
What is pacemaker Oversensing?
Oversensing. Oversensing occurs when the pacemaker senses electrical signals that it should not normally encounter, which results in inappropriate inhibition of the pacing stimulus.
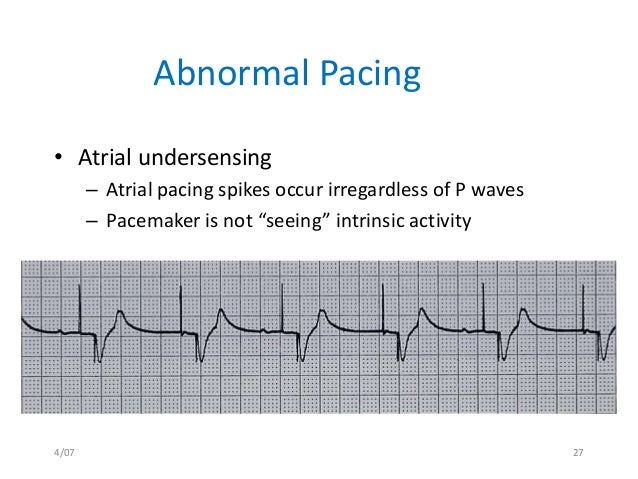
How do you fix a pacemaker Undersensing?
Failure to sense intrinsic beats• If the pacemaker is undersensing (it fires at the wrong times or for the wrong reasons), turn up the sensitivity control. Change the battery or pulse generator. Remove items in the room that might be causing electromechanical interference. Check that the bed plug is grounded.
What are 4 things to be avoided if you have a pacemaker device?
Discuss the following in detail with your doctor:It is generally safe to go through airport or other security detectors. ... Avoid magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines or other large magnetic fields. ... Avoid diathermy. ... Turn off large motors, such as cars or boats, when working on them.More items...
What are the 4 common issues with pacemakers?
Problems with the pacemaker the lead gets pulled out of position. the battery of the pulse generator fails. the circuits that control the pacemaker are damaged after being exposed to strong magnetic fields. the pacemaker has not been properly programmed.
How do you fix far field R wave Oversensing?
Solutions to Far-Field R–Wave Oversensing In patients with atrial electrograms of adequate amplitude and an amplitude ratio of atrial to far-field R wave >2:1, the simplest approach is to reduce the minimum atrial sensitivity (increase the programmed value) to 0.45 to 0.6 mV.
What are the most common problems with a pacemaker?
RisksInfection near the site in the heart where the device is implanted.Swelling, bruising or bleeding at the pacemaker site, especially if you take blood thinners.Blood clots (thromboembolism) near the pacemaker site.Damage to blood vessels or nerves near the pacemaker.Collapsed lung (pneumothorax)More items...•
What medicine should you not take if you have a pacemaker?
Medications to avoid if you're a heart patientAspirin. If you're on blood thinners, beware of aspirin. ... NSAID pain relievers, such as naproxen and ibuprofen. ... Certain antibiotics. ... Antihistamines. ... Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
What are the symptoms of a low battery in a pacemaker?
Chest pain, dyspnea accompanied by changes of pacing mode and rate in patient with pacemaker suggest the possibility of battery depletion of pacemaker.
What is the life expectancy of a person with a pacemaker?
Table 2.5 year20 year survivalOverall65.5%21.4%SSS73.5%26.6%AVB62.0%19.2%AFIB58.6%14.9%
What are the long term side effects of a pacemaker?
Five common permanent cardiac pacemaker complicationsHematoma. Of the various pacemaker complications, generator pocket hematoma is the most common, accounting for over 3% of pacemaker complications. ... Lead dislodgement requiring intervention. ... Infection. ... Lead perforation. ... Dysrhythmias. ... Conclusion.
Can your heart stop with a pacemaker?
