According to the ASCD, Understanding by Design (abbreviated as UbD) is a “planning process and structure to guide curriculum, assessment, and instruction” which contains two core concepts:
- The idea that all teaching and assessment should be focused on developing students’ deep understanding of course concepts and ability to transfer their knowledge and skills; and
- The design of curriculum “backwards” to achieve this goal
What is Understanding by Design in education?
Understanding by Design, or UbD, is an educational planning approach. UbD is an example of backward design, the practice of looking at the outcomes in order to design curriculum units, performance assessments, and classroom instruction. UbD focuses on teaching to achieve understanding.
How do you make a UbD lesson plan?
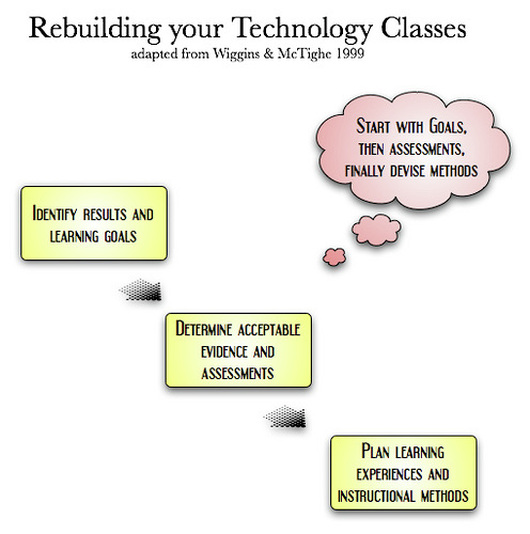
UbD is a process of backward curriculum design. There are three important steps to backward design planning: Identifying the desired outcome....Step 1: Identify desired results. ... Step 2: Determine a method of assessment. ... Step 3: Plan instruction and learning experiences.
What is understanding design?
Understanding by Design is a book written by Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe that offers a framework for designing courses and content units called “Backward Design.” Instructors typically approach course design in a “forward design” manner, meaning they consider the learning activities (how to teach the content), ...
What are the 3 stages of Understanding by Design?
Wiggins and McTighe (2005) described Understanding by Design through three stages: a) identify desired results, b) determine acceptable evidence, and c) plan learning experiences and instruction (see Figure 1).
Why should teachers use UbD?
The UbD framework helps to focus curriculum and teaching on the development and deepening of student understand- ing and transfer of learning (i.e., the ability to effectively use content knowledge and skill).
What is the goal of UbD?
A primary goal of UbD is developing and deepening student understanding: the ability to make meaning of learning via “big ideas” and transfer learning. Understanding is revealed when students autonomously make sense of and transfer their learning through authentic performance.
What is Understanding by Design example?
Simplified again: what your students will DO to understand the concept, and how they will do it. Examples could be performance tasks, where students demonstrate their understanding, or evidence like tests and quizzes, homework, prompts, and reflections.
How does Understanding by Design help students?
Understanding by design (UBD) helps students apply what they learn in a course to the real world, which deepens and enriches their learning experience. UBD is based on the principle of backward design and its three stages.
What are the strengths of Understanding by Design?
Through Understanding by Design, educators are able to develop curriculum and learning experiences that will help students develop and deepen their understanding of important ideas, and to ultimately transfer their learning in meaningful ways.
What are essential questions in UbD?
Essential questions are open-ended questions that naturally recur. They enable students to make meaning rather than simply take or receive them. They help students truly understand ideas by driving them to ponder, edit, debate, and discuss these questions.
What are the 5 D's of design thinking?
The 5 D's are Discovery, Design, Development, Delivery and Debrief. Anderson introduced the concept and discussed the first two D's in her first installment.
What are the 4 steps in design process?
Four Stages of Design ThinkingClarify. The clarification stage involves observing and framing findings. ... Ideate. With your problem statement or question defined, you can use observations to think of potential solutions. ... Develop. The third stage focuses on developing ideas from the ideation phase. ... Implement.
How do you use backward design planning?
There are three stages to the process of backwards design: Identify the desired results. Identify evidence of learning. Design the instructional plan.
What is the format of detailed lesson plan?
A detailed lesson plan (DLP) is exactly that, a detailed description of the exact steps to teach a specific topic. A DLP includes five parts of thorough explanation on, lesson topic, class objectives, procedure, time management and student practice.
