What causes ventricular depolarization?
Right bundle branch block is considered the most common cause of right ventricular conduction delay in healthy individuals. It is responsible for delayed right ventricular depolarization. There may be many reasons behind the right bundle branch block.
What are the risks of ventricular shunting?
- infection in the shunt or brain
- blood clots
- bleeding in the brain
- damage to brain tissue
- swelling of the brain
What is true regarding ventricular systole?
The ventricles begin to contract (ventricular systole), raising pressure within the ventricles. When ventricular pressure rises above the pressure in the atria, blood flows toward the atria, producing the first heart sound, S 1 or lub. As pressure in the ventricles rises above two major arteries, blood pushes open the two semilunar valves and moves into the pulmonary trunk and aorta in the ventricular ejection phase.
What does repolarization of ventricles mean?
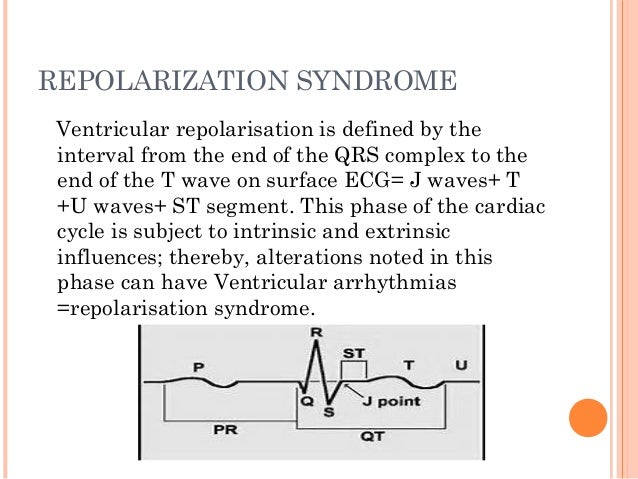
Ventricular repolarization is a complex electrical phenomenon which represents a crucial stage in electrical cardiac activity. It is expressed on the surface electrocardiogram by the interval between the start of the QRS complex and the end of the T wave or U wave (QT). Click to see full answer. Likewise, what happens ventricular repolarization?

Does ventricular repolarization mean contraction?
2:344:15Depolarization and Repolarization of Heart: Action Potential ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo now let's see the heart in action how it actually contracts and relax whenever it is stimulatedMoreSo now let's see the heart in action how it actually contracts and relax whenever it is stimulated by this electrical conduction system and creating this pqrst complex by looking at this animation.
What causes ventricular repolarization?
The mechanisms behind the abnormal ventricular repolarization of RV patients are not known. Factors such as hyperactivity of the sympathetic nervous system, and abnormality of intracellular ion currents and couplings may have a role in QT prolongation.
Where does ventricular repolarization occur in the heart?
A transmural gradient in repolarization in the human ventricle, therefore, seems to run from endocardium toward epicardium rather than in the opposite direction.
What is ventricular repolarization called?
The T wave represents ventricular repolarization. Generally, the T wave exhibits a positive deflection. The reason for this is that the last cells to depolarize in the ventricles are the first to repolarize.
What is depolarization vs repolarization?
The main difference between the two is: depolarization is described as the loss of resting membrane potential as a result of the alteration of the polarization of cell membrane. repolarization is described as the restoration of the resting membrane potential after every depolarization event.
What is abnormal repolarization on an ECG?
INTRODUCTION. Defects in the cardiac repolarization are known to be associated to several life-threatening diseases [1-4]. In the electrocardiogram (ECG) such defects appear as abnormalities of the ST segment and T-wave, which can be non-invasively characterized by means of indexes.
Does repolarization mean relaxation?
When the electrical signal of a depolarization reaches the contractile cells, they contract. When the repolarization signal reaches the myocardial cells, they relax. Thus, the electrical signals cause the mechanical pumping action of the heart.
Where does ventricular depolarization occur?
Ventricular depolarization occurs in part via an accessory pathway (AP) directly connecting the atrium and ventricle and thus capable of conducting electrical impulses into the ventricle bypassing the AV-His Purkinje conduction system.
How does depolarization and repolarization occur in the heart?
Each deflection (wave) of the ECG represents either depolarization or repolarization of the specific parts of the heart. Because depolarization occurs before mechanical contraction, the waves of depolarization can be associated with contraction and relaxation of the atria and the ventricles.
What is ventricular repolarization quizlet?
Electrical event of the heart that causes T wave. Ventricular Repolarization. Physically occurs in the heart with T Wave.
How does repolarization occur?
Repolarization is caused by the closing of sodium ion channels and the opening of potassium ion channels. Hyperpolarization occurs due to an excess of open potassium channels and potassium efflux from the cell.
Why can't you see atrial repolarization?
Because ventricular depolarization is so large, and atrial diastole is so small , you can't see atrial repolarization during the QRS complex. The atria are not large and therefore they don't require much electrical charge to go back to their resting state so atrial repolarization is hidden under the QRS complex. Yes, this indicates that while the ventricles are depolarizing the atrial are repolarizing. That's why the atrial repolar wave is hidden.
What is it called when a person's atria is depolarized?
Now when this happens in atria it's atrial depolarization, when it happens in ventricles, it's called ventricular depolarization .
What causes the contraction of the atria in the heart?
Atrial depolarisation is what causes the contraction of the atria in your heart. The depolarisation is triggered by an electrical impulse from the heart’s principal pace-maker, the sino-atrial node (SA Node), a small gland-like “patch” that resides near the upper right corner of the right atrium. From there, the depolarisation impulse travels rapidly to the left atrium through conductive fibers and branches off near the central wall of the heart through another node called the AV node (atrioventricular node) that delays the impulse for a very short time. Then the impulse travels trough a bunch
What is LVH in cardiology?
