Vegetative reproduction facts for kids. Kids Encyclopedia Facts. A bulb of Muscari has made two bulbs underground, each of which produces a flower stem. In this way it reproduces vegetatively. Bryophyllum daigremontianum produces plantlets along the margins of its leaves.
How does seed reproduction differ from vegetative reproduction?
Vegetative reproduction is not evolutionary advantageous; it does not allow for genetic diversity and could lead plants to accumulate deleterious mutations. Vegetative reproduction is favored when it allows plants to produce more offspring per unit of resource than reproduction through seed production.
What do organism use vegetative propagation to reproduce?
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is any form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or specialized reproductive structures, which are sometimes called vegetative propagules.
What are three types of vegetative propagation?
What are types of vegetative propagation?
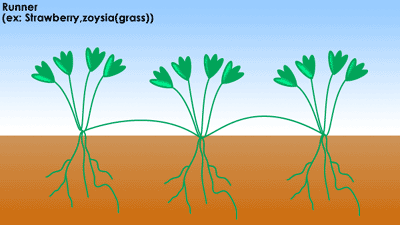
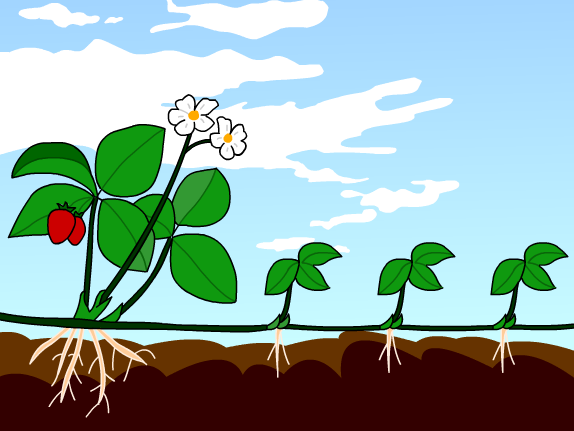
- Stem. Runners grow horizontally above the ground.
- Roots. New plants emerge out of swollen, modified roots known as tubers.
- Leaves. Leaves of a few plants get detached from the parent plant and develop into a new plant.
- Bulbs.
- Cutting.
- Grafting.
- Layering.
- Tissue Culture.
What are the methods of reproduction in plants?
Things to Remember Based on Reproduction in Plants
- Reproduction in plants occur via two modes- asexual and sexual.
- Asexual mode of reproduction includes, vegetative propagation, budding, fragmentation and spore formation.
- Vegetative propagation occurs through vegetative parts of the plant. ...
- Sexual reproduction involves formation of gametes. ...
What is vegetative reproduction in simple words?
vegetative reproduction, any form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment of the parent plant or grows from a specialized reproductive structure (such as a stolon, rhizome, tuber, corm, or bulb).
What is vegetative reproduction example with an example?
Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction that produces progeny by any vegetative propagule (rhizome, tubers, suckers etc.) without gamete formation and fertilization of male and female gametes. For example, Tuber of potato, the rhizome of ginger.
What is an example of vegetative?
Vegetative parts (figure 1) include roots, stems, shoot buds and leaves. They are not directly involved in sexual reproduction. Vegetative parts often are used in asexual forms of reproduction. Examples include cuttings, budding or grafting.
Why is it called vegetative reproduction?
In vegetative propagation, new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds. Since, asexual reproduction is done through the vegetative parts of the plant, it is known as vegetative propagation.
What plants use vegetative reproduction?
Food crops such as cassava, sweet potato, sugarcane, pineapple, banana, onion, etc. are propagated vegetatively. Plants produced in this way have characteristics identical to the parent plants; this is the main and most important advantage of vegetative propagation.
Why is vegetative reproduction important?
Vegetative reproduction is not evolutionary advantageous; it does not allow for genetic diversity and could lead plants to accumulate deleterious mutations. Vegetative reproduction is favored when it allows plants to produce more offspring per unit of resource than reproduction through seed production.
What is the difference between vegetative reproduction and asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction where only one parent is involved. The offspring produced is identical to the parent morphologically and genetically. Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction, wherein a new plant is produced from the vegetative parts of a plant.
What are the two types of vegetative reproduction?
Vegetative propagation is grouped into the following two types: Natural vegetative propagation including reproduction by stem, leaf, and root. Artificial vegetative propagation includes reproduction by cutting, layering, grafting, and micro-propagation.
