What is the major function of hypothalamus in the brain?
What is the main function of the hypothalamus?
- important function. It also secretes neurohormones. ...
- hypothalamus. Beside above, what is the structure and function of the hypothalamus? ...
- thalamus. The thalamus serves as a sensory relay center; its neurons project signals to both the amygdala and the higher cortical regions for further processing.
How is the hypothalamus involved in sleep AP Psychology?
How is the hypothalamus involved in sleep? A. Cell clusters in the hypothalamus stimulate the production of relatively slow alpha waves, signaling the transition from deep relaxation to sleep. B. The hypothalamus triggers the pituitary gland in the endocrine system to produce the hormone thryoxin, which leads you to sleep. C.
Does the midbrain include the thalamus and hypothalamus?
cephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, and subthalamus) (1). The named parts, from cranial to caudal, comprise the midbrain (mesencephalon), pons (metencephalon), and medulla oblongata (myelencephalon). Functions include regulation of the cardiac, respi-ratory, and central nervous systems including consciousness and the sleep cycle.
How does the hypothalamus influence the pituitary?
When deviations from homeostasis occur or when certain developmental changes are required, the hypothalamus stimulates cellular activity in various parts of the body by directing the release of hormones from the anterior and posterior pituitary glands. The hypothalamus communicates directives with these glands by one of the following two pathways:

What is the role of the ventromedial hypothalamus?
The ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMH) is important in the regulation of female sexual behavior, feeding, energy balance, and cardiovascular function. It is a highly conserved nucleus across species and a good model for studying neuronal organization into nuclei.
What is the ventromedial hypothalamus AP Psychology?
a region of the hypothalamus primarily associated with feelings of satiety. In studies in which the VMH is lesioned, animals overeat to the point of extreme obesity. The VMH also has a role in thermoregulation.
What is ventromedial nucleus in psychology?
a group of nuclei within the ventromedial hypothalamus that receives input from the amygdala and is associated particularly with eating and sexual behavior.
What is lateral hypothalamus in psychology?
The Lateral Hypothalamus is a part of the hypothalamus gland and is the portion that controls hunger. Research has shown that damage to this area can cause reduced food intake, presumably through loss of appetite, and that stimulation of this area can increase appetite.
What does the ventromedial hypothalamus signal about hunger?
The lateral hypothalamus responds to any internal or external stimulation that causes you to feel hungry. Once you've eaten, the ventromedial hypothalamus sends signals telling you when you're feeling full and have had enough food.
What is the difference between lateral hypothalamus and ventromedial hypothalamus?
The ventromedial nuclei is the satiety center, and when stimulated, it causes the sensation of fullness. On the other hand, the lateral hypothalamic area is the feeding center and when stimulated, it causes the sensation of hunger.
Where is the ventromedial hypothalamus?
The VMH is located near the left-right center of the brain and towards the front of the hypothalamus gland, giving it a good place to access these functions. For example, it's one of the most important brain systems that regulate appropriate level of food consumption.
What happens if the ventromedial hypothalamus is stimulated?
Electrical stimulation of the ventromedial hypothalamus enhances both fat utilization and metabolic rate that precede and parallel the inhibition of feeding behavior. Brain Res.
What happens when ventromedial hypothalamus is damaged?
Bilateral destruction of the ventromedial hypothalamus renders females non-receptive and virtually eliminates the tendency for females to approach males.
What is the purpose of the ventromedial hypothalamus in regard to food?
The Role of VMH in Central Regulation of Food Intake In fact, VMH is involved in controlling food intake and body weight (Gao and Horvath 2007; Flanagan-Cato et al. 2008). This nucleus is the center for integrating various food-related inputs from different areas of the brain.
What is anterior hypothalamus?
The anterior hypothalamus is a continuation of the preoptic region and extends caudally to the level of the arising of the median eminence. Its medial part comprises the anterior periventricular, suprachiasmatic, anterior hypothalamic, and paraventricular nuclei.
What is limbic system in psychology?
