Transduction Definition
- Transduction is the transfer of bacterial DNA from a donor to a recipient bacterium via a virus particle.
- The virus particle that infects bacteria is called a bacteriophage or phage, and the phages used for the transfer of DNA are called transfusing phages.
- Not all phages are transducing phages. The process of transduction can transfer DNA regions of tens to hundreds of kilobases.
What is required to carry out transduction?
Transduction does not require physical contact between the cell donating the DNA and the cell receiving the DNA (which occurs in conjugation), and it is DNAase resistant. Transduction happens through either the lytic cycle or the lysogenic cycle.
What is the process of transduction?
Transduction is the process by which a virus transfers genetic material from one bacterium to another. Viruses called bacteriophages are able to infect bacterial cells and use them as hosts to make more viruses.
Which is the bacteriophage used in transduction?
The use of transduction in molecular microbiology labs rely on lytic bacteriophages, as opposed to a lysogenic cycle where the bacteriophage DNA integrates into a specific site in the host chromosome and remains dormant.
What is transduction with example?
Transduction is the process by which foreign DNA is introduced into a cell by a virus or viral vector. An example is the viral transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another and hence an example of horizontal gene transfer.
What are the three types of transduction?
The three types of Transduction: Generalized transduction, Specialized transduction, and Lateral transduction adopted from [62]. Bacteriophages, bacteria-infecting viruses, are considered by many researchers a promising solution for antimicrobial resistance.
Where does the process of transduction occur?
The Inner Ear (Cochlea) is where transduction takes place.
Which of the following viruses will be useful for transduction?
Explanation: T phages mainly undergo lytic cell cycle, while lamda phages have lysogenic cell cycle. For transduction to occur, the viral genome must integrate within the nucleoid else it will never incorporate bacterial gene within itself. Thus, only lamda phage will be able to help in transduction. 2.
How does phage transduction work?
Generalized and specialized transduction It is the process by which phages can package any bacterial DNA (chromosomal or plasmid) and transfer it to another bacterium. The transducing particles of this mode of transduction form when bacterial host DNA is packaged into phage heads instead of viral DNA.
What is true for bacterial transduction?
Hence, whether the transduction is specialized or generalized, there is always a transfer of genetic material from one bacterial cell to another bacterial cell by means of a virus. So, the correct answer is 'Transfer of some genes from one bacteria to another bacteria through virus'.
What cells are responsible for transduction?
A receptor cell converts the energy in a stimulus into an electrical signal. Receptors are broadly split into two main categories: exteroceptors, which receive external sensory stimuli, and interoceptors, which receive internal sensory stimuli.
What is transduction simple?
1 : the action or process of converting something and especially energy or a message into another form. 2 : the transfer of genetic material from one organism (as a bacterium) to another by a genetic vector and especially a bacteriophage — compare transformation sense 2. Other Words from transduction.
What is transduction in cell signaling?
Signal transduction is the process in which binding of an extracellular messenger to the cell surface receptor is translated into changes in biochemistry, cell biology, and gene transcription that make it possible for the cell to respond to the information that was received.
What is transduction in cell signaling?
(SIG-nul tranz-DUK-shun) The process by which a cell responds to substances outside the cell through signaling molecules found on the surface of and inside the cell.
What is transduction in nervous system?
transduction: the translation of a sensory signal in the sensory system to an electrical signal in the nervous system.
What is transduction in the eye?
Visual phototransduction is the sensory transduction process of the visual system by which light is detected to yield nerve impulses in the rod cells and cone cells in the retina of the eye in humans and other vertebrates.
What are the three stages of a signal transduction pathway?
In effect, signal transduction is said to have three stages: First, reception, whereby the signal molecule binds the receptor. Then, signal transduction, which is where the chemical signal results in a series of enzyme activations. Finally, the response, which is the resulting cellular responses.
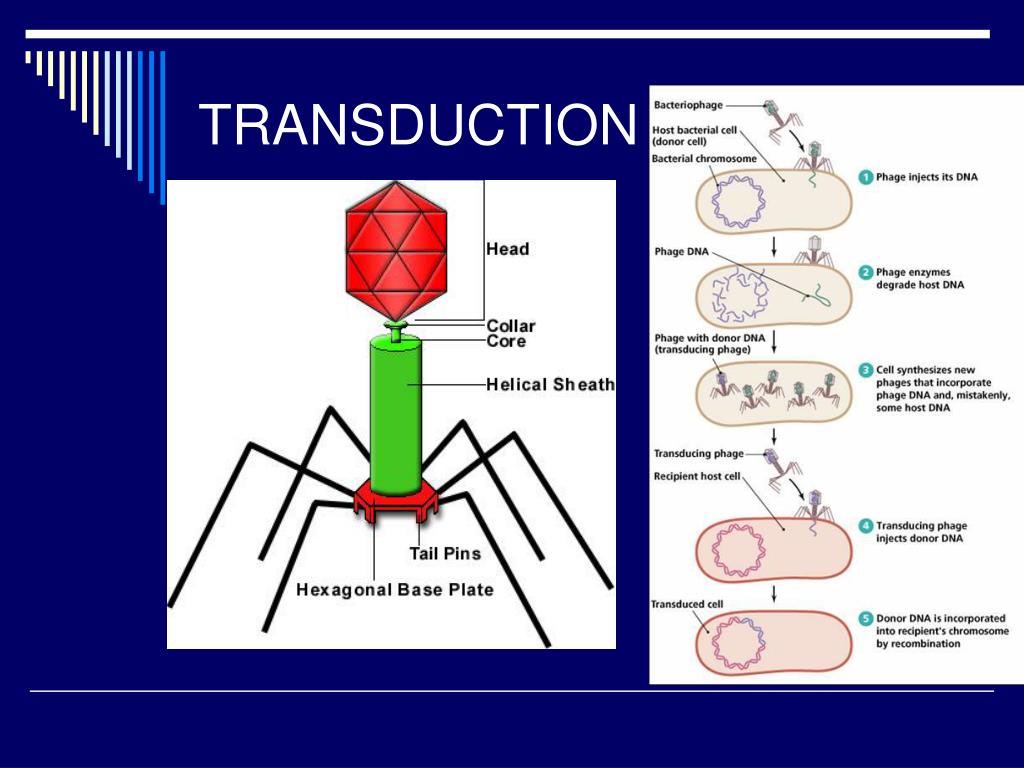
Bacterial Transduction Steps
In transduction, the transfer of bacterial DNA depends on viral infection. The steps involve:
Types of Transduction
Transduction is common in both virulent and temperate phages, i.e. by lytic or lysogenic cycle. Transduction is of two types:
Generalized Transduction
Generalized transduction can occur by both lytic or lysogenic cycle. Here, any random part of DNA gets packed in bacteriophages by mistake along with the viral genome. It occurs at the lytic stage of the phage life cycle.