What are the 3 types of vegetative propagation?
There are several ways of vegetative propagation. The three main types in forest tree propagation are grafting, air-layering and the use of cuttings. The three types are referred to as macropropagation, as alternative to micropropagation or tissue culture.
Which is a method of vegetative reproduction?
Methods of vegetative reproduction used for herbaceous landscape plants include cuttings, tissue culture, division of the original plant, or layering. A characteristic that distinguishes a herb from a woody; no persistent, woody tissue above ground.
What is vegetative plant part?
Vegetative parts- Parts of a plant which do not participate in sexual reproduction process are called vegetative parts. Roots, stems and leaves are the vegetative parts of a plant.
What are the 5 types of vegetative propagation?
Types of Vegetative PropagationStem. Runners grow horizontally above the ground. ... Roots. New plants emerge out of swollen, modified roots known as tubers. ... Leaves. Leaves of a few plants get detached from the parent plant and develop into new plants.Bulbs. ... Cutting. ... Grafting. ... Layering. ... Tissue Culture.
What are the 3 types of vegetative propagation?
There are several ways of vegetative propagation. The three main types in forest tree propagation are grafting, air-layering and the use of cuttings. The three types are referred to as macropropagation, as alternative to micropropagation or tissue culture.
Which process is an example of asexual reproduction?
Following are the examples of asexual reproduction: Bacterium undergoes binary fission in which the cell divides into two along with the nucleus. Blackworms or mud worms reproduce through fragmentation. Hydras reproduce through budding.
What are vegetative propagules name any four along with their examples?
Answer: Examples are - tuber, runner, rhizome , offset . Vegetative Propagule means a part of the plant becomes detached from the rest of the plant and grows into a new one. Example: seed, spore, bud or a plant cutting.
Explain vegetative propagation.
The process in which new plants are grown from the old parts of another plant like roots, shoots and leaves, without involving any reproductive org...
List the advantages of vegetative propagation.
The advantages of vegetative propagation are: a) The plants cultivated are genetically identical to their parents. b) Plants can be cultivated fa...
What are the disadvantages of vegetative propagation?
The disadvantages of vegetative propagation are: a) Vegetative propagated plants are short-lived, small compared to seed propagated plants b) No...
What is asexual reproduction?
Vegetative reproduction, any form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment of the parent plant or grows from a specialized reproductive structure (such as a stolon, rhizome, tuber, corm, or bulb ).
What is the definition of asexual propagation?
propagation: Asexual propagation. Some species of plants, in their cultivated forms, do not produce seed—e.g. , banana, pineapple, and sugarcane.
Do some plants produce seeds?
Some species of plants, in their cultivated forms, do not produce seed—e.g.,banana, pineapple, and sugarcane. In a great number of cultivated species, seedlings vary so much that the desired traits are found in only a small proportion. For these and other reasons,…
Is vegetative reproduction a natural process?
Asexual or vegetative reproductionis based on the ability of plants to regenerate tissues and parts. In many plants vegetative propagation is a completely natural process; in others it is an artificial one. Vegetative propagation has many advantages. These include the unchanged perpetuation of naturally cross-pollinated or…
What is artificial vegetative reproduction?
Artificial Vegetative Propagation. This is a type of vegetative reproduction carried out by humans on the fields and laboratories. The most common types of vegetative reproduction occurring artificially include:
What is vegetative propagation?
Vegetative propagation is an asexual method of plant reproduction that occurs in its leaves, roots and stem. This can occur through fragmentation and regeneration of specific vegetative parts of plants. Let us explore the different types of vegetative propagation and its examples in detail.
What are the structures of a plant that are vegetative?
The vegetative plant structures arising from the stem are known as rhizomes, bulbs, runners, tubers, etc.
What is the term for the stem of a plant that is bent to the ground and covered with soil?
Layering. In this, the stem of the plant is bent to the ground and covered with soil. Adventitious roots emerge from the plant parts covered with the soil. This attached stem with developing roots is known as a layer.
What is grafting in plants?
Grafting. In this, the cutting from some other plant is attached to the stem of plant rooted in the ground. The tissues of the graft become integrated with the tissues of the rooted plant and develop as a single plant over time.
Why are plant cells cultured?
In this, the plant cells from different parts of a plant are cultured in the laboratory to develop a new plant. This technique is helpful in increasing the number of rare and endangered plant species that are unable to grow under natural conditions.