The limbic system is the part of the brain involved in our behavioural and emotional responses, especially when it comes to behaviours we need for survival: feeding, reproduction and caring for our young, and fight or flight responses.
What is the lateral hypothalamus and what function does it serve?
The lateral hypothalamus is a nuclei within the hypothalamus. It regulates feeding behaviors, inflammatory pain responses, sleep cycles and autonom...
What ventromedial hypothalamus functions might be important in psychology?
The ventromedial hypothalamus regulates conspecific (social) fear. It can also facilitate aggressive social behaviors, and panic attacks. Furthermo...
What is the role of the ventromedial hypothalamus?
Within the hypothalamus is a nuclei called the ventromedial hypothalamus. Its role is to help regulate hunger and satiety, body temperature, fear r...
What can damage to the lateral hypothalamus cause?
Damage to the lateral hypothalamus can cause lack of appetite and excessive weight loss. It can also cause a sleep disorder called narcolepsy, wher...
What happens if the ventromedial hypothalamus is damaged?
When the ventromedial hypothalamus is damaged, lack of satiety, weight gain and obesity can occur. Emotional and behavior dysregulation can also ma...
What does the ventromedial hypothalamus signal about hunger?
The ventromedial hypothalamus is involved in leptin signaling pathways from brown fat cells. It regulates the ability to feel full, which is called...
Which part of the brain is responsible for instantiating emotion?
These data indicate that the hypothalamus plays an integral role to instantiate emotion states, and is not simply a passive effector of upstream emotion centers. Keywords: defense; emotion; fear; mouse; neuroscience; persistance; scalability; ventromedial hypothalamus.
What are the behavioral consequences of activating these neurons?
The behavioral consequences of activating these neurons, moreover, exhibit properties characteristic of emotion states in general, including scalability, (negative) valence, generalization and persistence.
Is the hypothalamus an emotion center?
Importantly, these neurons can also condition learned defensive behavior, further refuting long-standing claims that the hypothalamus is unable to support emotional learning and therefore is not an emotion center.
What is the hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus is a small brain structure (0.4 percent of total brain volume) primarily of gray matter providing important functions which can be summarized to maintain homeostasis. From an evolutionary perspective, the hypothalamus can be considered a very old component of the central nervous system.
What is the hypothalamus? What function does it serve?
This structure (at least some parts of it) regulates many fundamental programs such as keeping the body temperature, eating, drinking, and sexual behavior . Lesions of the hypothalamic nuclei interfere with several vegetative functions (such as thermal regulation, hunger and thirst) and some of the so-called motivational behaviors (such as sexuality, combativeness…).
What are the functions of the hypothalamic nucleus?
Lesions of the hypothalamic nuclei interfere with several vegetative functions (such as thermal regulation, hunger and thirst) and some of the so-called motivational behaviors (such as sexuality, combativeness…). The hypothalamus also plays an important role in emotion.
How thick is the hypothalamus?
Hypothalamus slices, including the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN), of 300–400 μm thickness, are prepared, using a vibratome, from the freshly excised brains of Wistar rats weighing about 100 g, and are fixed with nylon meshes in a superfusion chamber.
Which organ combines the characteristics of glands and neuronal tissue?
It became obvious that the hypothalamus combines characteristics of glands and neuronal tissue. However, the focus of interest remains in investigations of hypothalamic control via the pituitary gland, which led to the discovery and chemical characterization of vasopressin and oxytocin in the early 1950s.
Which part of the brain is involved in emotions?
Recall, that many of brain structures have not one but many functions. This is true for the hypothalamus. Indeed, lateral parts of the hypothalamus is involved in emotions such as pleasure and rage, while the median part is associated with aversion, displeasure, and a tendency to uncontrollable and loud laughing.
Where do fibers reach the hypothalamus?
In rats, fibers from the amygdala reach the hypothalamus via two pathways: a short, direct projection over the surface of the optic tract (the ventral amygdalofugal pathway, a component of the ansa peduncularis) and a long, looping projection through the stria terminals.
