Urea, also known as carbamide This medication has 2 types of ingredients that work together to treat or prevent dry, rough, scaly, itchy skin. Dry skin is caused by a loss of water in the upper layer of the skin. Emollients are substances that soften and moisturize the skin and decrease itching and flaking.Urea
What does urea mean?
Urea is a substance in the body during the liver’s protein and nitrogen compounds and generally excrete through urine and sweat. In case it is not eliminated correctly, the levels of urea in the blood rise above average (uremia), which causes health problems that significantly affect the liver.
What is urea and how is it formed?
- Urea is used in topical dermatological products to help the skin rehydrate. ...
- De-icing using urea is a safe, non-corrosive fertilizer solution. ...
- Physicians discovered that urea levels can be used to detect kidney diseases and disorders such acute kidney failure and end-stage renal disease (ESRD). ...
What are the different uses of urea?
Urea Uses - What Is Urea Used For?
- It is mainly used as a nitrogen release fertilizer to make the product water-soluble.
- Urea is used as a stabilizer in most of the nitrocellulose explosive products.
- It is used in manufacturing high explosive materials like urea nitrate (CH5N3O4)
- It is used as an important reagent in lanthanide chemistry.
What is the function of urea?
What is urea and what role does it play in the body?
- What is urea? Urea is the end product of protein metabolism in the body. ...
- What is the urea index? Normal blood urea nitrogen is at 0.2 – 0.4 g/l, can increase to about 0.1 – 0.5 g/l and is still assessed as normal ...
- The role of urea in the body
What is urea?
Urea is the chief nitrogenous end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in all mammals and some fishes. It occurs not only in the urine of...
What is the chemical name of urea?
The chemical name of urea is carbamide, the diamide of carbonic acid. Its formula is H2NCONH2.
Who first synthesized urea?
German chemist Friedrich Wöhler first synthesized urea from ammonium cyanate in 1828. It was the first generally accepted laboratory synthesis of a...
What is urea used for?
Urea is used as a fertilizer and feed supplement, as well as a starting material for the manufacture of plastics and drugs.
What is the purpose of urea?
Urea is used as a fertilizer and feed supplement, as well as a starting material for the manufacture of plastics and drugs. Urea is the chief nitrogenous end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in all mammals and some fishes. The material occurs not only in the urine of all mammals but also in their blood, bile, milk, and perspiration.
What is the formula for urea in encyclopedia?
See Article History. Alternative Title: carbamide. Urea, also called carbamide, the diamide of carbonic acid. Its formula is H 2 NCONH 2.
What is the end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in all mammals and some fishes?
Urea is the chief nitrogenous end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in all mammals and some fishes. It occurs not only in the urine of mammals but also in their blood, bile, milk, and perspiration.
What is the formula for urea?
Urea, also called carbamide, the diamide of carbonic acid. Its formula is H 2 NCONH 2. Urea has important uses as a fertilizer and feed supplement, as well as a starting material for the manufacture of plastics and drugs. It is a colourless, crystalline substance that melts at 132.7° C (271° F) and decomposes before boiling.
When was urine first isolated?
Urea was first isolated from urine in 1773 by the French chemist Hilaire-Marin Rouelle. Its preparation by the German chemist Friedrich Wöhler from ammonium cyanate in 1828 was the first generally accepted laboratory synthesis of a naturally occurring organic compound from inorganic materials.
Who made urea?
German chemist Friedrich Wöhler first synthesized urea from ammonium cyanate in 1828. It was the first generally accepted laboratory synthesis of a naturally occurring organic compound from inorganic materials. Urea is now prepared commercially in vast amounts from liquid ammonia and liquid carbon dioxide.
Is urea nitrogen a protein?
Although urea nitrogen is in nonprotein form, it can be utilized by ruminant animals (cattle, sheep), and a significant part of these animals’ protein requirements can be met in this way. The use of urea to make urea–formaldehyde resin is second in importance only to its use as a fertilizer.
Why Is Urea Important?
Furthermore, urea plays a role in the reabsorption of water in the kidneys, and is important for maintaining a good water balance in the body. It functions as a signal to the body to produce hyper-concentrated urine, rather than further draining the body of water.
Where is urea produced?
