
What is crossmatching and how does it work?
Crossmatching is a way for your healthcare provider to test your blood against a donor's blood to make sure they are fully compatible. It's essentially a trial transfusion done in test tubes to see exactly how your blood will react with potential donor blood. It's important for donor blood to match your own as closely as possible.
What is the goal of blood typing and crossmatching?
The goal of blood typing and crossmatching is to find a compatible blood type for transfusion. The results of blood typing will tell you if you are type A, B, AB, or O and if you are Rh negative or positive. The results will tell your healthcare provider what blood or blood components will be safe to give you.
What is the difference between type-type and screen and crossmatching?
-Type and screen is the first thing you do. -Think of crossing or crossbreeding two animals. And think of mixing of bloods. -Crossmatching takes the patient’s blood that has been typed and screened above (e.g. say AB+) and uses that information to pull out a back of PRBC that is compatible (e.g. it is also labeled AB+).
What happens during a blood crossmatch?
To crossmatch your blood against donor blood or organs, the technician will mix a sample of your blood with a sample of the donor material. Again, they’ll check for signs of reaction. What do the test results mean? Depending on the results of your blood typing, your blood will be classified as type A, B, AB, or O.
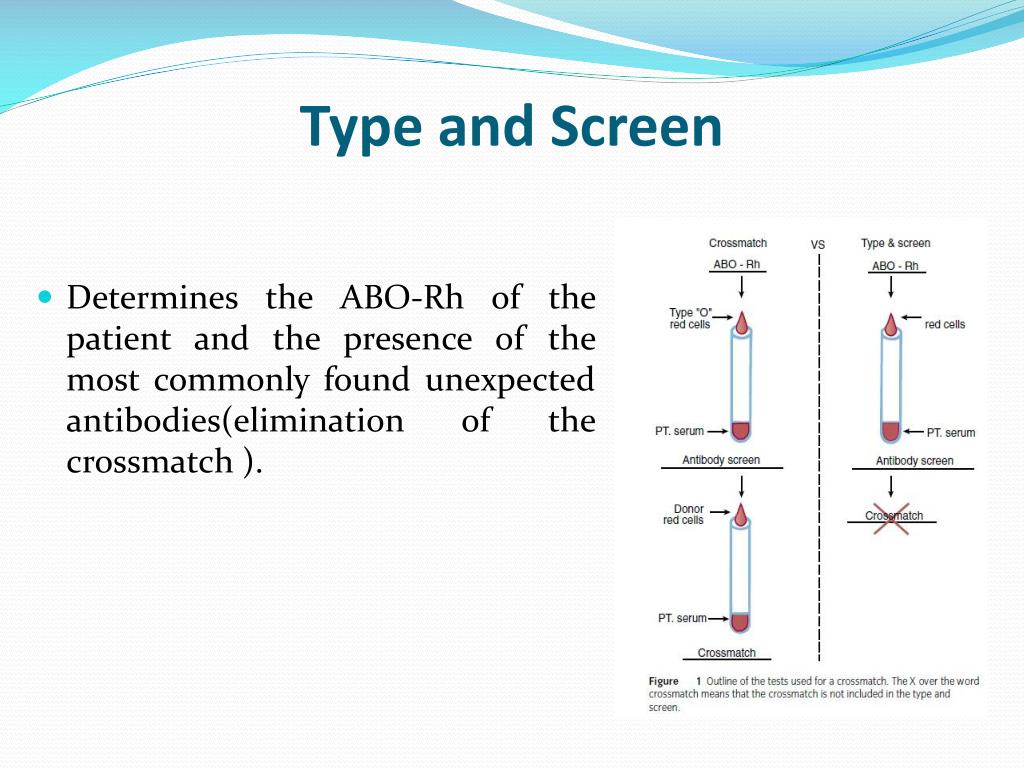
What is the difference between a type and screen and a crossmatch?
A type and screen is ordered if blood transfusion is likely but not certain, while a crossmatch order indicates to the transfusion service that blood transfusion is required.
What crossmatch means?
Crossmatching is a way for your healthcare provider to test your blood against a donor's blood to make sure they are fully compatible. It's essentially a trial transfusion done in test tubes to see exactly how your blood will react with potential donor blood.
What does type and screen mean?
