
What is Valency and atomic number? Atomic number is equal to total number of protons present in an atom while Valency is number of electrons required in the outermost shell of an atom to become stable.
What is the valency of an element?
What is Valency and atomic number? Atomic number is equal to total number of protons present in an atom while Valency is number of electrons required in …
How to find the valence of an atom?
Jul 09, 2017 · An atom’s valence is equal to the number of electrons in the outer shell when that number is four or fewer. Then the valence in the outer shell is equal to eight minus the number of electrons. Once you are aware of the number of electrons you can calculate the valence easily.
What is a valency chart?
Valency is the number of unpaired electrons that is present in the outside shell of the atomic orbits. The last unpaired in an electronic configuration is known as the valency of that element. For example, the atomic number of sodium is 11 and the number of last unpaired electrons contributes to the valency with the unpaired electron being 1.
Why is the valency of an atom with 7 electrons 1?
How do you find atomic number from valency? Mathematically we can say that if the outermost shell of an atom contains 4 or less than 4 electrons, then the valency of an element is equal to the number of electrons present in the outermost shell and if it is greater than 4, then the valency of an element is determined by subtracting the total number of electrons.
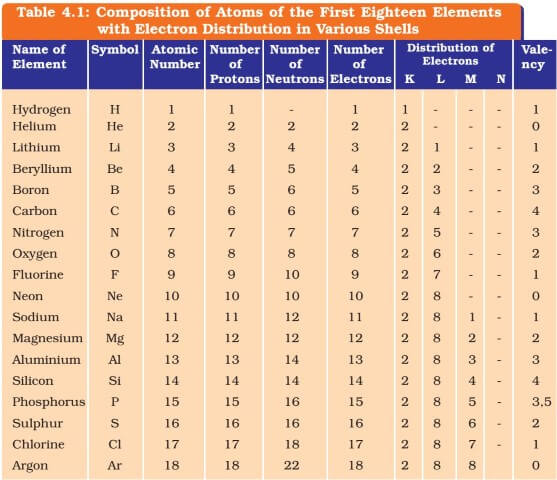
What is valency?
What is valency number?
Is valency and number of atoms same?
What is the atomic number?
What is valency class 11?
What is atomic number class 9th?
What is valency example?
What is the valency of first 20 elements?
| Element | Symbol | Valency |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon | C | 4 |
| Nitrogen | N | 3 |
| Oxygen | O | 2 |
| Fluorine | F | 1 |
What is valency formula?
What is valency class 9th?
How do you find the atomic number?
What is the atomic number of CL?
What is Valency and example?
An element’s valence is the number of hydrogen atoms which can combine with or replace (directly or indirectly) one of the element’s atoms. Oxygen,...
Can Valency be negative?
Loss of electron or electron gain called atom charge, Positive charge will be attained by donating an electron and negative charge vice versa. So v...
What is the importance of Valency?
The importance of valence: when two atoms react, their outer shell first comes into contact and it is, therefore, the outer shell electron that is...
Why is the Valency of nitrogen is 5?
Nitrogen has either 3 or 5 valence electrons and is on the periodic table at the top of Group 15. It can have either 3 or 5 valence electrons, as i...
How can we calculate Valency?
An atom’s valence is equal to the number of electrons in the outer shell when that number is four or fewer. Then the valence in the outer shell is...
1. What are valency and example?
Valency is the number of unpaired electrons that is present in the outside shell of the atomic orbits. The last unpaired in an electronic configura...
2. Can valency be negative?
With the loss and gain of an electron, there is again and loss of charge on the atom. The loss and gain of the charge can be of positive or negativ...
3. What is valency? How does valency help organize atoms into molecules?
Valency refers to the combining power of an atom in regard to making a chemical bond with another atom or with itself. Valency organizes atoms into...
4. What are some examples of valencies we encounter every day?
Some common examples of Valency include ionic bonds, covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds valency is used to understand how molecules interact with each...
