What are the parts of a typical vertebra?
Vertebra
- two pedicles ( pedicle of vertebral arch)
- two laminae, and
- seven processes.
What is the structure of a typical vertebrae?
Vertebral column (spine)
- Vertebrae. The spine, vertebral column, or backbone is defined as the bony structure that runs from the inferior aspect of the occipital bone of the skull to the tip of ...
- Joints and ligaments. ...
- Spine curvature and movements. ...
- Nerves and vasculature. ...
What are the characteristics of the vertebrae?
- A stiff rod running through the length of the animal (it could either be the vertebral column and/or notochord)
- Humans and all other vertebrates possess a notochord as an embryo and it eventually develops into the vertebral column.
- A bundle of nerves run above the vertebral column (spinal cord) and the alimentary canal exists below it.
What is the difference between vertebrae and invertebrates?
• Vertebrates have a backbone with a spinal cord, whereas invertebrates do not. • The diversity is exceptionally high among the invertebrates compared to vertebrates. • Vertebrates are always bilaterally symmetrical, while invertebrates could show either bilateral or radial symmetry.

What does typical vertebra mean?
Typical vertebrae are the vertebrae of the vertebral column, consisting of the general structure of a vertebra. Also, this includes the presence of a vertebral body, vertebral arch, and transverse processes.
Where is the typical vertebra?
Typical Vertebrae It consists of the body and the vertebral arch. The vertebral arch is made of laminae and pedicles. Most of the adult vertebral columns are typical in nature. A typical vertebra includes most of the thoracic, lumbar and cervical vertebrae.
What are typical and atypical cervical vertebrae?
C7 may be considered typical or atypical but has two distinct features. The first is that unlike the rest of the cervical vertebrae, is that the vertebral artery does not traverse the transverse foramen. The second is that it contains a long spinous process, also known as “vertebra prominens.”
What are the two atypical vertebrae?
Of the cervical vertebrae, the atlas (C1), axis (C2) and vertebra prominens (C7) are considered atypical cervical vertebrae. The atlas (C1) lacks a body or spinous process.
What are the 3 main parts of a typical vertebra?
Figure 7.23 Parts of a Typical Vertebra A typical vertebra consists of a body and a vertebral arch. The arch is formed by the paired pedicles and paired laminae. Arising from the vertebral arch are the transverse, spinous, superior articular, and inferior articular processes.
How many atypical vertebrae are there?
Of the twelve thoracic vertebrae, five are said to be atypical. While sharing many similarities with the typical thoracic vertebrae, T1, and T9 to T12 have specific characteristics that make them easily identifiable.
What are the characteristics of typical vertebrae?
A typical vertebra consists of a body and a vertebral arch. The arch is formed by the paired pedicles and paired laminae. Arising from the vertebral arch are the transverse, spinous, superior articular, and inferior articular processes. The vertebral foramen provides for passage of the spinal cord.
What is a typical cervical vertebrae?
Cervical vertebrae C3 through C6 are known as typical vertebrae because they share the same basic characteristics with most of the vertebrae throughout the rest of the spine.
What is the difference between typical and atypical ribs?
Most of the ribs are typical ribs ie they have all these features. The atypical ribs which do not have all these features are: First rib (wide and short, has two costal grooves, and one articular facet)
Why is L5 vertebra atypical?
Of the five lumbar vertebrae, L5 is considered atypical due to its shape. The remaining lumbar vertebrae are largely typical. For a basic anatomic description of the structure a generic vertebra, see vertebrae.
Why is the 1st vertebral bone called atypical?
The 1st thoracic vertebra is considered an "atypical" because of the complete costal facet for the head of the 1st rib.
How is L5 atypical?
The L5 vertebra is atypical amongst the 5 lumbar vertebrae in that: body: deeper anterior margin than posterior margin. transverse processes: medially, fused mainly with posterolateral margin of body and only slightly with pedicle.
What is a typical cervical vertebrae?
Cervical vertebrae C3 through C6 are known as typical vertebrae because they share the same basic characteristics with most of the vertebrae throughout the rest of the spine.
Why is 5th lumbar atypical?
Of the five lumbar vertebrae, L5 is considered atypical due to its shape. The remaining lumbar vertebrae are largely typical. For a basic anatomic description of the structure a generic vertebra, see vertebrae.
What are typical lumbar vertebrae?
The lumbar region contains five vertebrae, denoted L1-L5. The intervertebral discs, along with the laminae, pedicles, and articular processes of adjacent vertebrae, create a space through which spinal nerves exit. The lumbar vertebrae, as a group, produce a lordotic curve.
What are the 4 types of vertebrae?
CONTENTSCervical vertebrae.Thoracic Vertebrae.Lumbar Vertebrae.Sacrum and Coccyx.
What are the characteristics of a vertebra?