Once someone stops breathing, his body can no longer get oxygen and the heart muscle will die and stop beating, even with a pacemaker. Therefore, the pacemaker will not prevent death and a patient will die from his terminal illness without turning off the pacemaker.
Does a pacemaker weaken the heart?
But activating the pacemaker function in the right side of a patient's heart may be throwing off synchronization with the left side, causing the heart to lose efficiency and deteriorate, said the report, which is to appear next Wednesday in The Journal of the American Medical Association.
What happens when a pacemaker lead comes loose?
Pacemaker lead dislodgement may cause malfunction in the pacing system, which may lead to severe adverse events.
What is functional Undersensing?
Functional undersensing occurs when the pacemaker does not sense intrinsic activity during the period when sensing is disabled. This is an appropriate form of undersensing, and was discussed previously (refer to PVARP). Undersensing can lead to overpacing, because the pacemaker does not sense ongoing activity.
How is pacemaker failure treated?
Medical Care Apply transcutaneous pacing pads if external pacing is necessary. Administer intravenous fluids and inotropic support if symptomatic hypotension. Reprogram the pulse generator based on underlying pacing malfunction. Any sign of hemodynamic instability should prompt intensive care and close monitoring.
What does it look like when a pacemaker fails to capture?
2:385:19Cardiac Pacing (Failure to Capture/Failure to Sense) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo failure to sends is very very bad and it can lead to an R on T situation which can trigger v-fib.MoreSo failure to sends is very very bad and it can lead to an R on T situation which can trigger v-fib. Now in this example spike appears on the T wave and that's seen as the third pace or spike.
What is upper rate behavior?
Upper-rate behavior refers to the pacing characteristics seen in dual-chambered pacemakers programmed to an atrial tracking mode as the atrial rate increases and approaches a certain upper threshold. In dual-chambered devices, it is necessary to limit the rate at which the ventricle can pace in the presence of high atrial rates. This limit is called the maximum tracking rate (MTR) and is a programmable value. The upper-rate behavior depends upon MTR and total atrial refractory period (TARP). The TARP is equal to AV delay + PVARP. When the atrial rate exceeds MTR, it results in pacemaker Wenckebach. If the atrial rate keeps increasing and exceeds the TARP, it will result in pacemaker 2:1 AV block.3
What is a pacemaker mediated tachycardia?
Pacemaker-Mediated Tachycardia. Pacemaker-mediated tachycardia is an endless-loop tachycardia, sustained, in part, by the presence of the pacemaker. Pacemaker-mediated tachycardia requires the presence of retrograde ventriculoatrial conduction and a triggering event like premature ventricular contraction or loss of AV synchrony. Pacemaker-mediated tachycardia is similar to a re-entrant tachycardia, except that the pacemaker forms part of the re-entrant circuit; the tachycardia could therefore be avoided by programming a sufficiently long postventricular atrial refractory period (PVARP).10Placing a magnet on the device during the PMT will change the pacemaker's mode to dual-chamber pacing mode (in DOO, intrinsic P waves and R waves are ignored), which results in the termination of tachycardia by suspending the pacemaker's sensing function (Fig. 7).4,10
What is crosstalk in ECG?
Surface electrocardiogram (ECG) with intracardiac atrial and ventricular electrograms (EGMs). This is an example of crosstalk wherein the pacing signal from one channel (in this case, the atrium) is sensed on the other channel (in this case, the ventricle). In this example, the cross-sensed signal is ignored and no action is taken by the pacemaker. In other situations, the cross-sensed signal can be misconstrued as a pacemaker malfunction and can trigger ventricular safety pacing.
What is ventricular safety pacing?
Ventricular Safety Pacing. Ventricular safety pacing (SP) prevents ventricular asystole due to crosstalk. Pacemaker crosstalk in a dual-chamber pacemaker refers to the detection of a paced signal in one chamber by the lead in another chamber, and to the misrepresentation of the paced signal as a cardiac depolarization signal. This, in turn, results in inappropriate inhibition of pacing in the 2nd chamber.8
What does a sinus P wave mean on an electrocardiogram?
