How do you calculate ventilation?
How to quantify the ventilation rate of an indoor space using an affordable CO2 monitor
- (1) Leave the CO2 monitor outside for at least 5 minutes to record the background concentration.
- (2) Stay in the location of interest (with the CO2 monitor there) for a while, so that CO2 builds up (see Appendix 3 for ideas if that is not enough ...
- (3) Best to leave a fan (s) on the whole time, to mix the air in the space. ...
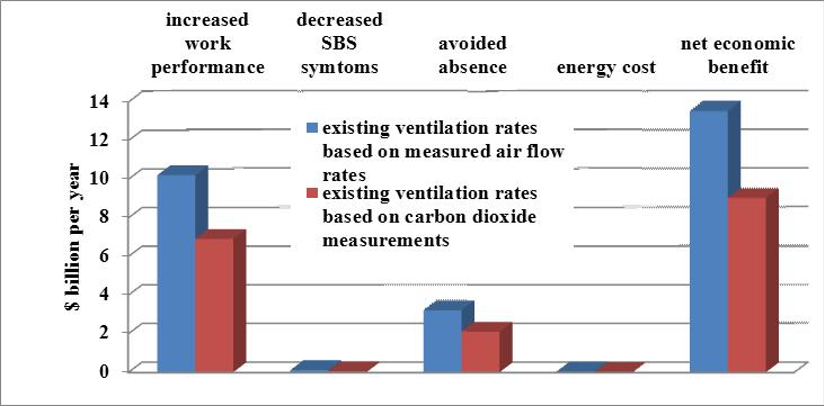
How much ventilation is needed?
How much ventilation is too much? The minimum ventilation needed for an attic is specified by the building code of that area. Normally it is 1 sq.ft of vent area per 150 sq.ft of attic area. However, this value can be 1/300 of the attic area if both of the following two conditions are met;
What is the average minute ventilation?
Normal minute ventilation is between 5 and 8 L per minute (Lpm). Tidal volumes of 500 to 600 mL at 12–14 breaths per minute yield minute ventilations between 6.0 and 8.4 L, for example. Minute ventilation can double with light exercise, and it can exceed 40 Lpm with heavy exercise.
What does ventilation do I Need?
- Mechanically circulating air should be established between the upper conditioned area of the home and crawl space.
- The air-circulating device must move at least 1 cubic foot of air per 50 square feet of crawl space area.
- The crawl space floor area must be completely sealed with a vapor-retarding material.

What ventilation means?
1 : the act or process of ventilating. 2a : circulation of air a room with good ventilation. b(1) : the circulation and exchange of gases in the lungs or gills that is basic to respiration. (2) : artificial respiration of the lungs specifically : mechanical ventilation ventilation to supply oxygen to the patient's ...
How do you calculate vent rate?
Experimental Event Rate (EER) = a/a+b. Control Event Rate (CER) = c/c+d. Relative Risk Reduction (RRR) = CER-EER/CER.
What is ventilation rate Pdhpe?
Ventilation rate is a measure of how many breaths a person takes per minute, and is also known as the respiratory rate. As with the heart rate, an athlete's ventilation rate will have an immediate increase in response to training.
How do you calculate rate per 100000?
A crime rate is calculated by dividing the number of reported crimes by the total population. The result is then multiplied by 100,000.
How do you calculate per 100000 population?
(That's what "per capita" means. It's Latin for "for each head.") To find that rate, simply divide the number of murders by the total population of the city. To keep from using a tiny little decimal, statisticians usually multiply the result by 100,000 and give the result as the number of murders per 100,000 people.
What happens to ventilation rate during exercise?
When you exercise and your muscles work harder, your body uses more oxygen and produces more carbon dioxide. To cope with this extra demand, your breathing has to increase from about 15 times a minute (12 litres of air) when you are resting, up to about 40–60 times a minute (100 litres of air) during exercise.
What is the max VO2 max?
What is VO2 max? VO2 max is the maximum volume (V) of oxygen (O2) your body can process. A VO2 max score is a little like horsepower in a car—it's a measure of the capacity your body (engine) has to use oxygen when exercising. If you have a high VO2 max, you have a big engine.
What is normal tidal volume?
Tidal volume is the amount of air that moves in or out of the lungs with each respiratory cycle. It measures around 500 mL in an average healthy adult male and approximately 400 mL in a healthy female. It is a vital clinical parameter that allows for proper ventilation to take place.
How do you calculate ventilation in liters per minute?
0:002:53Ventilator Basics- Minute Ventilation - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou guys basically easy this topic is to be a part of our ventilation topic. Series we're in timeMoreYou guys basically easy this topic is to be a part of our ventilation topic. Series we're in time about a minute ventilation or MV minute ventilation in other words is how much air are you moving per
How do you calculate ventilation rate in a confined space?
