: an autonomic ganglion of the maxillary nerve that is situated in the pterygopalatine fossa and that receives preganglionic parasympathetic fibers from the facial nerve and sends postganglionic fibers to the nasal mucosa, palate, pharynx, and orbit.
What is the primary function of nerve tissue?
Nervous Tissue
- Function of Nervous Tissue. Nervous tissue makes up the nervous system. ...
- Types of Nervous Tissue. Neurons are cells that can transmit signals called nerve impulses, or action potentials. ...
- Related Biology Terms. Tissue – An organized group of cells that carries out a certain function. ...
- Quiz. Which is NOT a type of neuroglia? ...
What function does nerve cell perform?
What is the function of nerve cells?
- Energy transformers bounded by a double membrane endoplasmic reticulum
- Network of tubes and flattened sacs cytoplasm
- Contains dissolved substances, enzymes, and the cell organelles found inside plasma membrane, where organelles occur nucleus contains most of cell's DNA nuclear membrane double-layered structure ribosomes
What is the function of a nerve impulse?
Nerve Impulse
- Membrane potential – It is the difference in the total charge between the inside of the cell and the outside of the cell.
- Resting membrane potential – It is the difference in voltage across the cell membrane in a resting state. ...
- Action potential – It is a short-term change in the electrical potential that travels across the neuron cell.
What is the function of the phrenic nerve?
Your phrenic nerve also provides touch and pain sensory information to your:
- Diaphragm and diaphragmatic pleura (thin tissue covering the upper part of your diaphragm).
- Mediastina pleura (thin tissue covering the chest cavity between your lungs).
- Pericardium (sac covering your heart).
- Peritoneum (thin tissue covering your abdominal organs).
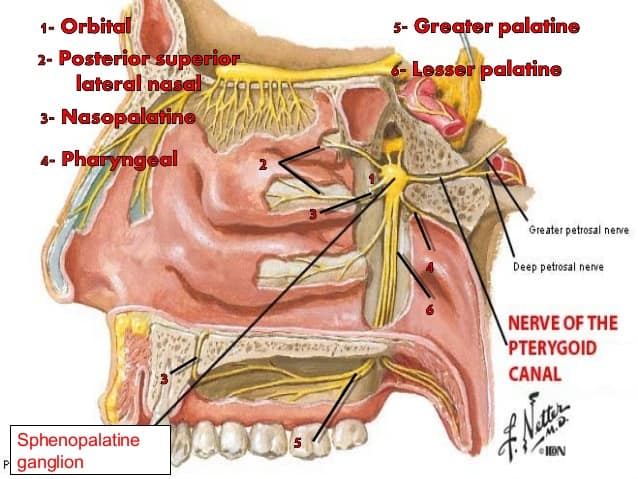
Where does the Vidian nerve come from?
The nerve of the pterygoid canal (Vidian nerve) is formed by the junction of the greater petrosal nerve and deep petrosal nerve, which passes from the foramen lacerum to the pterygopalatine fossa through the pterygoid canal.
What nerves make up the Vidian nerve?
It is formed by the confluence of two nerves: greater superfical petrosal nerve (from the geniculate ganglion of the facial nerve) carrying parasympathetic fibers from the superior salivary nucleus. deep petrosal nerve (from the sympathetic plexus on the internal carotid artery) carrying sympathetic fibers.
What is a Vidian neurectomy?
Vidian neurectomy is an alternative treatment for intractable vasomotor rhinitis that is unresponsive to other interventions and in patients with significantly impaired quality of life because of their symptoms.
Where does Vidian nerve synapse?
Preganglionic fibers follow the greater superficial petrosal nerve and the vidian nerve until they synapse on neurons clustered in the sphenopalatine ganglion (also known as the pterygopalatine ganglion).
Where is the 7th nerve located?
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue.
What does the 7th cranial nerve control?
The facial nerve is the 7th cranial nerve and carries nerve fibers that control facial movement and expression. The facial nerve also carries nerves that are involved in taste to the anterior 2/3 of the tongue and producing tears (lacrimal gland).
