What is variation in science? Variation , in biology, any difference between cells, individual organisms, or groups of organisms of any species caused either by genetic differences (genotypic variation ) or by the effect of environmental factors on the expression of the genetic potentials (phenotypic variation ).
What is the importance of a variable in science?
variation, in biology, any difference between cells, individual organisms, or groups of organisms of any species caused either by genetic differences (genotypic variation) or by the effect of environmental factors on the expression of the genetic potentials (phenotypic variation).
What is the meaning of a variable in science?
Jun 03, 2020 · Variation, in biology, any difference between cells, individual organisms, or groups of organisms of any species caused either by genetic differences (genotypic variation) or by the effect of environmental factors on the expression of the genetic potentials (phenotypic variation).
What are the variables of a science experiment?
What is meant by variation in science? Variation, in biology, any difference between cells, individual organisms, or groups of organisms of any species caused either by genetic differences (genotypic variation) or by the effect of environmental factors on the expression of the genetic potentials (phenotypic variation).
What are the types of variation?
Mar 02, 2022 · In genetics, variation describes an individual who offers characteristics not the same as others of the identical kind. Genetic variation usually arises like a mutation inside a gene that encodes a protein or perhaps an RNA.

What is a variation easy definition?
1a : the act or process of varying : the state or fact of being varied. b : an instance of varying. c : the extent to which or the range in which a thing varies.
What is variation and example?
What is meant by variation in genetics?
What is variation in reproduction?
What is variation class 10?
What is a variation of a gene called?
What is variation and its sources?
What is variation in biology?
Medical Definition of variation. 1 : divergence in one or more characteristics of an organism or biotype from those typical of or usual for its group. 2 : something (as an individual or group) that exhibits variation.
What is variation in music?
: something that is similar to something else but different in some way. music : a repeated version of a short piece of music with changes in its rhythm, tune, or harmony.
What is variation in biology?
The differences in characteristics between individuals of the same species is called variation. Some variation is passed on from parents to offspring, via genes, during reproduction. This is inherited variation. Some variation is the result of differences in the surroundings, or what an individual does. This is called environmental variation.
What is environmental variation?
Some variation is the result of differences in the surroundings, or what an individual does. This is called environmental variation. A guide dog breeder explains the effect of variation on his puppies.
What are some examples of species?
Humans, dogs and goldfish are examples of species. Different species have very different characteristics from each other. For example, dogs have tails and humans do not. Dogs have fur, but goldfish have scales. The individual members of a species also have differences in characteristics.
What are the characteristics of an individual?
Characteristics in an individual are the result of both genetic and environmental variation. For example, the weight of a dog depends partly on its genes (inherited) and partly on what it eats (environmental). The height of a sunflower depends partly on its genes and partly on how much light and water it gets.
What is the survival of the fittest?
As a result of their genes, some individuals of a species might have better camouflage, or be able to run faster. These individuals are more likely to survive. This is called the survival of the fittest. The members of a species that survive may reproduce.
Do goldfish have scales?
Dogs have fur, but goldfish have scales. The individual members of a species also have differences in characteristics. For example, humans have different coloured eyes, and dogs have different length tails. This means that no two members of a species are identical.
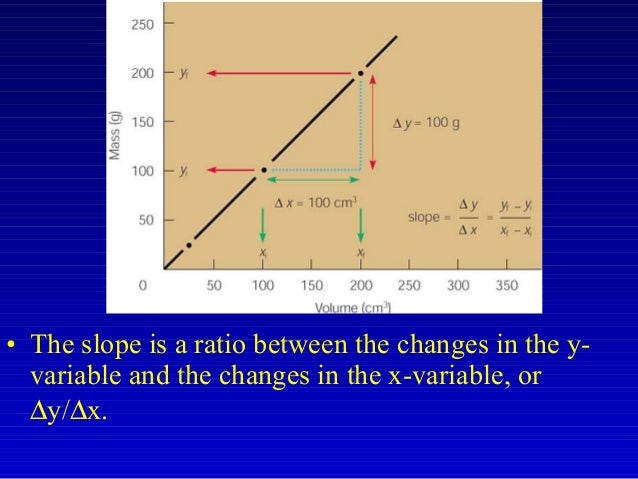
What is a variable in science?