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is serious when the muscle is very thick (max thickness >3 cm), or if the increased muscle mass is impeding blood flow through the heart (defined as increased outflow pressure gradient). When an outflow gradient is excessively high, the affected individual will likely experienced related symptoms, such as decreased exercise tolerance, lightheadedness, or fainting. In these cases, medication or surgical treatment may be required to relieve the obstruction. Increased thickness predisposes to dangerous heart rhythms arising from the ventricles (ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation) which may be life threatening, and patients may qualify for an implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD). The decision for an ICD is typically based on the presence of several risk factors, such as the degree of muscle thickening, history of faint, documentation of ventricular tachycardia, or a family history of sudden cardiac death due to LVH.
What is LVH in medical terms?
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is serious when the muscle is very thick (max thickness >3 cm), or if the increased muscle mass is impeding blood flow through the heart (defined as increased outflow pressure gradient). When an outflow gradient is excessively high, the affected individual will likely experienced related symptoms, such as decreased exercise tolerance, lightheadedness, or fainting. In these cases, medication or surgical treatment may be required to relieve the obstruction. Increased thickness predisposes to dangerous heart rhythms arising from the ventricles (ventricular ta
What is the contraction of cardiac muscle?
Systole is the contraction of cardiac muscle & Diastole is the relaxation of the cardiac muscles.
Which is thicker, the ventricle or the atrium?
The ventricle is much thicker than the atrium. Depolarization and repolarization rate is different in different layers. Depolarization starts from endocardium (innermost layer) and ends with epicardium (outermost layer). Repolarization of the ventricle is opposite, epicardium to endocardium. This is another reason that ventricular repolarization is longer than atrium.
What is a type 1 block in a ventricular atria?
Mobits Type I block is characterized by a gradual and progressive conduction defect between atria and ventricles until an impulse is completely blocked and ventricular stimulation lacks as a result of a single beat ( Pastore et al., 2016; Lilly, 2012 ). The ECG shows a progressive P–R interval increment and R–R interval reduction between beats, until the next QRS complex is absent, starting the cycle anew. During the pause, the R–R interval is twice shorter than the previous, see Fig. 1.14 (this figure was published in Textbook of Medical Physiology, Arthur C. Guyton and John E. Hall, Chapter 13: Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation, Page 149, Copyright Elsevier Inc. (2006)) ( Pastore et al., 2009 );
How long does the QRS complex last?
The QRS complex reflects depolarization of the right and left ventricles which in the normal heart lasts for about 70–110 ms. The first negative deflection of the QRS complex is denoted the Q wave, and the first positive is denoted the R wave, while the negative deflection subsequent to the R wave is denoted the S wave ( Figure 6.10 ). Although the QRS complex may be composed of less than three individual waves, it is nevertheless referred to as a QRS complex. The morphology of the QRS complex is highly variable and depends on the origin of the heartbeat: the QRS duration of an ectopic beat may extend up to 250 ms, and is sometimes composed of more than three waves.
What are the P QRS T features?
The P-QRS-T complex features for an ECG signal basically correspond to the locations, durations, amplitudes, and shapes of particular waves or deflections inside the signal [ 106,107 ]. Typically, an ECG signal has a total of five major deflections, including P, Q, R, S, and T waves, plus a minor deflection, namely, the U wave, as shown in Fig. 2 [ 108]. The P wave is a small low-voltage deflection away from the baseline that is caused by the depolarization of the atria prior to atrial contraction as the activation (depolarization) wave-front propagates from the sinoatrial node through the atria. The Q wave is a downward deflection after the P wave. The R wave follows as an upward deflection, and the S wave is a downward deflection following the R wave. Q, R, and S waves together indicate a single event. Hence, they are usually considered to be the QRS complex. The features based on the QRS complex are among the most powerful features for ECG analysis. The QRS-complex is caused by currents that are generated when the ventricles depolarize prior to their contraction. Although atrial repolarization occurs before ventricular depolarization, the latter waveform (i.e., the QRS-complex) has a much greater amplitude, and atrial repolarization is, therefore, not seen on an ECG. The T wave, which follows the S wave, is ventricular repolarization, whereby the cardiac muscle is prepared for the next cycle of the ECG. Finally, the U wave is a small deflection that immediately follows the T wave. The U wave is usually in the same direction as the T wave.
What is ECG signal?
Electrocardiography (ECG) involves recording of electrical impulses generated by heart muscles during its regular or irregular beating activity, by using electrodes placed over specific regions on the human torso (mostly around the chest region). The intention is to capture minute heart beat signal changes which happens when the heart muscles depolarize during each beating cycle [33]. A typical ECG wave is characterized by three morphological patterns: a P-wave (atrial polarization wave), a QRS-complex wave (ventricular depolarization wave) and a T-wave (ventricular repolarization wave). In terms of signal properties, a surface ECG signal has a frequency range of 0.05–150 Hz in diagnostic mode and 0.5–40 Hz in monitoring mode, with amplitude ranging from 0.1 to 5 mV [33].
What causes AV block?
1.13 ). It can be caused by structural defects of the conduction pathway as seen, for example, in chronic conduction degenerative diseases and myocardial infarction ( Lilly, 2012 ).
Does ventricular depolarization occur before atrial repolarization?
Although atrial repolarization occurs before ventricular depolarization, the latter waveform (i.e., the QRS-complex) has a much greater amplitude, and atrial repolarization is, therefore, not seen on an ECG.