Divide the volume of the room by the fan's flow rate, using the same unit system. The volume unit will cancel out, leaving only the time unit. The number achieved here is the time it takes for the air in the space to be replaced once using that ventilation system.
How many CFM do I need for a 12x12 room?
One cfm per square foot of floor area is the average air quantity required for a room or entire building.
How do I calculate CFM?
CFM = (fpm * area), where fpm is the feet per minute. To find the cubic feet per minute, substitute the FPM value with the area after the area is squared.
What is the ventilation rate?
The ventilation flow rate can be referred to as either an absolute ventilation flow rate in l/s or m3/s, or an air-change rate relative to the volume of the space . In this guideline, the ventilation rate is referred to as the absolute amount of inflow air per unit time (litre per second or l/s, cubic meter per hour or m3/hr) and the air-change rate as the relative amount of inflow air per unit time. For example, in an airborne infection isolation room, we need a 12 ACH air-change rate (CDC, 2005), while in an office, we need a 10 l/s per person ventilation rate.
What happens to indoor concentration when ventilation rate is higher?
the higher the ventilation rate, the lower the indoor concentration
What is the standard for ventilation rates?
Standards ISO 17772, EN 16798 and EN 15251 employ definitions of low polluting , very low polluted and non-low polluted buildings. The standards ISO 17772, EN 16798 refer to standards CEN/TS 16516 or ISO 1600 to define limits of different compounds in the air per building category, and it differs from the EN 15251 approach as shown in Table 8.
What is the minimum ventilation rate for EN 16798?
According to AS 1668.2, the occupancy-based outdoor air supply may be reduced in accordance with actual occupancy, but not below the minimum area-based outdoor air ventilation rate of 0.35 l/s-m 2.
What is the ASHRAE standard for ventilation?
Due to the increase in the number of occupant complaints regarding poor IAQ and the increase in buildings diagnosed with sick building syndrome, the control and measurement of outside air intake rates has come to the forefront of attention of many HVAC engineers and designers. The majority of HVAC system designers today rely on the ASHRAE “Ventilation Rate Procedure” described in ASHRAE Standard 62 (2004), Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor Air Quality. ASHRAE Standard 62 specifies minimum ventilation rates as a function of building use and occupancy to provide adequate IAQ for conditioned spaces.
Why is ventilation required in car parks?
Enclosed (manually driven) car parks below natural ground level under large buildings present special ventilation requirements because generally natural ventilation cannot be utilized. Thus, mechanical ventilation is required to dilute or remove exhaust pollutants generated by vehicles with engines operating within the car park. Principal engine exhaust pollutants are carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and oxides of nitrogen. The dilution principle is used in car park ventilation to maintain a safe level of carbon monoxide within the car park space. In calculating the ventilation requirement for car parks, design standards are based on ventilation space volume, parking area, number of vehicles with engine operating, engine exhaust emission rate, and allowable carbon monoxide exposure level and duration. In multilevel underground car parks where the number of cars per level may exceed 500, the quantity of ventilation air required may be very large. It is understood that sensible design may be obtained with a balance between energy conservation and allowable carbon monoxide exposure level and duration.
What are the factors that affect air quality?
However, other pollutants , such as oxides of nitrogen, oxides of sulfur, and odorous compounds, also contribute to poor air quality. In the United States, basic design criteria, as quoted by [6], are 4 to 6 air changes per hour, with a minimum ventilation rate of 7.5 liter/s/m2, and a maximum ventilation rate of 10 to 15 liter/s/m 2. The maximum recommended carbon monoxide concentration is 50 ppm for an 8-hr, time-weighted average and 125 ppm for a 1-hr, time-weighted average. In Japan, as quoted by [7], the mean carbon monoxide level per 8-hr average is 20 ppm; the environmental standard for inhabitable rooms is 10 ppm over the same period. The ventilation requirement for car parks in Finland is determined by the carbon monoxide concentration [8]. The limit for carbon monoxide concentration is 30 ppm for an 8-hr average and 75 ppm for a 15-min average. The minimum supply air flow rate is 2.7 liter/s/m 2. This rate would require 9.72 air changes per hour per meter length of ceiling height. Australian Standard [9] specifies that a minimum flow rate of fresh air of 3000 liter/s is to be maintained. This would give an indoor carbon monoxide level of about 136 ppm if a loading value of 52 ft 3 /hr (0.4 liter/s or 1.4 m 3 /hr) of carbon monoxide discharged, as proposed by [10], is used. Australian standards also specify the average driving lengths of cars for a heavy-loads car park.
What is variable air volume?