What are the parts of lesson plan?
The most effective lesson plans have six key parts:Lesson Objectives.Related Requirements.Lesson Materials.Lesson Procedure.Assessment Method.Lesson Reflection.
What are big ideas in UbD?
The term “big ideas” comes from Understanding by Design (UBD), an approach to designing academic courses that values “backward design,” which means starting the design of your course with a big idea and working backward through learning outcomes, assessments, activities and lessons.
What is understanding by design?
Understanding by Design is a book written by Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe that offers a framework for designing courses and content units called “Backward Design.”. Instructors typically approach course design in a “forward design” manner, meaning they consider the learning activities (how to teach the content), ...
What is the first stage of a lesson?
In the first stage, the instructor must consider the learning goals of the lesson, unit, or course. Wiggins and McTighe provide a useful process for establishing curricular priorities. They suggest that the instructor ask themselves the following three questions as they progressively focus in on the most valuable content:
Why are big ideas and important understandings referred to as enduring understandings?
The big ideas and important understandings are referred to as enduring understandings because these are the ideas that instructors want students to remember sometime after they’ve completed the course.
What is the second stage of backward design?
The second stage of backward design has instructors consider the assessments and performance tasks students will complete in order to demonstrate evidence of understanding and learning. In the previous stage, the instructor pinpointed the learning goals of the course. Therefore, they will have a clearer vision of what evidence students can provide to show they have achieved or have started to attain the goals of the course. Consider the following two questions at this stage:
Why is backward design beneficial?
As previously stated, backward design is beneficial to instructors because it innately encourages intentionality during the design process.
What is the second stage of learning?
Once the learning goals have been established, the second stage involves consideration of assessment. The backward design framework suggests that instructors should consider these overarching learning goals and how students will be assessed prior to consideration of how to teach the content.
What is deliberate instructional design?
“Deliberate and focused instructional design requires us as teachers and curriculum writers to make an important shift in our thinking about the nature of our job. The shift involves thinking a great deal, first, about the specific learnings sought, and the evidence of such learnings, before thinking about what we, as the teacher, will do or provide in teaching and learning activities.”
What is UBD in teaching?
Understanding By Design, or UBD, is a framework and accompanying design process for thinking decisively about unit lesson planning. The concept was developed by Jay McTighe and Grant Wiggins, and as part of their principles they state that UBD “…is not a philosophy of education”. It is not designed to tell teachers what or how to teach; it is a system to help them teach more effectively. In fact, its flexibility is one reason it has gained so much acclaim. With UBD, the ultimate goal is to think backward, focusing on the big picture: at the end of a unit what is the essential question your students should be able to answer?
What are essential questions?
Your essential questions are the base of your UBD unit, so it is important that you know what essential questions are. To keep it simple, the questions are open-ended, thought-provoking, and engaging. These are often characterized by a call for higher-order thinking which points towards transferable ideas. They are not simple questions; they need support and justification, and often require that the student ask other questions before getting an answer. Most importantly, an essential question recurs over time. Without a strong essential question, you cannot move forward in your design and implementation. To assist you, see the examples below.
What is the acronym for "whereto"?
WHERETO is an acronym to help execute Stage 3 and is explained below. (Another acronym to help with the process of writing Stage 3 is GRASPS) When considering your unit you must recognize what is expected of your students throughout the process. This table includes how will they be evaluated, judged, and graded:
What is the goal of writing an essay?
Writing is a way to express your knowledge of a topic and show your interest in it.
Why is writing important?
Writing allows you to express multiple levels of color, including connotation, mood, and tone. Writing is a process to strengthen ideas and clarify perceptions. Becoming a better writer helps you to become a better reader. Writing is a powerful form of communication where you can express ideas in a systematic fashion.
Is Storyboards private?
All storyboards are private and secure to the portal using enterprise-class file security hosted by Microsoft Azure. Within the portal, all users can view and copy all storyboards. In addition, any storyboard can be made “sharable”, where a private link to the storyboard can be shared externally. Education Pricing.
Can you see storyboards on Google?
All storyboards are public and can be viewed and copied by anyone. They will also appear in Google search results.
What is backwards design?
