What is the Vaughan Williams classification of antiarrhythmic medications?
Vaughan-Williams Classification. ERP: Effective Refractory Potential. APD: Action Potential Duration. Anti-arrhythmic medications have a variety of different actions and mechanisms, and the Vaughan-Williams classification groups them accordingly.
What are the limitations of the Vaughan Williams classification scheme?
The clinical usefulness of the Vaughan Williams classification scheme is limited by the complexity of the mechanisms of arrhythmia formation in man, which offer multiple potential sites for intervention. The properties of antiarrhythmic drugs may be considerably altered in abnormal myocardium.
What is Vaughan Williams cardiology?
Cardiology The system by EM Vaughan Williams, used to categorize effects of antiarrhythmics by class. See Antiarrhythmic drugs. Cf Sicilian Gambit. Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content .

What is the Vaughan Williams antiarrhythmic classification of procainamide?
Procainamide (PCA) is a medication of the antiarrhythmic class used for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. It is classified by the Vaughan Williams classification system as class Ia; thus it is a sodium channel blocker of cardiomyocytes.
What Vaughan Williams Class lidocaine?
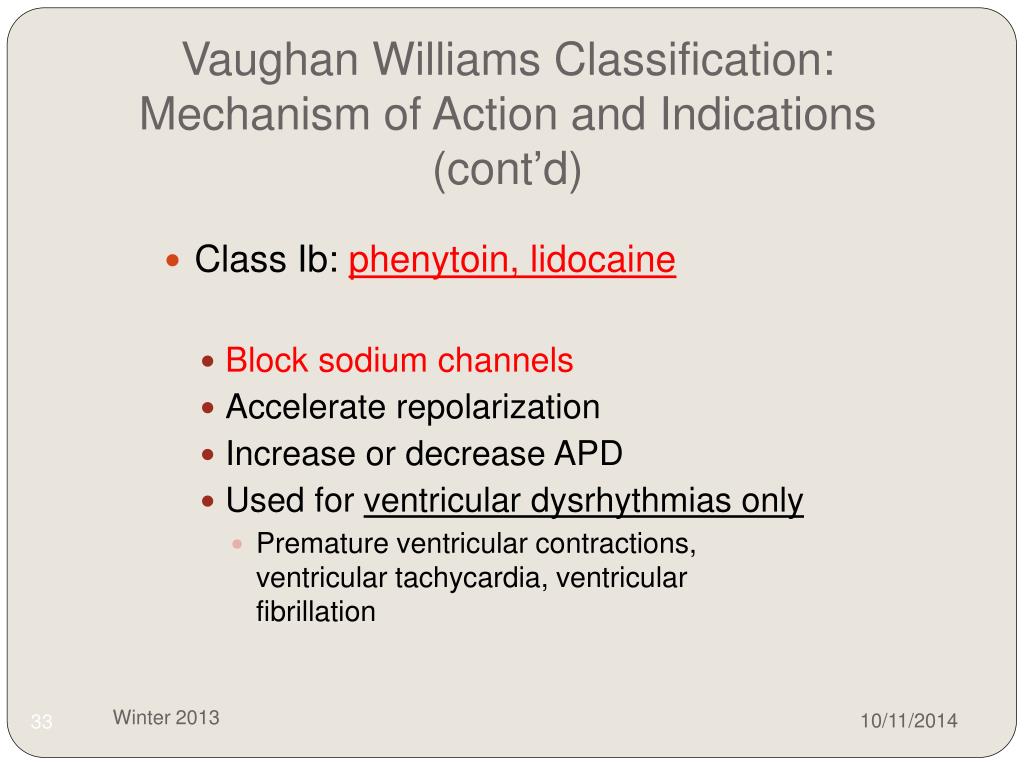
Class Ib (rapid dissociation): Lidocaine, mexilitine.
What class is amiodarone Vaughan?
Class III Drugs: Amiodarone. Ibutilide. Sotalol (also a β-blocker)
What is antiarrhythmic classification?
