What is the difference between ventilation and respiration?
• The ventilation is the movement of air into and out of the lungs whereas the respiration is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. • The ventilation mainly involves the lungs while the respiration mainly involves the respiratory surfaces, including alveoli and blood capillary walls.
What is airway pressure release ventilation?
Airway pressure-release ventilation (APRV) is a mode of ventilatory support in which the patient breathes spontaneously at a high level of continuous airway pressure, with periodic releases to a low positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP).
What does ventilation include?
Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs which facilitates gas exchange. It occurs via the respiratory muscles, which contract and relax rhythmically to fill the lungs with air in inspiration and empty them in expiration.
What is adult ventilation rate?
Ventilation rate/frequency for an adult patient without a pulse and with an advanced airway in place . Rate of Ventilation: 8-10 per minute (100 compressions/min; no pause for ventilations) Frequency of Ventilation: One ventilation every 6-7.5 seconds ...
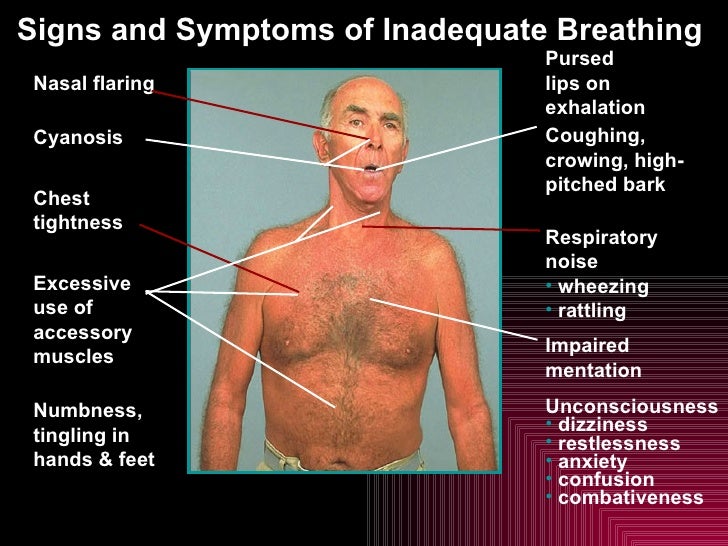
When should an EMT be ventilated?
Once the airway has been opened, the EMT-Basic must determine if breathing is adequate. Patients with inadequate breathing must be artificially ventilated using mouth-to-mouth, mouth-to-mask, bag-valve-mask or flow restricted, oxygen-powered ventilation device.
What is ventilation in the body?
Ventilation, or breathing, is the movement of air through the conducting passages between the atmosphere and the lungs. The air moves through the passages because of pressure gradients that are produced by contraction of the diaphragm and thoracic muscles.
How do you ventilate a patient EMT?
Ventilate the patient. While the rescuer positioned at the crown of the patient's head maintains airway position and mask seal with two hands, a second rescuer should encircle the bag with two hands and provide steady, regular ventilations at a volume of approximately 800 cc (adult).
What is ventilation vs respiration?
Respiration vs Ventilation Ventilation is mechanical and involves the movement of air, Respiration is physiologic and involves the exchange of gases in the alveoli (external respiration) and in the cells (internal respiration). RESPIRATION: The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
What is ventilation and examples?
Ventilation is a circulation of air, or an opening that lets air in. An example of ventilation is a window being open in a house. noun. 1. A ventilating or being ventilated.
What are the 4 types of ventilation?
What are The Different Types of Ventilation?NATURAL VENTILATION.MECHANISED FANS. In some cases, a natural ventilation solution isn't possible due to the design and location of building. ... EXHAUST VENTILATION. ... SUPPLY VENTILATION. ... BALANCED VENTILATION. ... SMOKE VENTILATION.
How do you ventilate a patient?
A mechanical ventilator is a machine that helps a patient breathe (ventilate) when they are having surgery or cannot breathe on their own due to a critical illness. The patient is connected to the ventilator with a hollow tube (artificial airway) that goes in their mouth and down into their main airway or trachea.
How do you provide ventilation?