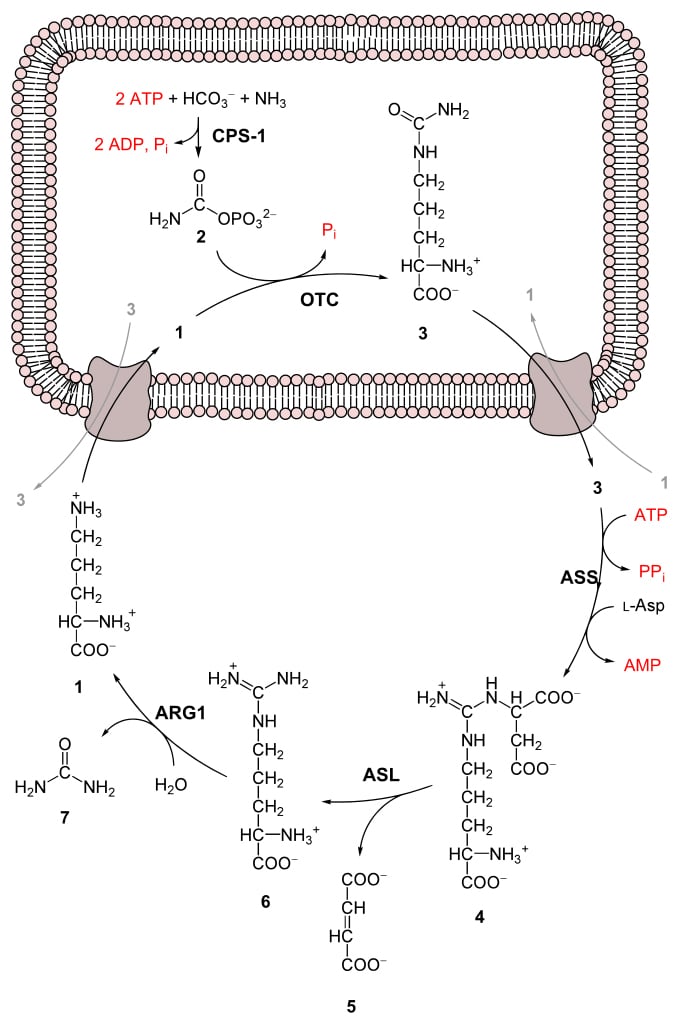
Urea is produced in the liver through the Urea Cycle, which occurs in both the mitochondria and cytoplasm of liver cells.
What is the process of metabolizing amino acids?
The Urea Cycle, also known as the Krebs-Henseleit Cycle, is how these small chains of amino acids, that are not reconstituted for new protein production, can ultimately be metabolized to generate energy for the body. When amino acids are metabolized in the liver, they produce free ammonia, as well as carbon dioxide.
What is the urea cycle?
The Urea Cycle. The majority of the food that we eat can be categorized as either fats, proteins or carbohydrates, all of which can produce energy for the body when it is metabolized or broken down. Carbohydrates are broken down into sugars through a number of enzymatic processes, which can then be metabolized for energy.
Where are proteins broken down?
Fats and oils are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol in the small intestines. Finally, proteins are broken down into amino acids by hydrochloric acid and specialized enzymes, at which point those amino acids move into the small intestine. The Urea Cycle, also known as the Krebs-Henseleit Cycle, is how these small chains of amino acids, ...
Is urea a chemical reaction?
On a cellular level, however, these metabolic activities can be broken down into chemical reactions, some of which create byproducts that the body needs to eliminate. Urea is the final, non-toxic product of such a metabolic cycle, which can then be eliminated from the body.
What is urea used for?
Automobile systems. Urea is used in Selective Non-Catalytic Reduction (SNCR) and Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) reactions to reduce the NO x pollutants in exhaust gases from combustion from diesel, dual fuel, and lean-burn natural gas engines.
How is urea produced?
For use in industry, urea is produced from synthetic ammonia and carbon dioxide. As large quantities of carbon dioxide are produced during the ammonia manufacturing process as a byproduct from hydrocarbons (predominantly natural gas, less often petroleum derivatives), or occasionally from coal (steam shift reaction), urea production plants are almost always located adjacent to the site where the ammonia is manufactured. Although natural gas is both the most economical and the most widely available ammonia plant feedstock, plants using it do not produce quite as much carbon dioxide from the process as is needed to convert their entire ammonia output into urea. In recent years new technologies such as the KM-CDR process have been developed to recover supplementary carbon dioxide from the combustion exhaust gases produced in the fired reforming furnace of the ammonia synthesis gas plant, allowing operators of stand-alone nitrogen fertilizer complexes to avoid the need to handle and market ammonia as a separate product and also to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions to the atmosphere.
How much protein is in a gram of nitrogen?
Furthermore, 1 gram of nitrogen is roughly equivalent to 6.25 grams of protein, and 1 gram of protein is roughly equivalent to 5 grams of muscle tissue.
What happens when urae breaks down?