The type and screen are the primary pre-transfusion tests performed. Testing includes the determination of patient's ABO group, RhD type, and a screen for the detection of atypical antibodies. Additional testing for red cell antibody identification is performed when atypical antibodies are detected.
When would a type and crossmatch be performed on a patient?
A type and cross determines the same information, but additionally performs a crossmatch between the patient's sample and a unit of blood to prepare a product for immediate transfusion. A type and cross should only be ordered if there is a high likelihood of transfusion. A T&S is “active” for three calendar days.
What are the 3 phases of crossmatching?
Crossmatch TestingMajor crossmatch: This is the most important one. ... Minor crossmatch: This detects antibodies in the donor serum to the recipient's red blood cells. ... Autocontrol: We also perform an auto-control with our crossmatches, i.e. recipient serum with recipient red blood cells.
What blood types can crossmatch?
Blood typingIf you have type A blood, you should only receive types A or O blood.If you have type B blood, you should only receive types B or O blood.If you have type AB blood, you can receive types A, B, AB, or O blood.If you have type O blood, you should only receive type O blood.
How long does type and cross take?
Emergencies. As the complete cross-matching process takes approximately 1 hour, it is not always used in emergencies. In the case of an emergency, a type-specific blood to which the recipient has no antibodies, can be requested.
What is a positive type and screen?
This test is performed to determine the patient's blood group (ABO) and Rh type, as well as to detect the presence of irregular antibodies in the patient's plasma or serum. If the antibody screen is positive, ABID “Antibody Identification, Erythrocytes” is performed (at an additional charge).
What are the 8 human blood types?
In addition to the A and B antigens, there is a protein called the Rh factor, which can be either present (+) or absent (–), creating the 8 most common blood types (A+, A-, B+, B-, O+, O-, AB+, AB-).
How is crossmatch done?
Major crossmatching is a mandatory test that checks to see if the blood recipient has any antibodies that might resist the donor's blood cells. To do this test, blood cells from the donor are combined with blood serum from the recipient. Without this test, a blood bank cannot release blood donations to a patient.
Why Coombs test is done?
The direct Coombs test is used to detect antibodies that are stuck to the surface of red blood cells. Many diseases and drugs can cause this to happen. These antibodies sometimes destroy red blood cells and cause anemia.
How do you do a crossmatch test?
Minor Cross Match Prepare donor and recipient's blood sample: Recipient's red cells and donor's serum/plasma. Label a test tube. Add two drops of donor's serum and one drop of recipient's cell suspension. Mix and incubate the tubes at 37 degree Celsius for about 60 minutes.
How do you crossmatch blood?
To do a blood compatibility test, a blood sample is taken by needle from a vein in your arm. Then, tests can be run in a lab using your blood samples, or a computer program can analyze them. Computer crossmatching can be done using results collected from antibody screens and blood group screens.
What does crossmatch mean for kidney transplant?
The crossmatch checks if the recipient's immune system may react to your donated kidney. The test mixes a sample of your blood and the recipient's blood together to see if there's a reaction. It can take several weeks to get this result.
How do you read crossmatch results?
If donor-specific antibodies are not present, no lysis occurs and the result is deemed negative (B). If donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies bind to the lymphocytes and then activate complement, cell lysis will occur and the crossmatch result will be deemed positive (C).
What is crossmatching test?
Crossmatching is a test used to check for harmful interactions between your blood and specific donor blood or organs. It can help your doctor predict how your body will react to those donor materials.
What is blood typing and crossmatching?
What are blood typing and crossmatching? If you need a blood transfusion or transplant, your doctor can use blood typing and crossmatching to learn if your blood is compatible with donor blood or organs. Blood typing reveals what type of blood you have.
Why do doctors use blood typing?
Blood typing helps your doctor determine what type of donor blood is compatible with your own. Some blood types contain antibodies that trigger immune reactions against other blood types. In general:
What does it mean when your blood cells clump together?
If your blood cells agglutinate, or clump together, it means your sample has reacted with one of the antibodies. This is called forward typing .
How to crossmatch blood?
To crossmatch your blood against donor blood or organs, the technician will mix a sample of your blood with a sample of the donor material. Again, they’ll check for signs of reaction.
What does blood typing reveal?