Bring as much fresh air into your home as possibleIf it's safe to do so, open doors and windows as much as you can to bring in fresh, outdoor air. ... If you can, open multiple doors and windows to allow more fresh air to move inside.More items...
When should you ventilate someone?
Many conditions, such as pneumonia, COPD, brain injuries, and strokes require the use of a ventilator. If you have a loved one with a disease or condition that impairs their lung function, a ventilator will be employed. The use of a ventilator is also common when someone is under anesthesia during general surgery.
What are the types of ventilation?
There are three methods that may be used to ventilate a building: natural, mechanical and hybrid (mixed-mode) ventilation.
What is the importance of ventilation?
Proper ventilation keeps the air fresh and healthy indoors. Like the lungs, homes need to be able to breathe to make sure that fresh air comes in and dirty air goes out. Air indoors can build up high levels of moisture, odors, gases, dust, and other air pollutants.
What are the two types of medical ventilation?
Positive-pressure ventilation: pushes the air into the lungs. Negative-pressure ventilation: sucks the air into the lungs by making the chest expand and contract.
What is ventilation in simple words?
Definition of ventilation 1 : the act or process of ventilating. 2a : circulation of air a room with good ventilation. b(1) : the circulation and exchange of gases in the lungs or gills that is basic to respiration.
What are the 3 types of ventilation?
There are three basic types of whole-house mechanical ventilation, and by understanding each you can choose the best one for you.Exhaust-only ventilation. This ventilation type uses a fan to move indoor air out of your home, while outdoor air is drawn in through leaks. ... Supply-only ventilation. ... Balanced ventilation.
What is the meaning of ventilation in biology?
Ventilation (physiology), the movement of air between the environment and the lungs via inhalation and exhalation.
What's another name for ventilation?
ventilation; airing; respiration; breathing; external respiration; ventilating system; ventilation system; public discussion.
Which volume of air reaches the alveoli and can participate in gas exchange?
Alveolar volume: air that reaches the alveoli and can participate in gas exchange.
What is the process of gas exchange?
Respiration: the entire process of gas exchange.
Why do hospitals use mechanical ventilators?
For hospitalized patients, mechanical ventilators have been show in studies to provide more reliable ventilation during intra-facility transports (i.e., trips to CAT scan, the cath lab, OR, etc) when compared to manual ventilation 8 .
What is the goal of ventilation?
The primary goal in ventilation is to maintain oxygenation 9. This is best evidenced by a pulse oximeter oxygen saturation of 90% or greater. If BVM ventilation is not achieving this result, consider mask size, adequate mask seal, positioning (ideal is aligning the ear canal with the sternal notch), use of a jaw thrust, and insertion of an oral pharyngeal or nasal airway (OPA or NPA).
What is the role of capnography in ventilation?
Whether or not an advanced airway is in place and whether or not the patient is spontaneously breathing, capnography provides accurate reading of respiratory rate and important information about ventilation. During bag valve ventilation, ...
What is the message for any level provider in dealing with an airway emergency?
The message for any level provider in dealing with an airway emergency is, “get help!” Depending on your resources, help may be at the closest ED. An interesting case report 12 from Survival Flight in Michigan used a S.A.L.T. airway (EcoLab, Columbus, MS) to improve oxygen saturations from the mid 60’s to mid 90’s in a 74 year-old trauma patient the crew was unable to intubate in the field.
How many breaths per minute for a rescuer?
Each breath should be delivered over 1 second with the minimum volume needed to produce chest rise. Initial ventilation rate for an adult should be 10 to 12 breaths per minute 1. Optimally two rescuers should perform this task, one creating an effective mask seal and head position, while the other focuses on correct tidal volume and rate.
How to learn to ventilate spontaneously breathing patients?
The best way to learn and refine your ability to track respirations and ventilate a spontaneously breathing patient is to practice on a coworker. It is not a simple skill to learn.
What are the two BLS tools used for assessing the adequacy of ventilation?
Two important BLS tools for monitoring and assessing the adequacy of ventilation are respiratory rate and pulse oximetry.
What is chapter 41 of EMT?
EMT chapter 41- A Team Approach to Health Care
What is the name of the collection of blood in the space between the chest wall and the lung?
Hemothorax (a collection of blood in the space between the chest wall and the lung)