Why is vegetative reproduction favored?
Vegetative reproduction is favored when it allows plants to produce more offspring per unit of resource than reproduction through seed production. In general, juveniles of a plant are easier to propagate vegetatively. Although most plants normally reproduce sexually, many can reproduce vegetatively, or can be induced to do so via hormonal ...
What is the process of plant reproduction?
Plant propagation is the process of plant reproduction of a species or cultivar, and it can be sexual or asexual. It can happen through the use of vegetative parts of the plants, such as leaves, stems, and roots to produce new plants or through growth from specialized vegetative plant parts.
How does Bryophyllum daigremontianum reproduce?
Bryophyllum daigremontianum produces plantlets along the margins of its leaves. When they are mature enough, they drop off and root in any suitable soil beneath. Vegetative reproduction from a stem cutting less than a week old. Some species are more conducive to this means of propagation than others.
Why is vegetative propagation important?
Vegetative propagation also allows plants to circumvent the immature seedling phase and reach the mature phase faster. In nature, that increases the chances for a plant to successfully reach maturity, and, commercially, it saves farmers a lot of time and money as it allows for faster crop overturn.
How do plants reproduce?
Most common methods of natural vegetative reproduction involves the development of a new plant from specialized structures of a mature plant. In addition to adventitious roots, roots that arise from plant structures other than the root, such as stems or leaves, modified stems, leaves and roots play an important role in plants' ability to naturally propagate. The most common modified stems, leaves and roots that allow for vegetative propagation are:
What is the term for a plant that grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant?
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is any form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or a specialized reproductive structure.
What is the name of the plant that produces seeds instead of flowers?
In flowering plants, unfertilized seeds are produced, or plantlets that grow instead of flowers. Hawkweed ( Hieracium ), dandelion ( Taraxacum ), some citrus ( Citrus) and many grasses such as Kentucky bluegrass ( Poa pratensis) all use this form of asexual reproduction.
What is Vegetative Propagation?
When a plant reproduces asexually through the means of its roots, stem and leaves, then this process is said to be Vegetative Propagation. The respective part of a plant will be useful to produce new plant species, apart from its seeds. Banana, sweet potato, cassava, pineapple, are some of the real-time vegetative propagation examples.
What are some examples of real-time vegetative propagation?
Banana, sweet potato, cassava, pineapple, are some of the real-time vegetative propagation examples. Note that only 1 plant would be involved in the process of vegetative propagation. Natural reproduction results in an offspring which will be a new plant that is genetically similar to the parent plant. There are 2 means by which a plant can ...
Why is vegetative propagation important?
The biggest advantage of growing plants through vegetative propagation is that the newly born plants are clones to their parents since only 1 plant is involved in the entire process. This helps in getting multiple plant alternatives that are genetically similar.
Why is participation important in plant reproduction?
The participation of a human being is an important factor to plant reproduction since man has the potential to manipulate plant growth. Before we distinguish and define vegetative propagation with its types, it is important to learn the 2 main ways of how a plant can reproduce asexually - Natural and Artificial.
What is the process of plant reproduction?
Vegetative propagation/reproduction defines to the asexual method of plant reproduction to form new plant variants either through regeneration or by fragmentation. This process usually occurs in the roots, leaves and stem of a plant.
What are the disadvantages of vegetative propagation?
Some of the disadvantages of vegetative propagation include less environmental adaptation, poorly visible variations, easy plant decaying and also overcrowding may occur.
How do roses grow?
Roses grow in this method. Layering - The layer is the part that will produce new plants. This layer is formed when the plant’s stem is bent downward and buried into the soil. The plant’s shoot tip will be under the ground. The covering soil helps in the growth of adventitious roots, thus forming plant variants.
Vegetative Propagation
Vegetative is a word that comes from vegetation and refers to plants or parts of a plant. Propagation is the breeding or making of offspring in plants or animals. Vegetative propagation can be described as the process of making new plants from a part (stems, leaves, or other structure) of the parent plant.
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
Reproduction is the making or production of offspring. The most familiar type of reproduction that occurs in humans involves a mother (female) and a father (male). The male sperm cell and female egg created in meiosis each provide half the genetic information to the offspring.
Types of Vegetative Propagation
Grafting is a vegetative propagation technique used frequently in the plant nursery industries. Grafting is the attaching of a bud, stem, or branch from one plant to the stem and roots of a different plant. The section or part of the plant attached to the root stock is called a scion.