Variable air volume air handling systems are often employed in modern laboratory and hood systems. A fast and stable control system for the hoods, exhaust fans, supply fans, and all HVAC equipment is suggested. The airflows required are determined by the highest demand of the minimum ventilation rates prescribed, the cooling or heating loads required, and the total amount of exhaust from the hoods themselves. The airflow in and out of the room is controlled to meet these needs. Sometimes, the airflow required is below the amount needed to cool or heat the room to its comfort settings; therefore, the room supply air must be increased to meet the load. The lab control system must react to exhaust additional air through a “general exhaust” damper or air valve to compensate and maintain room pressurization and hood equilibrium.
What is the air supply for ventilation?
Air supply for ventilation purposes is usually taken to be the supply of outdoor air into the occupied spaces. Where the building is air conditioned, this is supplied via the ductwork system, the purpose being to maintain a satisfactory indoor air quality by reducing the concentration of airborne contaminants to levels acceptable to the occupants and/or for the activities taking place within the building. A common requirement is the dilution of body odours originating from normal body processes. In the United Kingdom, there are no statutory requirements with regard to specific minimum ventilation rates. For the United Kingdom, the recommendation in the CIBSE Guide is for a minimum ventilation rate of 10 l/s per person; in the United States, a figure of 7.5 l/s is likely to become the accepted standard.
Why are ventilation rates specified for spaces where smoking is permitted?
It also included provisions for cigarette smoking, recognizing that “higher ventilation rates are specified for spaces where smoking is permitted because tobacco smoke is one of the most difficult contaminants to control at the source.”.
What is the purpose of the ventilation standard?
The intent was to provide a comprehensive and defensible method for establishing ventilation rates. The standard has had many revisions since it was first published, each with the intent of improving ventilation in buildings. For existing buildings, it is important to understand the iterations and evolution of the standard to identify how existing buildings might be ventilated based on which version was used at the time of construction or retrofit.
What is the third option for natural ventilation?
The third option is the natural ventilation procedure (Standard Section 6.4)), which is a prescriptive procedure where outdoor air is provided through outdoor openings. The VRP is the most commonly used for compliance. Frequently overlooked in the VRP is the requirement for outdoor-air treatment.
What is VRP requirement?
Frequently overlooked in the VRP is the requirement for outdoor-air treatment. When using the VRP, it is important to verify if outdoor-air treatment is required. The requirements are outlined in Section 6.2.1 and are for ventilation systems that provide outdoor air through a supply fan.
How many minimum airflows are there in the air intake flow chart?
The minimum outdoor-air intake flowchart illustrates that for 2004-2016 there are four potential compliant minimum flows. It illustrates the impact that diversity can have as well as how the designer allows for minimum flows within each zone and if Appendix A is used.
Where do VRP calculations begin?
Calculations begin in Section 6.2.2. Each zone in a system must be looked at individually, and then systems can be analyzed. Figure 2 outlines the steps required when using the VRP, and Figure 3 provides the definitions of the symbols used in the calculations.
What is the difference between IAQP and VRP?
The VRP is the most commonly used procedure. It is a prescriptive design procedure in which outdoor-air rates are dependent on space type, occupancy, and floor area. The IAQP is a performance procedure in which minimum outdoor-air requirements are based on analysis of contaminant sources, contaminant concentration limits, and the level of perceived indoor-air acceptability (Standard Section 6.3). The third option is the natural ventilation procedure (Standard Section 6.4)), which is a prescriptive procedure where outdoor air is provided through outdoor openings.
How long does an outdoor air ventilation system operate?
Exception: The outdoor air ventilation system is not required to operate continuously where the system has controls that enable operation for not less than 1 hour of each 4-hour period. The average outdoor air flow rate over the 4-hour period shall be not less than that prescribed by Equation 4-9.
Where are local exhaust systems required?
Local exhaust systems shall be provided in kitchens, bathrooms and toilet rooms and shall have the capacity to exhaust the minimum airflow rate determined in accordance with Table 403.3.2.3.
What is primary airflow?
Primary airflow: The airflow rate supplied to the zone from the air-handling unit at which the outdoor air intake is located. It includes outdoor intake air and recirculated air from that air-handling unit but does not include air transferred or air recirculated to the zone by other means. For design purposes, Vpz shall be the zone design primary airflow rate, except for zones with variable air volume supply and Vpz shall be the lowest expected primary airflow rate to the zone when it is fully occupied.
What is the definition of occupant diversity?
Occupant diversity: the ratio of the system population to the sum of the zone populations, determined in accordance with Equation 4-7.
Is recirculation of air prohibited?
Recirculation of air that is contained completely within such spaces shall not be prohibited. Where recirculation of air is prohibited, all air supplied to such spaces shall be exhausted, including any air in excess of that required by Table 403.3.1.1. 4.