Using a backwards design offers a concrete way of communicating learning expectations. Creating a clear set of learning expectations using Understanding by Design often creates higher student achievement because the organized approach outlines what is to be learned at the end of a lesson or unit. Wiggins and McTighe (2005) described Understanding by Design through three stages: a) identify desired results, b) determine acceptable evidence, and c) plan learning experiences and instruction (see Figure 1).
Why should instructors consider prior knowledge and skills when creating instructional objectives?
The instructor should consider the learners' prior knowledge and skills when creating instructional objectives in order to challenge learners while providing scaffolding opportunities. The WHERETO elements, described below, serve as a framework for best practices when creating learning experiences and instruction.
How to hook learners into a lesson?
This can be done as an interest approach through questioning key ideas from the lesson before, asking learners to watch a short clip that ties into the lesson, or having something at the front of the classroom that is unusual or different. There are many other activities that may hook the learners into the lesson.
How does perspective help in critical thinking?
Using perspective often helps build critical- thinking skills in learners by examining conclusions, implications, traditions, or assumptions created . An example of this in an Agricultural Foundations course may include hosting a debate in class on views of animal welfare versus animal rights. The instructor may ask learners to think about their viewpoint as to which they most agree with. Once the instructor has collected learner viewpoints, the instructor would divide learners into groups based on viewpoints. Learners must use critical thinking skills to argue why their point of view differs from the other group, why tradition leads society to believe one or the other, create conclusions based on facts, and discuss implications with associations from one viewpoint to the other. It is important that the instructor have the least amount of bias when utilizing this facet of understanding in instruction.
What is the ability to describe illustrations, theories, events, ideas, or actions?
Explanation is the ability to describe illustrations, theories, events, ideas, or actions. In this facet of understanding, the learner must make an account of how things work, why they work, why certain events occurred, and what they imply. This facet of understanding was first coined by Dewey (1933), who described this facet through explanation of things by noting how things work or operate, how certain things relate to one another, what are the results of those things occurring, and why certain things happen the way they do. An example of this in an Animal Science class may include having learners explain the ruminant digestive system through multiple short-answer responses. The instructor may ask what the functions of certain digestive system organs are, how the organs work together, have learners explain the nutritional components that may be associated with various digestive problems, or have learners explain what causes certain digestive issues to occur.
How is application measured in food science?
Application is often measured through performance-based learning (Kolb, 1984; Wiggins & McTighe, 2005). An example of this in a Food Science course may be though a class field trip to a local dairy packaging facility. Many of the learners have never been to a dairy packaging facility in the past. At the conclusion of the field trip, the instructor asks the learners to reflect on some of the safety and handling practices initiated at the facility. Learners then use their reflections from their experience to create their own dairy food safety HACCP plan for a local start-up dairy packaging facility.
What does the instructor ask students to read in a lab?
In lab, the instructor might ask learners to read a section of the lab report to interpret the background information on light reactions associated with photosynthesis. At the conclusion on the lab, the instructor might ask learners to interpret a series of data collected by the class.

Overview
- Understanding by Designis a book written by Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe that offers a framework for designing courses and content units called “Backward Design.” Instructors typically approach course design in a “forward design” manner, meaning they consider the learning activities (how to teach the content), develop assessments around their lear...
The Benefits of Using Backward Design
- “Our lessons, units, and courses should be logically inferred from the results sought, not derived from the methods, books, and activities with which we are most comfortable. Curriculum should lay out the most effective ways of achieving specific results… in short, the best designs derive backward from the learnings sought.” In Understanding by Design, Wiggins and McTighe argue t…
The Three Stages of Backward Design
- “Deliberate and focused instructional design requires us as teachers and curriculum writers to make an important shift in our thinking about the nature of our job. The shift involves thinking a great deal, first, about the specific learnings sought, and the evidence of such learnings, before thinking about what we, as the teacher, will do or provide in teaching and learning activities.”
The Backward Design Template
- A link to the blank backward design template is provided here (https://jaymctighe.com/resources/), and it is referred to as UbD Template 2.0. The older version (version 1.0) can also be downloaded at that site as well as other resources relevant to Understanding by Design. The template walks individuals through the stages of backward desig…
References
- Sample, Mark. (2011). Teaching for Enduring Understanding. Retrieved from http://www.chronicle.com/blogs/profhacker/teaching-for-enduring-understanding/35243.
- Wiggins, Grant, and McTighe, Jay. (1998). Backward Design. In Understanding by Design(pp. 13-34). ASCD.