Vegetative Propagation: Word Search Activity
This activity will help you assess your knowledge of the methods and examples of vegetative propagation.
What is vegetative reproduction?
Vegetative propagation or vegetative reproduction is the growth and development of a plant by asexual means. This development occurs through the fragmentation and regeneration of specialized vegetative plant parts. Many plants that reproduce asexually are also capable of sexual propagation.
How is vegetative propagation accomplished?
Vegetative propagation may be accomplished by artificial or natural means. Though both methods involve the development of a plant from parts of a single mature part, the way that each is carried out looks very different.
What are the vegetative structures of plants?
In non-vascular plants such as mosses and liverworts, vegetative reproductive structures include gemmae and spores. In vascular plants, vegetative reproductive structures include roots, stems, and leaves. Vegetative propagation is made possible by meristem tissue, commonly found within stems and leaves as well as the tips of roots, ...
How do rhizomes help plants grow?
Rhizomes are modified stems that typically grow horizontally along the surface of or beneath the ground. Rhizomes are storage sites for growth substances such as proteins and starches. As rhizomes extend, roots and shoots may arise from segments of the rhizome and develop into new plants. Certain grasses, lilies, irises, and orchids propagate in this manner. Edible plant rhizomes include ginger and turmeric.
Why do commercial growers use vegetative propagation?
Commercial crop growers can employ artificial vegetative propagation techniques to ensure advantageous qualities in their crops. A major disadvantage, however, of vegetative propagation is that it does not allow for any degree of genetic variation.
Where is vegetative propagation made?
Vegetative propagation is made possible by meristem tissue, commonly found within stems and leaves as well as the tips of roots, that contains undifferentiated cells. These cells actively divide by mitosis to allow widespread and rapid primary plant growth. Specialized, permanent plant tissue systems also originate from meristem tissue.
What are the most common types of artificial vegetative reproductive techniques?
The most common types of artificial vegetative reproductive techniques include cutting, layering, grafting, suckering, and tissue culturing. These methods are employed by many farmers and horticulturists to produce healthier crops with more desirable qualities.
What is sexual reproduction?
To reproduce sexually, plants have both male and female reproductive organs in their flowers.
What is the term for a cell producing another cell?
Sometimes a cell may produce another of its kind and that is also defined as reproduction. Like regenerating a part of tissue, or the healing of a wound. Reproduction to produce another independent living organism, can either be sexual or asexual, in the plant or animal kingdom.
What is pollen and pollination?
To reproduce sexually, pollen from the male part is transferred to the female part, stigma, from where it descends into the Ovary, where fertilisation occurs to form a zygote, which eventually turns into a seed. This seed will germinate and sprout to become a new plant.

Overview
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is any form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or specialized reproductive structures, which are sometimes called vegetative propagules.
Background
Plant propagation is the process of plant reproduction of a species or cultivar, and it can be sexual or asexual. It can happen through the use of vegetative parts of the plants, such as leaves, stems, and roots to produce new plants or through growth from specialized vegetative plant parts.
While many plants reproduce by vegetative reproduction, they rarely exclusively use that method to reproduce. Vegetative reproduction is not evolutionary advantageous; it does not allow for ge…
Mechanisms
Meristem tissue makes the process of asexual reproduction possible. It is normally found in stems, leaves, and tips of stems and roots and consists of undifferentiated cells that are constantly dividing allowing for plant growth and give rise to plant tissue systems. The meristem tissue's ability to continuously divide allows for vegetative propagation to occur.
Another important ability that allows for vegetative propagation is the ability to develop adventiti…
Advantages and disadvantages
There are several advantages of vegetative reproduction, mainly that the produced offspring are clones of their parent plants. If a plant has favorable traits, it can continue to pass down its advantageous genetic information to its offspring. It can be economically beneficial for commercial growers to clone a certain plant to ensure consistency throughout their crops. Vegetative propagation also allows plants to avoid the costly and complex process of producin…
Types
Natural vegetative propagation is mostly a process found in herbaceous and woody perennial plants, and typically involves structural modifications of the stem, although any horizontal, underground part of a plant (whether stem, leaf, or root) can contribute to vegetative reproduction of a plant. Most plant species that survive and significantly expand by vegetative reproduction would be perennial almost by definition, since specialized organs of vegetative reproduction, like seeds of …
See also
• Micropropagation
• Hemerochory
• Escaped plant