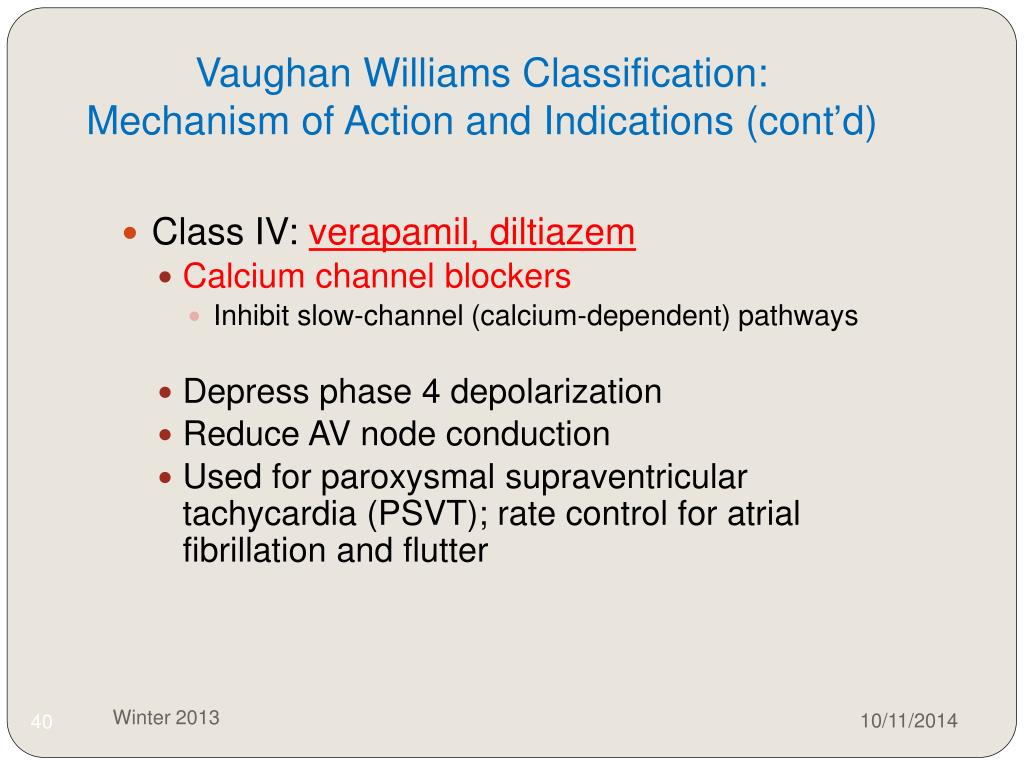
This classification system is comprised of four categories. Class I agents block sodium channels. Class II agents are Beta blockers. Class III agents prolong the cardiac action potential. Class IV agents are calcium channel blockers.
What is a class 3 antiarrhythmic?
Class 3 antiarrhythmics are drugs that block cardiac tissue K channels Channels The Cell: Cell Membrane . The medications in this class include amiodarone. It increases the duration of ventricular and atrial muscle action by inhibiting potassium channels and voltage-gated sodium channels.
What are Class 1C drugs?
Background. Class 1C antiarrhythmic drugs (AADs) are effective first‐line agents for atrial fibrillation (AF) treatment. However, these agents commonly are avoided in patients with known coronary artery disease (CAD), due to known increased risk in the postmyocardial infarction population.
What are the Class 1 antiarrhythmic drugs?
Quinidine, disopyramide, procainamide, lidocaine, mexiletine, flecainide, and propafenone are all class I antiarrhythmic drugs (table 1) used for the treatment of various atrial and ventricular arrhythmias. This topic will review the major side effects of the various drugs.
What are the 4 classes of antiarrhythmic drugs?
Antiarrhythmic drug classes:Class I - Sodium-channel blockers.Class II - Beta-blockers.Class III - Potassium-channel blockers.Class IV - Calcium-channel blockers.Miscellaneous - adenosine. - electrolyte supplement (magnesium and potassium salts) - digitalis compounds (cardiac glycosides)
Which antiarrhythmic drug has Class II and Class III activity?
Amiodarone also exerts sympatholytic, sodium, and calcium antagonistic properties that decrease conduction through the AV and sinus node. Sotalol shares class II and class III antiarrhythmic properties.
What are the Class 2 antiarrhythmics?
Class II: Beta blockers (partial list)Propranolol (decreases slope of phase 4)Esmolol (decreases slope of phase 4)Timolol (decreases slope of phase 4)Metoprolol (decreases slope of phase 4)Atenolol (decreases slope of phase 4)
How many classes of antiarrhythmic drugs are there?
What are the classes of antiarrhythmic medications? There are four classes of antiarrhythmics, based on the Vaughan-Williams (VW) classification system: Class I, sodium channel blockers: These drugs prevent sodium from getting through cell membranes. This can slow electrical impulses in the heart muscle.
How do class I antiarrhythmics work?
Class 1a antiarrhythmics inhibit the Na+ channels and the K+ channels on atrial and ventricular myocytes and cells of the purkinje fibers. When Na+ channels are blocked, it decreases the amount of sodium entering the cell so this causes a slower depolarization, which means a decrease in the slope during phase 0.
Which drug is considered a Class 1A antiarrhythmic drug?
Antiarrhythmics, Class IaDrugDrug DescriptionDisopyramideA class 1A antiarrhythmic agent used to treat life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.QuinidineA medication used to restore normal sinus rhythm, treat atrial fibrillation and flutter, and treat ventricular arrhythmias.7 more rows
Which antiarrhythmic drug has Class II and Class III activity?
Amiodarone also exerts sympatholytic, sodium, and calcium antagonistic properties that decrease conduction through the AV and sinus node. Sotalol shares class II and class III antiarrhythmic properties.
What class of drug is quinidine?
Quinidine is in a class of medications called antiarrhythmic medications. It works by making your heart more resistant to abnormal activity.
What kind of drug is Bretylium?
Bretylium is a norepinephrine release inhibitor used for the prophylaxis and therapy of ventricular fibrillation, as well as the treatment of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.
What is the Vaughan Williams classification?
Vaughan-Williams Classification. Anti-arrhythmic medications have a variety of different actions and mechanisms, and the Vaughan-Williams classification groups them accordingly.
Is the Vaughan Williams system shaky?
The class system is shaky when considering class I and III drugs, given that lots of the drugs in these classifications have similar mechanisms, ergo, could easily fit in the other class category. Even so, whilst the Vaughan-Williams system has limitations, it is still the one through which most physicians base their treatment strategies.