What does the ventromedial hypothalamus tell you?
Once you've eaten, the ventromedial hypothalamus sends signals telling you when you're feeling full and have had enough food. To develop your intuitive eating skills, t's important to listen to both. Here's how it works: You feel hungry. ->. You eat. ->.
How does the brain work with the stomach?
The wall of your stomach is used to holding a certain amount of food before it distends enough to send out signals of fullness to your brain.
What does the brain tell you when you're hungry?
In your brain, hunger and fullness signals come from two nerve centers within the hypothalamus that help control eating behavior: the lateral hypothalamus and the ventromedial hypothalamus.
Why is the lateral hypothalamus important?
The lateral hypothalamus is very important for nutrition and food intake. In experiments, when this area was artificially stimulated with electrical impulses, the animals began to eat and drink, even when they were full, and when the nuclei were destroyed, they refused to eat at all.
Which part of the hypothalamus is responsible for the regulation of food intake?
The lateral hypothalamus is a part of the hypothalamus that plays an important role in the regulation of food intake: electrical stimulation of this area causes animals to start eating and drinking.
Which cells regulate body temperature, digestion, pressure, and reduce the perception of pain?
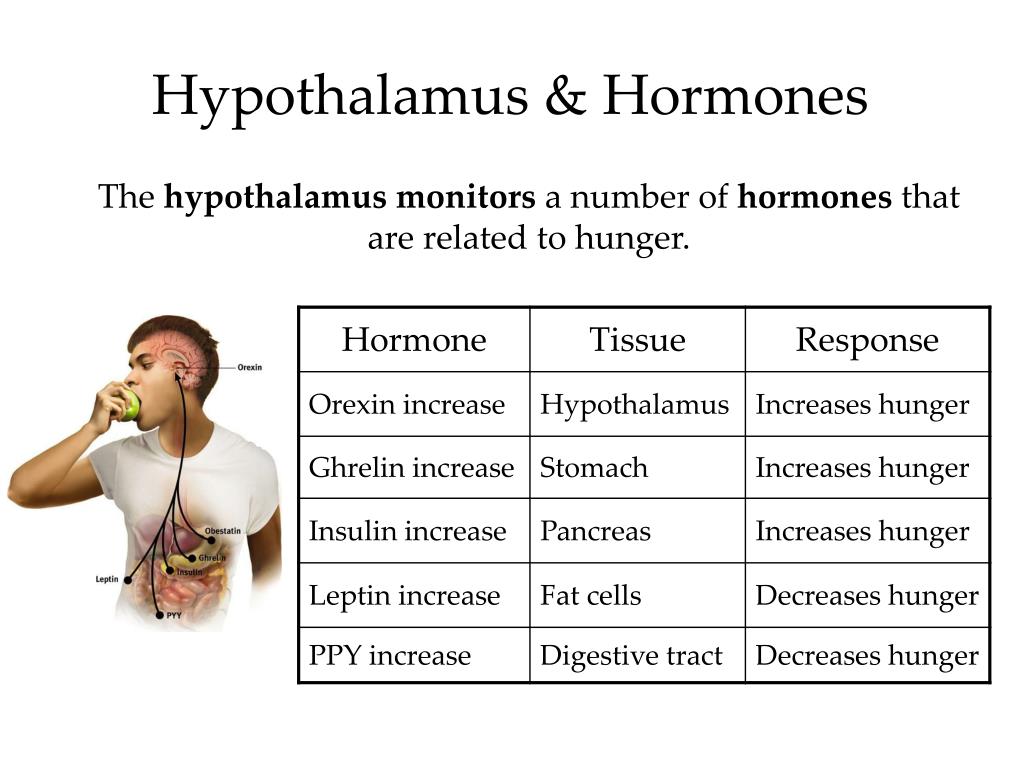
Here are located neurons that regulate body temperature, digestion, pressure, and reduce the perception of pain. The lateral hypothalamus cells synthesize orexins which maintain wakefulness and affect metabolism.