Ventricular oversensing. Surface electrocardiogram shows sinus rhythm with ventricular pacing. After the 3rd sinus P wave, the pacing spike is absent—which suggests oversensing by the pacemaker, with inappropriate inhibition of pacing and an asystolic pause in a pacemaker-dependent patient.
What causes a pacemaker to oversensor?
Oversensing occurs when the pacemaker senses electrical signals that it should not normally encounter, which results in inappropriate inhibition of the pacing stimulus. In addition to the native cardiac depolarization signals (P or R waves), any electrical signal with sufficient amplitude and frequent occurrence can be sensed and can inhibit the pacemaker when pacing is needed. Oversensing can be caused by physiologic signals like T waves or by myopotential (and nonphysiologic) signals like electromagnetic interference or a lead failure (an insulation break or a lead fracture) (Fig. 4).7
What is the rate of a ventricular noncapture?
Pacing spikes are visible at a rate of 65 beats/min and are marching through without capture, even though the ventricular myocardium is not expected to be refractory at those times.
What is oversensing PM?
That's the easy one. Now for OVERSENSING. Oversensing is the PM sensing inappropriate electrical activity. That's a fancy way of saying it senses NOISE. Noise is any activity that is NOT supposed to be there - like static on a radio.
Why is it called oversensing when the PM is at a low voltage?
If the noise is at .2 Volts, they set sensitivity at .3 Volts - the PM will ignore the noise. Any time the PM acts on the noise, it is called OVERSENSING, because the sensitivity is set too LOW.
What does F'rinstance mean?
F'rinstance - the electrical trace shows a Blip that is not supposed to be there or you're undergoing surgery & the surgeon uses electro-cautery that causes electrical activity to occur in the heart area & the PM senses it. There can be other stray electrical activity caused by the nervous system that may occur.
How does the strip tell you that you are oversensed?
How does the strip tell them that you are oversensed? Also easy. there is a marker channel on the strip that shows where each PM output pulse is located. They find one for the Atria (or Ventricles) & look up to the ECG trace & look for the corresponding squiggle on it. If it's not there, you have been oversensed.
Is the ventricle voltage higher than the atrial voltage?
The same definitions apply to the Ventricle voltages & their sensing - except that they are MUCH higher than the Atrial voltages.
Problems with Sensing
Problems with Pacing
- Output failure 1. Output failure occurs when a paced stimulus is not generated in a situation where expected. 2. Results in decreased or absent pacemaker function. 3. Multiple causes including oversensing, wire fracture, lead displacement, or interference. Failure to capture 1. Failure to capture occurs when paced stimulus does not result in myocardial depolarisation. 2. …
Pacemaker Associated Dysrhythmias
- Several types of pacemaker associated dysrhythmias can occur including pacemaker-mediated tachycardia (PMT), sensor-induced tachycardia, runaway pacemaker, pacemaker-mediated Wenckebach AV block and lead dislodgement dysrhythmia. 1. Also known as endless-loop tachycardia or pacemaker circus movement tachycardia. 2. PMT is a re-entry tachycardia in whi…
ECG in Pacemaker Malfunction
- Normal pacemaker rhythms can result in absent pacing activity, irregular pacing and absence of pacing spikes.
- Diagnosis of pacemaker malfunction on the ECG is very difficult and may be impossible depending on the underlying native rhythm.
- If pacemaker malfunction is suspected cardiology review is required to facilitate pacemaker i…
- Normal pacemaker rhythms can result in absent pacing activity, irregular pacing and absence of pacing spikes.
- Diagnosis of pacemaker malfunction on the ECG is very difficult and may be impossible depending on the underlying native rhythm.
- If pacemaker malfunction is suspected cardiology review is required to facilitate pacemaker interrogation and testing.