Valley Flood of 1996 cost $500 million and displaced 3,000 people throughout the Pacific Northwest.
What are some examples of habitats in the floodplain?
Floodplains are rich and biologically diverse environments that can support an abundance of plants, birds, and other species on land and in the water. For example, Chinook Salmon (pictured to the left) rely on floodplains during the freshwater phase of their life cycle.
What are the recreational opportunities in floodplains?
Floodplains provide numerous recreational opportunities, including lakes, rivers, hiking trails, and spaces to see thriving wildlife. In addition, the long history of settlement in floodplains as people have been drawn to the fertile land and abundant resources create a shared culture and sense of place in these locations.
What are the floodplains in the Midwest?
Riverine floodplains range from narrow, confined channels (as in steep river valleys in h illy and mountainous areas) to wide, flat areas (as in much of the Midwest and in many coastal areas). In the steep narrow valleys, flooding usually occurs quickly and is of short duration, but is likely to
Why do rivers flood?
Flooding in large rivers usually results from large-scale weather systems generating prolonged rainfall over wide areas. These same weather systems may cause flooding in hundreds of smaller basins that drain into the major river system. The streams and small rivers are also susceptible to flooding from more localized weather systems that cause intense rainfall over only a small area. In parts of the northern and western United States, annual spring floods result from spring snowmelt and the extent of flooding is dependent upon winter snowpack and spring weather patterns.
What causes erosion and flooding?
Flooding and flood-related erosion can result from several types of ground failures. Subsidence and liquefaction of soil may cause flooding of areas in the immediate vicinity of the ground failure, while mudflows and mudfloods may cause damages downstream or downslope of the location where the initial ground failure occurred.
What is overbank flooding?
Overbank flooding of rivers and streams – the increase in volume of water within a river channel and the overflow of water from the channel onto the adjacent floodplain – represents the classic flooding event that most people associate with the term “flood.” In fact, this is also the most common type of flood event. Hundreds of riverine floods, great and small, occur annually in the United States.
What are alluvial fans?
Alluvial fans, which occur mainly in dry mountainous regions, are deposits of rock and soil that have eroded from mountainsides and accumulated on valley floors in a fan-shaped pattern. The deposits are narrow and steep at the head of the fan, broadening as they spread out onto the valley floor. Fans provide attractive development sites due to their commanding views, but harbor severe flood hazards along with unique behavior. Channels along fans are not well defined and flow paths are unpredictable. As rain runs off steep valley walls, it gains velocity, carrying large boulders and other debris. When the debris fills the runoff channels of the fan, floodwaters spill out, spreading laterally and cutting new channels. The process is then repeated, resulting in shifting channels and combined erosion and flooding problems over a large area.
What is flash flood?
The National Weather Service defines a flash flood as “A rapid and extreme flow of high water into a normally dry area, or a rapid rise in a stream or creek above a predetermined flood level, beginning within six hours of the causative event (e.g., intense rainfall, dam failure, ice jam). However, the actual time threshold may vary in different parts of the country. Ongoing flooding can intensify to flash flooding in cases where intense rainfall results in a rapid surge of rising flood waters.”1Flash floods are also characterized by a rapid rise in water, high velocities, and large amounts of debris. Major factors in flash flooding are the intensity and duration of rainfall and the steepness of
What are the most significant losses due to the failure of flood control structures?
Some of the most significant losses due to the failure of flood control structures can be attributed to the construction of inadequate dams and levees or to a flood that exceeds the design protection level. Many private or locally built levees and dams may provide only limited flood protection or are sometimes poorly designed and maintained. Many were built with no design standards. Levee overtopping or failure typically occurs from floods beyond their capacity to handle, often with spectacular and tragic results.
What happened after the creek was lined with concrete?
After the creek was lined with concrete, developers were allowed to build homes and businesses right up to the edge of the channel, eliminating the natural floodplain into which the coursing waters previously would have swelled during storms.
What is floodplain in geography?
Definition of floodplain. 1 : level land that may be submerged by floodwaters. 2 : a plain built up by stream deposition.
What sediments form in the middle course of the river?
The sandy sediments in the middle course of the river are form…
What is the meaning of "watershed"?
One part of a watershed can impact another part of the watersh…. Watershed. an area or ridges that water flows from. Floodplain. an area of water next to a stream or river under high waters. 6 Terms. dschenk17. Floodplain.