Blood typing reveals what type of blood you have. This depends on the presence of certain antigens on your red blood cells (RBCs). Antigens are proteins that trigger your immune system to produce antibodies. There are four main types of blood: type A, which contains type-A antigens. type B, which contains type-B antigens.
What is a type O donor?
If you have type O blood, you’re known as a “universal donor,” as anyone can receive type O blood. Type O blood is often used in emergencies when there isn’t enough time to perform blood typing tests.
What is this test?
This is a set of tests that looks for harmful interactions between your blood and donor blood. The tests are done before a blood transfusion.
Why do I need this test?
You may need this test if you need or may need a blood transfusion. For example, you might need a blood transfusion if you have an acute hemorrhage that causes a severe loss of blood.
What do my test results mean?
Test results may vary depending on your age, gender, health history, the method used for the test, and other things. Ask your healthcare provider what your test results mean for you.
How is this test done?
The test is done with a blood sample. A needle is used to draw blood from a vein in your arm or hand.
What might affect my test results?
A crossmatch that's done more than 3 days before a transfusion could have inaccurate results.
Why is it important to know your blood type?
It's important for your healthcare provider to know your blood type in order to select a donor blood that's compatible before doing the crossmatch. An intermediate step between blood typing and crossmatching is called a recipient antibody screen. This test checks for unexpected antibodies in your blood. If unexpected antibodies are found, this ...
Why is it important to match your own blood?
It's important for donor blood to match your own as closely as possible. Otherwise, your immune system might create antibodies against the donor blood cells. In this case, your immune system correctly views the donor cells as foreign, but incorrectly views them harmful. This can lead to a dangerous and possibly fatal reaction.
What is this test?
This is a set of tests that looks for harmful interactions between your blood and donor blood. The tests are done before a blood transfusion.
Why do I need this test?
You may need this test if you need or may need a blood transfusion. For example, you might need a blood transfusion if you have an acute hemorrhage that causes a severe loss of blood.
What do my test results mean?
Test results may vary depending on your age, gender, health history, the method used for the test, and other things. Ask your healthcare provider what your test results mean for you.
Does this test pose any risks?
Having a blood test with a needle carries some risks. These include bleeding, infection, bruising, and feeling lightheaded. When the needle pricks your arm or hand, you may feel a slight sting or pain. Afterward, the site may be sore.
What might affect my test results?
A crossmatch that's done more than 3 days before a transfusion could have inaccurate results.
What is crossmatching in blood?
Crossmatching is a way for your healthcare provider to test your blood against a donor's blood to make sure they are fully compatible. It's essentially a trial transfusion done in test tubes to see exactly how your blood will react with potential donor blood.
What is the intermediate step between blood typing and crossmatching?
An intermediate step between blood typing and crossmatching is called a recipient antibody screen. This test checks for unexpected antibodies in your blood. If unexpected antibodies are found, this can delay the selection of compatible donor blood.
What does crossmatching mean?
Crossmatching really is physically mixing two people’s bloods (that you have screened and think should be compatible) in a container to see if agglutination happens . If agglutination happens, it tells you that there are some unknown antigens on the patient’s RBCs that are reacting badly with the donor’s blood.
What is it called when you mix blood in a container?
Actually mixing blood in a container is called Manual Crossmatching. Electronic crossmatching allows the known identified antigens on the two bloods (from typing and screening) to be matched electronically without actually mixing the bloods. It’s not as foolproof as manual crossmatching.
When is manual crossmatching done?
Manual crossmatching has to be done when 1) the patient screened positive for some antigen or 2) if the patient has a history of previous transfusions.
Why is venipuncture important?
Although correct patient identification is important for test specimens, it is crucial when blood is collected for type and crossmatch because clerical error is the most frequent cause of life-threatening ABO incompatibility.
What is blood typing?
Blood typing is a series of tests that include the ABO and Rh blood-group system performed to detect surface antigens on red blood cells (RBCs) by an agglutination test and compatibility tests to determine antibodies against these antigens. The major antigens in the ABO system are A and B, although AB and O are also common phenotypes. The patient with A antigens has group A blood; the patient with B antigens has group B blood. The patient with both A and B antigens has group AB blood (universal recipient); the patient with neither A nor B antigens has group O blood (universal donor). Blood group and type is genetically determined. After 6 mo of age, individuals develop serum antibodies that react with A or B antigen absent from their own RBCs. These are called anti-A and anti-B antibodies.