5. What are some valency concepts?
Some common valency concepts include ionic bonding, covalent bonding, hydrogen bonding, and valency states. Valency states describe elements that h...
6. What can valency be used to explain? How does valency help us understand chemical reactions?
Valency can be used to explain the behaviour of molecules, large biological structures like proteins, and even the arrangement of elements in solid...
7. What should I do if I don't understand something about valency?
If you don't understand something about Valency, ask your teacher or classmates for help. Nobody knows everything and collaboration can be very eff...
8. How much time does it take to prepare for exams?
Valency is not an easy topic to learn, but practising Valency regularly can help students better understand Valency. It takes time and dedication i...
9. What final tips do you have about Valency?
First of all, study the basics of Valence thoroughly before moving on to more difficult topics like coordinate covalent bonds or electron pair repu...
What is the valence of an element?
The Valence, or known as valency, in Chemistry, is the characteristics of an element that indicates the number of other atoms with which an atom of a particular element can form a covalent bond. Introduced in 1868, the term is used for the expression of both the possibility of combination of an element in general and the numerical value ...
What is the meaning of valence?
Thus valence meaning is the number of electrons as most of the bonds are formed by the exchange of the valence electrons . The valence electrons determine ...
What is the formula for valence?
Hence, valency definition in chemistry can be shown by the formula as. Valence or Valency = Number of bonds formed + Formal charge of the atom.
What is the atomic number of sodium?
For example, the atomic number of sodium is 11 and the number of last unpaired electrons contributes to the valency with the unpaired electron being 1. Hence, the valency of sodium is 1. 2.
What is the role of electrons in the nucleus?
The Rutherford Model of the nucleus of an atom shows that the outside of an atom is filled by electrons, suggesting that the electrons are the ones responsible for the interaction of the atoms and the formation of the chemical bonds. Later, G. N. Lewis explained the valence and chemical bonding in terms of the nature of atoms to acquire a stable octet of eight valence-shell electrons. According to the theory proposed by Lewis, covalent bond formation leads to octet structure by sharing of the electrons, while ionic bonding leads to octet structure by the transfer of electrons from one atom to the other.
What does valency mean in chemistry?
What does the term ‘Valency’ mean? The valency of an element is a measure of its combining capacity and can be defined as. the number of electrons that must be lost or gained by an atom to obtain a stable electron configuration.
What is the valency of an element?
The valency of an element is a measure of its combining capacity and can be defined as. the number of electrons that must be lost or gained by an atom to obtain a stable electron configuration.
What is the oxidation state of an atom?
What does the term ‘Oxidation State’ mean? The oxidation state of an atom is the number of electrons lost or gained by it. Oxidation State and valency are one of the most fundamental properties of elements and can be studied with the help of electron configurations.
What are periodic trends in the oxidation states of elements?
Periodic Trends in the Oxidation States of Elements. 1. Variation Of Oxidation State Along a Period. While moving left to right across a period, the number of valence electrons of elements increases and varies between 1 to 8. But the valency of elements, when combined with H or O first, increases from 1 to 4 and then it reduces to zero.
Which element has a +1 oxidation state?
Similarly, hydrogen has +1. But in Metal Hydrides, such as NaH, LiH, etc, it has -1. Some elements have the same oxidation states as in their compounds such as. Halogens have -1 except the time they form a compound with one another or Oxygen. Alkali Metals such as Na, K, Rb, Li, Cs; have +1.

Atomic Number
Representation of Atomic Number
Atomic Numbers' Importance
Atomic Mass
Periodic Table
Valency
- The valency of an atomic orbit is the number of unpaired electrons in the outer shell. The valency of an element is the last unpaired electron in an electronic configuration. The atomic number of sodium, for example, is 11, and the valency is determined by the number of last unpaired electrons, with the unpaired electron numbering one. As a result,...
Things to Remember
Sample Questions