Specialized Transduction
Specialized transduction can occur only through the lysogenic cycle, i.e. by temperate phage. Here, only the specific part of the bacterial DNA is packed into the virus. It occurs when the prophage, i.e. viral DNA, which gets inserted into the bacterial genome in the lysogenic cycle excises.
Application of Transduction
Transduction is one of the most important tools for genetic engineering.
Types
The transduction in bacteria occurs in two ways, either through a lytic or lysogenic cycle:
Generalized Transduction
It is the kind of Lytic phase, in which the bacteriophage only carries the pure bacterial DNA, not the phage DNA and this pure bacterial gene is inserted into the recipient cell.
Specialized Transduction
It is the kind of Lysogenic phase, in which the gene transfer occurs from one bacterial cell to the next via bacteriophages that do not carry the pure bacterial DNA, i.e. it contains both the bacterial DNA and the phage DNA.
Discovery (bacterial transduction)
Transduction was discovered by Norton Zinder and Joshua Lederberg at the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1952 in Salmonella.
In the lytic and lysogenic cycles
Transduction happens through either the lytic cycle or the lysogenic cycle. When bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) that are lytic infect bacterial cells, they harness the replicational, transcriptional, and translation machinery of the host bacterial cell to make new viral particles ( virions ).
As a method for transferring genetic material
The packaging of bacteriophage DNA into phage capsids has low fidelity. Small pieces of bacterial DNA may be packaged into the bacteriophage particles. There are two ways that this can lead to transduction.
Signal Transduction Definition
Signal transduction is the process of transferring a signal throughout an organism, especially across or through a cell. Signal transduction relies on proteins known as receptors, which wait for a chemical, physical, or electrical signal.
Signal Transduction Pathway
During signal transduction, a signal may have many components. There is the primary messenger, which may be a chemical signal, electrical pulse, or even physical stimulation. Then, the receptor protein embedded in the cellular membrane must accept the signal. Upon receiving the signal, this protein goes through a conformational change.
Examples of Signal Transduction
The signal transduction pathway of touch and vision works in the same way that many nerve signals do. Instead of creating a second messenger or processing a signal internally, the stimulation of the receptor protein causes an influx of ions into the cell. This causes the cell membrane to depolarize.
Quiz
1. Which of the following is NOT an example of signal transduction? A. A molecule found in blood binds to a protein in a shark’s olfactory cells. A signal is sent to the brain. B. Cow’s milk contains growth hormones. Upon receiving these hormones, a baby cow’s cells grow and divide. C.
Experimental Design
As we all remember from microbiology class, viruses need cells to “survive” as they lack the replication machinery to produce more copies of their genome. So one of the most important aspects of lentiviral vector delivery system experiments is the actual production of lentiviral vectors, which often takes place in HEK293 cells (or some variety).
Small RNAs For Targeted Knock-Down
Thanks to the user friendly web applications like siRNA Wizard, BLOCK-iT™ RNAi Designer, shRNA Designer and others, it has now become very easy to design shRNAs. Core facilities in universities may also offer to design and synthesize shRNAs according to your preferences.
Are Your HEK293 Cells Happy?
It is essential to maintain cells in good condition. Cells should be routinely checked and split when they reach about 80% confluency. HEK293 cells are fast growing and trypsinize quickly, so do not allow for HEK293 cells to incubate for long in trypsin (30-60s should do it), or you could witness large cell death.
Packing up for the Transduction
The next step is to package the lentiviral vector plasmid, along with viral packaging vectors, into liposomes for delivery into HEK293 cells.
Getting the Virus into the Cells
Now that we have the virus, it’s time to infect the target cells. In the majority of cases, it is important to titer your virus so that you know the concentration used for your experiment and can reliably repeat your results!
You Did It!
Check your cells for knockdown or your specific end point by the appropriate analytical method, typically this would involve a Western Blot.
References
Davis, H. E., J. R. Morgan, and M. L. Yarmush. 2002. Polybrene increases retrovirus gene transfer efficiency by enhancing receptor-independent virus adsorption on target cell membranes. Biophys. Chem. 97:159–172