What blood type is used to determine if a newborn has hemolytic disease?
Determine Rh blood type and perform antibody screen of prenatal patients on initial visit to determine maternal Rh type and to indicate whether maternal RBCs have been sensitized by any antibodies known to cause hemolytic disease of the newborn, especially anti-D antibody. Rh blood type, antibody screen, and antibody titration (if an antibody has been identified) will be rechecked at 28 wk of gestation and prior to injection of prophylactic standard dose of Rho(D) immune globulin RhoGAMIM or RhophylacIM or IV for Rh-negative mothers. These tests will also be repeated after delivery of an Rh-positive fetus to an Rh-negative mother and prior to injection of prophylactic standard dose of Rho(D) immune globulin (if maternal Rh-negative blood has not been previously sensitized with Rh-positive cells resulting in a positive anti-D antibody titer). A postpartum blood sample must be evaluated for fetal-maternal bleed on all Rh-negative mothers to determine the need for additional doses of Rh immune globulin. One in 300 cases will demonstrate hemorrhage greater than 15 mL of blood and require additional Rho(D) immune globulin.
What is the purpose of ABO and rh testing?
ABO and Rh testing is also performed as a prenatal screen in pregnant women to identify the risk of hemolytic disease of the newborn.
Why is blood transfused with the same ABO group and Rh type as the recipient?
Generally, only blood with the same ABO group and Rh type as the recipient is transfused because the anti-A and anti-B antibodies are strong agglutinins that cause a rapid, complement-mediated destruction of incompatible cells.
What are the major antigens of the Rh system?
Major antigens of the Rh system are D (or Rho), C, E, c, and e. Individuals whose RBCs possess D antigen are called Rh-positive; those who lack D antigen are called Rh-negative, no matter what other Rh antigens are present. Individuals who are Rh-negative produce anti-D antibodies when exposed to Rh-positive cells by either transfusions or pregnancy. These anti-D antibodies cross the placenta to the fetus and can cause hemolytic disease of the newborn or transfusion reactions if Rh-positive blood is administered.
What are the two most common types of reactions that occur in blood product transfusions?
Febrile nonhemolytic reaction and urticarial/allergic reaction are the two most common types of reactions that occur in blood product transfusions. Many institutions have a policy that provides for premedication with acetaminophen and diphenhydramine to avoid initiation of mild transfusion reactions, where appropriate.

What are blood typing and crossmatching?
- If you need a blood transfusion or transplant, your doctor can use blood typing and crossmatchin…
Blood typing reveals what type of blood you have. This depends on the presence of certain antigens on your red blood cells (RBCs). Antigens are proteins that trigger your immune system to produce antibodies. There are four main types of blood: - •type A, which contains type-A antigens
•type B, which contains type-B antigens
What are these tests used for?
- Your doctor uses blood typing and crossmatching to learn if donor blood or organs are compatibl…
Your doctor may order blood typing, crossmatching, or both if: - •you’re scheduled to receive a blood transfusion or organ transplant
•you’re scheduled to undergo a medical procedure where you face the risk of significant blood loss
How are these tests performed?
- Collecting the sample
A trained healthcare practitioner can draw a sample of your blood at your doctor’s office, blood bank, or other sites. They’ll use a needle to draw the sample from one of your veins, usually on the inside of your elbow. They’ll likely start by disinfecting the area with an antiseptic. An elastic … - Blood typing the sample
In the laboratory, a technician can conduct several tests to type your blood. They will mix some of your blood with commercially prepared anti-A and anti-B antibodies. If your blood cells agglutinate, or clump together, it means your sample has reacted with one of the antibodies. Thi…
What do the test results mean?
- Depending on the results of your blood typing, your blood will be classified as type A, B, AB, or …
The results of your crossmatching test will help your doctor assess if it’s safe for you to receive specific donor blood or organs.
What are the risks?
- Blood draws are generally safe for most people, but they do pose some risks. You may experien…
In most cases, the potential benefits of blood typing and crossmatching outweigh the risks. Talk to your doctor to learn more about the procedure. They can also help you understand your test results and recommend appropriate follow-up steps.