Furthermore, one of the main characteristic features of a vertebra is the presence of a large body. Also, the posterior part of the vertebra forms the vertebral arch. Significantly, this vertebral arch contains eleven parts, including two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. Also, pedicles like vertebral notches form intervertebral foramina ...
Where are the vertebrae located?
Vertebrae occur in the middle portion of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae, the sacrum, and the coccyx are typical vertebrae while atypical vertebrae occur in the transitioning regions of the vertebral column.
What are atypical vertebrae?
Atypical vertebrae are the vertebrae in the vertebral column with different structures when compared to the structure of a typical vertebra. However, only cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae contain atypical vertebrae.
How many vertebrae are there in the vertebral column?
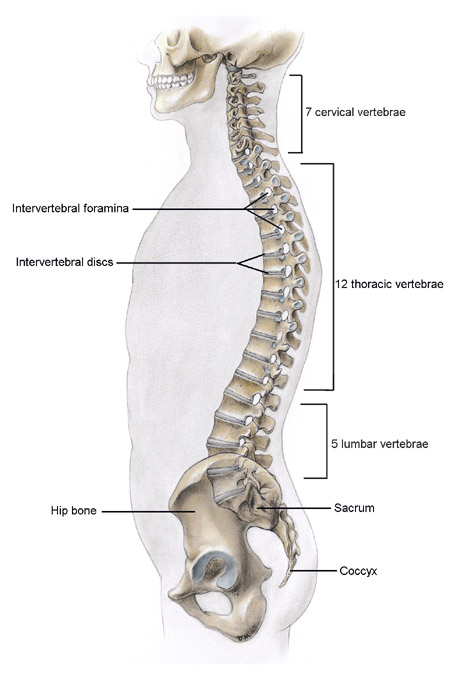
Typical vertebrae are the vertebrae, which have the standard structure of a vertebra of the vertebral column. Generally, the vertebral column contains 33 individual vertebrae; 24 presacral vertebrae (7 cervical, 12 thoracic, and 5 lumbar) followed by the sacrum (5 fused sacral vertebrae) and the coccyx ...
What is the difference between atypical and typical vertebrae?
The main difference between typical and atypical vertebrae is that typical vertebrae consist of a body, vertebral arch, and transverse processes, whereas atypical vertebrae contain deviated structures based on their functional requirements. Furthermore, cervical vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae, lumbar vertebrae, sacrum, and coccyx are the types of vertebrae occur in the vertebral column while the cervical vertebrae, C1, C2, and C7, thoracic vertebrae, T1, T9, and T12, lumbar vertebrae, L5, are atypical vertebrae. Moreover, other vertebrae are typical vertebrae.
What are the two types of vertebrae?
Typical and atypical vertebrae are two types of vertebrae occur in the vertebral column. Except for the sacrum and the coccyx, other vertebrae consist of a vertebral body, vertebral arch, and transverse processes. They are mainly responsible for protecting the spinal cord while providing support to the body.
What are the three cervical vertebrae?
However, the three cervical vertebrae are atypical. They include C1, C2, and C7 . Here, C1 or atlas is the most superior cervical ...
How many vertebrae are there in the vertebral column?
It is a typical characteristic of vertebrates. An adult has 26 vertebrae in the vertebral column. The basic structure of a vertebra differs according to the position and function.
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
Out of the seven cervical vertebrae, C2, C3, C4, C5, and C6 are typical vertebrae which posses basic anatomic structure of a vertebra. Most of the thoracic vertebrae are typical (T2 – T8) too. In addition to these, the four lumbar vertebrae are also typical (L1- L4).
What is the Difference Between Typical and Atypical Vertebrae?
Atypical Vertebrae are the vertebrae with modified structures due to their function and position.
What are Atypical Vertebrae?
Atypical vertebrae are the vertebrae with modified structures due to their function and position. Out of the seven cervical vertebrae, C1 (atlas), C2 (axis) and C7 (vertebra prominens) are atypical vertebrae. Moreover, C1 vertebra lacks spinous process. Axis vertebra contains a vertical projection called dens. C7 vertebra has a non-bifid longer spinous process. T1, T9, T10, T11, and T12 are also atypical.
What are the bones that make up the vertebral column?
In brief, vertebrae are individual cylindrical bones which make up the vertebral column of vertebrates. Typical vertebrae exhibit a basic anatomical structure composed of all components. Atypical vertebrae are the vertebrae whose structure is a little bit different from that of the basic anatomy due to vertebra function and position.
Which vertebra has the largest and bulkiest transverse processes?
Among lumbar vertebrae, L5 is an atypical vertebra since it has a small spinous process and the largest and bulkiest transverse processes.
How many processes are in the vertebral arch?
Also, they contain two major parts: vertebral body and vertebral arch. Furthermore, the vertebral arch contains pedicles, laminae, and seven processes. These seven processes include spinous process, two transverse processes, two superior articular processes and two inferior articular processes. Moreover, most vertebrae in an adults’ vertebral ...
How many vertebrae are there in the human body?