In some soils, the ammonium is oxidized by bacteria to give nitrate, which is also a plant nutrient. The loss of nitrogenous compounds to the atmosphere and runoff is both wasteful and environmentally damaging.
How does the liver use urea?
The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules (NH 3) with a carbon dioxide (CO 2) molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important raw material for the chemical industry .
What is the chemical formula for urea?
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO (NH 2) 2. This amide has two –NH 2 groups joined by a carbonyl (C=O) functional group .
When was urine first discovered?
Urea was first discovered in urine in 1727 by the Dutch scientist Herman Boerhaave, although this discovery is often attributed to the French chemist Hilaire Rouelle as well as William Cruickshank.
Which organ is responsible for the regulation of water and inorganic ions?
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions. The kidneys are responsible for the regulation of water and inorganic ions. Read this tutorial to learn about the different parts of the kidneys and its role in homeostasis...
What is the final product of many organisms?
Urea. urea. (Science: biochemistry) The final nitrogenous excretion product of many organisms. The chief solid component of mammalian urine; synthesized from ammonia and carbon dioxide and used as fertilizer and in animal feed and in plastics.A molecules created from ammonia and carbon dioxide as a result of the urea cycle.
What are the roles of proteins in the body?
Proteins have a crucial role in various biological activities. Get to know how proteins are able to perform as enzymes, cofactors, or regulators. In this tutorial, you will also know the common metabolic pathways of biomolecules, such as glucose and other carbohydrates, fats, proteins and amino acids, and essential nutrients...
What is the inhibitor of urease?
Effects of drugs and other therapeutic measures: Urease is inhibited by acetohydroxamic acid, suramin, furacin and other compounds 22–25; hydroxyurea is a substrate and competitive inhibitor of urease 26.
How does urea reabsorption affect the proximal tubules?
Urea may experience passive reabsorption in the proximal tubules, depending on tubular flow rate. Increased tubular flow , as occurs during diuresis, is the result of decreased reabsorption of water from the tubular fluid. This decreases the tubular fluid urea concentration and decreases the concentration gradient of urea across the tubular epithelium. Thus less urea is reabsorbed at higher tubular flow rates. With decreased tubular flow, as occurs during dehydration, there is increased reabsorption of water from the tubular fluid. This increases the concentration gradient of urea across the tubular epithelium and increases passive urea reabsorption. In dehydrated patients, increased reabsorption of urea may lead to an increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) even before GFR is decreased. This contributes to the observation that the BUN/creatinine ratio tends to be higher in patients with prerenal azotemia than in hydrated patients with primary renal azotemia.
Where is UT2 located?
UT2 is found in the descending thin limbs of Henle's loops and allows urea to reenter the descending thin limbs, thus preventing its escape from the renal medulla (so-called urea recycling). UT3 is found in the descending vasa recta and participates in countercurrent exchange between ascending and descending vasa recta.
Where is urine formed?
Urea is formed in the liver and composes the major fraction of the organic substances present in urine.
Is urea ionic or non-ionic?
In general commercially available urea contains some level of ionic species. To avoid any ionic species from contaminating the IEF system, the urea was de-ionized prior to use by passing through amberlyte mixed bed ion-exchanger. Three different urea concentrations, 0 M, 2 M, and 4 M were used in this study.
Where is urea found?
urea. 1. the diamide of carbonic acid found in urine, blood, and lymph, the chief nitrogenous constituent of urine, and the chief nitrogenous end-product of protein metabolism; it is formed in the liver from amino acids and from ammonia compounds. 2. a pharmaceutical preparation of this compound, administered intravenously as an osmotic diuretic ...
What is urea nitrogen?
urea nitrogen the urea concentration of serum or plasma, conventionally specified in terms of nitrogen content and called blood urea nitrogen (BUN), an important indicator of renal function.
Why is urea toxic to the body?
Because urea contains ammonia, which is toxic to the body, it must be quickly filtered from the blood by the kidneys and excreted in the urine. Mentioned in: Blood Urea Nitrogen Test, Escherichia Coli, Kidney Function Tests. Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
Why does urea increase with protein?
The amount of urea in the urine increases with the quantity of protein in the diet because urea is an endogenous and exogenous waste product: endogenous because some of it is derived from breakdown of body protein as tissues undergo disintegration and repair, and exogenous because some of it is derived from the deamination of amino acids absorbed from the intestinal tract but not utilized by the body. In severe nephritis or other disorders leading to renal failure, the concentration of urea in the blood may be greatly increased, as revealed by measurement of the blood urea nitrogen (BUN).
What is the BUN test for renal failure?