Basically, a variable is any factor that can be controlled, changed, or measured in an experiment. Scientific experiments have several types of variables. The independent and dependent variables are the ones usually plotted on a chart or graph, but there are other types of variables you may encounter.
What are the two types of variables?
Types of Variables. Independent Variable: The independent variable is the one condition that you change in an experiment. Example: In an experiment measuring the effect of temperature on solubility, the independent variable is temperature. Dependent Variable: The dependent variable is the variable that you measure or observe.
What is the difference between dependent and independent variables?
Independent Variable: The independent variable is the one condition that you change in an experiment. Example: In an experiment measuring the effect of temperature on solubility, the independent variable is temperature. Dependent Variable: The dependent variable is the variable that you measure or observe.
What is the dependent variable in an experiment?
Dependent Variable: The dependent variable is the variable that you measure or observe. The dependent variable gets its name because it is the factor that is dependent on the state of the independent variable.
What is dependent variable?
Dependent Variable: The dependent variable is the variable that you measure or observe. The dependent variable gets its name because it is the factor that is dependent on the state of the independent variable. Example: In the experiment measuring the effect of temperature on solubility, solubility would be the dependent variable.
Why is the dependent variable called the dependent variable?
The dependent variable gets its name because it is the factor that is dependent on the state of the independent variable. Example: In the experiment measuring the effect of temperature on solubility, solubility would be the dependent variable.
What is a controlled variable?
Controlled Variable: A controlled variable or constant variable is a variable that does not change during an experiment. Example: In the experiment measuring the effect of temperature on solubility, controlled variable could include the source of water used in the experiment, the size and type of containers used to mix chemicals, ...
What is genetic variation?
Genetic Variation. Genetic variation refers to differences among the genomes of members of the same species. A genome is all the hereditary information—all the genes—of an organism. For instance, the human genome contains somewhere between twenty and twenty-five thousand genes. Genes are units of hereditary information, ...
What is the definition of environment?
Noun. (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule in every living organism that contains specific genetic information on that organism. environment. Noun. conditions that surround and influence an organism or community. evolution. Noun. change in heritable traits of a population over time. gene.
What is the genome?
A genome is all the hereditary information—all the genes—of an organism. For instance, the human genome contains somewhere between twenty and twenty-five thousand genes. Genes are units of hereditary information, and they carry instructions for building proteins. The genes that are encoded within these proteins are what enable cells to function.
Why do organisms reproduce sexually?
Most organisms that reproduce sexually have two copies of each gene, because each parent cell or organism donates a single copy of its genes to its offspring. Additionally, genes can exist in slightly different forms, called alleles, which further adds to genetic variation.
What is the definition of DNA?
DNA. Noun. (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule in every living organism that contains specific genetic information on that organism. environment. Noun. conditions that surround and influence an organism or community. evolution. Noun. change in heritable traits of a population over time.
What is the basic unit of heredity?
Noun. change in heritable traits of a population over time. gene. Noun. part of DNA that is the basic unit of heredity. gene flow. Noun. movement and exchange of genes between interbreeding populations. genotype.
What is the meaning of "genes"?
movement and exchange of genes between interbreeding populations. genotype. Noun. genetic makeup on an individual organism. heredity. Noun. the passing on of characteristics from ancestors to descendants. mutation. Noun.
Why do species have variations?
Variations in species help them to adapt themselves to that particular environment and give them a chance of survival. For example, thermophilic bacteria are variants that are resistant to extreme temperature. They have a chance of survival in high temperate zones while others die.
What is the process of reproduction?
We can say that the fundamental process of reproduction is DNA replication. When a reproducing cell commences division, it primarily starts to make a replica of its DNA. This replica will be separated from the original DNA. Since a DNA can’t build up an organism all by itself, the cell also divides into two.
How do living organisms increase their population?
Using the ability to reproduce, living organisms increase their population and feed on available resources in their niche. Changes in DNA and body design may result in difficulty to sustain themselves in their habitat. But we know that the environment is not consistent.
Is it necessary to reproduce to stay alive?
Reproduction means creation. It is not necessary for an organism to reproduce to stay alive. But for the continuity of life on earth, reproduction is inevitable. Organisms ensure themselves to be a part of the ecosystem through the process of reproduction. In this life process, one or more new offsprings are produced from the parent organisms. Do organisms create exact copies of themselves? No, there is always a chance of variation. Before we talk about variation, we need to know what exactly reproduction is and what are the processes involved.