How many vertebrae do we have? The vertebral column consists of 33 vertebrae in total, divided as follows:
What is the spine of the vertebrae?
Vertebral column (spine) The vertebral column (spine or backbone) is a curved structure composed of bony vertebrae that are interconnected by cartilaginous intervertebral discs. It is part of the axial skeleton and extends from the base of the skull to the tip of the coccyx. The spinal cord runs through its center.
How many vertebrae are there in the cervical spine?
The seven cervical vertebrae form the cervical spine of the neck. They are located between the skull and the thoracic vertebrae and have the smallest and thinnest intervertebral discs. However, they are the most mobile in the entire vertebral column. In addition, cervical vertebrae have distinctive features like transverse foramina, two tubercles (anterior, posterior) and split (bifid) spinous processes. Here’s an illustration depicting the cervical spine anatomy.
What are the two parts of the vertebrae?
No two vertebrae are identical. They vary in size and characteristics, especially from one region to the next. However, they all have the following basic structure: 1 Vertebral body - the large cylindrical part located anteriorly that gives strength to the spine. They are involved in weight bearing. Their size increases as one descends down the vertebral column. Adjacent vertebral bodies are separated by intervertebral discs. 2 Vertebral arch - the structure located posterior to the body. It consists of two pedicles and two laminae. The pedicles contain vertebral notches (superior, inferior) which form intervertebral foramina. These facilitate the passage of spinal nerves from the spinal cord. The pedicles, laminae, and body of each vertebra form a cavity (vertebral foramen). The vertebral canal is the space throughout the spinal column that is enclosed by the vertebral foramina. 3 Vertebral processes - there are seven in total all projecting from the vertebral arch: one spinous process (posteroinferior), two transverse processes (posterolateral), and four articular processes. The latter contain articular facets. The vertebral processes serve as attachment points for ligaments and back muscles. They also take part in joint formation.
What is the large cylindrical part located anteriorly that gives strength to the spine?
Vertebral body - the large cylindrical part located anteriorly that gives strength to the spine. They are involved in weight bearing. Their size increases as one descends down the vertebral column. Adjacent vertebral bodies are separated by intervertebral discs.
How many vertebrae are in the axial skeleton?
The spinal cord runs through its center. The vertebral column is divided into five regions and consists of 33 vertebrae interlaced by strong joints and ligaments .
What is the spinal cord?
However, the spinal cord is the tubular nervous tissue that travels through the vertebral canal of the vertebral column.
What is the difference between vertebrae and vertebrae?
The vertebrae are separated by intervertebral discs of fibrocartilage, which are flexible cartilage discs located between the bodies of two adjacent vertebrae that allow movement in the spine and have a shock absorbing or cushioning function as well. An intervertebral disc consists of an inner gelatinous nucleus pulposus surrounded by a ring of fibrocartilage, the annulus fibrosus.
How many vertebrae are there in the thoracic spine?
Two muscles also interact with those twelve vertebrae, these being the spinalis and longissimus.
What is the body of a thoracic vertebra?
The body of a thoracic vertebra is somewhat “heart-shaped,” and is larger than the cervical but smaller than the lumbar vertebrae in size. The body also has small, smooth, and somewhat concave costal facets for the attachment of the ribs. Ribs are generally inserted between two vertebrae, such that each vertebra contributes to articulating with half of the articular surface. Each vertebra therefore has a pair of superior articular facets that face posteriorly and a pair of inferior articulating facets that face anteriorly (except for T12). This means that the rib will articulate with the inferior costal facet of the upper vertebrae and the superior costal facet of the lower vertebrae. Transverse processes arise from the arch found behind he superior articular processes and pedicles, and are thick and strong with a clubbed end and a small concave surface for the articulation with the tubercle of a rib. These processes are directed obliquely backward towards the spinous process and lateralward.
How long is the reading time for the thoracic vertebrae?
Last reviewed: May 31, 2021. Reading time: 15 minutes. The twelve thoracic vertebrae are strong bones that are located in the middle of the vertebral column, sandwhiched between the cervical ones above and the lumbar vertebrae below. Like typical vertebrae, they are separated by intervertebral discs. However, they are various anatomical features ...
Why do thoracic vertebrae increase in size?
Thoracic vertebrae increase in size as they descend towards the lumbar vertebrae; this is because the lower vertebrae must be able to support more of the body’s weight when a person is standing due to the effects of gravity. To summarize, the main anatomical components of a thoracic vertebra are: Body. Spinous process.
How many discs are there in the human body?
In total, the adult human body typically has 23 discs, with the first found between cervical vertebrae 2 and 3, and the last one is found between the lumbar vertebra and the sacrum.
What is the ribs of a vertebra?
Ribs are generally inserted between two vertebrae, such that each vertebra contributes to articulating with half of the articular surface. Each vertebra therefore has a pair of superior articular facets that face posteriorly and a pair of inferior articulating facets that face anteriorly (except for T12).