In severe nephritis or other disorders leading to renal failure, the concentration of urea in the blood may be greatly increased, as revealed by measurement of the blood urea nitrogen (BUN). urea concentration test a test of renal efficiency, based on the fact that urea is absorbed rapidly from the stomach into the blood ...
What is the name of the compound that is found in urine?
urea. n. A water-soluble compound, CO (NH2) 2, that is the major nitrogenous end product of protein metabolism and is the chief nitrogenous component of the urine in mammals and certain other animals. Also called carbamide. The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company.
How is nitrogen produced in the liver?
It may be obtained artificially by heating a solution of ammonium cyanate.
What is the breakdown of amino acids called?
The breakdown of amino acids is called deamination. Photo credit: James X - Biology Blog. Urea is returned to the bloodstream (into the hepatic vein) and filtered out when it reaches the kidneys. The body treats alcohol as a poison.
Can amino acids be stored in the bloodstream?
Surplus amino acids in the bloodstream cannot be stored. They are removed by the liver and broken down into the urea (which is the nitrogen-containing part of the amino acid) and a sugar residue, which can be respired to release energy. The breakdown of amino acids is called deamination.
What is the difference between a ureter and a urethra?
Note that ‘ureter’ differs from the word ‘urethra’. The ureters are tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder, whereas the urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the body.
What is excretion in biology?
Excretion in plants and animals. Excretion is the removal of substances from plants, animals and other living organisms. In humans, the skin, lungs and kidneys are excretory organs. Part of. Biology (Single Science) Nutrition, digestion and excretion.
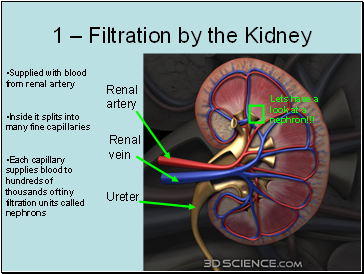
Where does blood go in the kidney?
Blood is brought to the kidney in the renal artery. The kidneys filter the blood and then reabsorb useful materials such as glucose. After it has been purified, the blood returns to the circulation through the renal vein.

Overview
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH2)2. This amide has two –NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl (C=O) functional group.
Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic (LD50 is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it i…
Uses
More than 90% of world industrial production of urea is destined for use as a nitrogen-release fertilizer. Urea has the highest nitrogen content of all solid nitrogenous fertilizers in common use. Therefore, it has a low transportation cost per unit of nitrogen nutrient. The most common impurity of synthetic urea is biuret, which impairs plant growth. Urea breaks down in the soil to give ammo…
Adverse effects
Urea can be irritating to skin, eyes, and the respiratory tract. Repeated or prolonged contact with urea in fertilizer form on the skin may cause dermatitis.
High concentrations in the blood can be damaging. Ingestion of low concentrations of urea, such as are found in typical human urine, are not dangerous with additional water ingestion within a reasonable time-frame. Many animals (e.g. dogs) have a much more concentrated urine and it c…
Physiology
Amino acids from ingested food that are used for the synthesis of proteins and other biological substances — or produced from catabolism of muscle protein — are oxidized by the body as an alternative source of energy, yielding urea and carbon dioxide. The oxidation pathway starts with the removal of the amino group by a transaminase; the amino group is then fed into the urea cycle. The first step in the conversion of amino acids from protein into metabolic waste in the liver is re…
Analysis
Urea is readily quantified by a number of different methods, such as the diacetyl monoxime colorimetric method, and the Berthelot reaction (after initial conversion of urea to ammonia via urease). These methods are amenable to high throughput instrumentation, such as automated flow injection analyzers and 96-well micro-plate spectrophotometers.
Related compounds
Ureas describes a class of chemical compounds that share the same functional group, a carbonyl group attached to two organic amine residues: RR'N–C(O)–NRR'. Examples include carbamide peroxide, allantoin, and hydantoin. Ureas are closely related to biurets and related in structure to amides, carbamates, carbodiimides, and thiocarbamides.
History
Urea was first discovered in urine in 1727 by the Dutch scientist Herman Boerhaave, although this discovery is often attributed to the French chemist Hilaire Rouelle as well as William Cruickshank.
Boerhaave used the following steps to isolate urea:
1. Boiled off water, resulting in a substance similar to fresh cream
2. Used filter paper to squeeze out remaining liquid
Production
Urea is produced on an industrial scale: In 2012, worldwide production capacity was approximately 184 million tonnes.
For use in industry, urea is produced from synthetic ammonia and carbon dioxide. As large quantities of carbon dioxide are produced during the ammonia manufacturing process as a byproduct from hydrocarbons (predominantly natu…