What triggers vasomotor rhinitis?
Some common triggers that may produce this reaction include: irritants in the environment such as perfumes, odors, smog, or secondhand smoke. changes in the weather, particularly dry weather. viral infections such as those associated with a cold or flu.
What passes through the vidian canal?
The vidian canal (VC), a bony tunnel in which the vidian artery and nerve pass, has been widely known as an important landmark to identify the anterior genu of the petrous carotid artery (AGPCA) especially during lateral extended endoscopic endonasal approachs (LEEEAs).
What are the symptoms of atrophic rhinitis?
What are the symptoms of atrophic rhinitis?Chronic nosebleeds (epistaxis).Nasal discharge of pus.Nasal dryness and crusting.Sinus infections (sinusitis).
Which of the following nerves contributes parasympathetic fibers to the Vidian nerve?
23.1). The vidian nerve is formed by the confluence of the greater superficial petrosal and deep petrosal nerves and travels in the pterygoid canal carrying the parasympathetic fibers, which synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion, and the postganglionic fibers are distributed with the branches of the maxillary nerve.
Where is the Vidian canal?
sphenoid boneThe pterygoid canal, also known as the Vidian canal, is a foramen in the base of skull, located in the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone, superior to the pterygoid plates, and inferomedial to the foramen rotundum.
Which is called nerve of Wrisberg?
The intermediate nerve, nervus intermedius, nerve of Wrisberg or Glossopalatine nerve, is the part of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) located between the motor component of the facial nerve and the vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII). It contains the sensory and parasympathetic fibers of the facial nerve.
What passes through Vidian Canal?
The pterygoid canal (also vidian canal) is a passage in the sphenoid bone of the skull leading from just anterior to the foramen lacerum in the middle cranial fossa to the pterygopalatine fossa....Pterygoid canalArteryartery of the pterygoid canalNervenerve of pterygoid canalIdentifiersLatinCanalis pterygoideus7 more rows
Which is called nerve of wrisberg?
The intermediate nerve, nervus intermedius, nerve of Wrisberg or Glossopalatine nerve, is the part of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) located between the motor component of the facial nerve and the vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII). It contains the sensory and parasympathetic fibers of the facial nerve.
What does the nerve of the pterygoid canal supply?
The nerve of the pterygoid canal (Vidian nerve) is formed by the junction of the greater petrosal nerve and the deep petrosal nerve within the pterygoid canal containing the cartilaginous substance, which fills the foramen lacerum....Nerve of pterygoid canalFMA67584Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy7 more rows
What does the lesser petrosal nerve do?
The lesser petrosal nerve (small superficial petrosal nerve) is the General visceral efferent (GVE) component of the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), carrying parasympathetic fibers from the tympanic plexus to the parotid gland.
Why should the entire bony rim of the vidian canal be identified?
The entire bony rim of the vidian canal should be identified to ensure that complete neural transection has occurred.
Which nerve is tethering the pterygopalatine contents?
Posterior dissection leads to the pharyngeal nerve and the vidian nerve tethering the pterygopalatine contents and preventing them from mobilizing laterally. The pharyngeal nerve runs laterally and thus sits at almost right angles to the vidian nerve. Both nerves are divided using a sickle knife.
Where does the sympathetic nerve originate from?
Most of the sympathetic neural output to the human nose originates from cholinergic preganglionic fibers in the thoracolumbar region of the spinal cord; these fibers synapse on neurons in the superior cervical ganglion. The postganglionic fibers form the petrosal nerve, which joins the greater superficial nerve to form the vidian nerve. The vidian nerve therefore contains both the parasympathetic and the sympathetic innervation to the nasal mucosa. The postganglionic sympathetic nerves in the mammalian nose typically contain catecholamines, but may also contain adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) and neuropeptides, most notably neuropeptide Y (NPY).
Which ganglion neurons are cholinergic?
The pterygopalatine (or sphenopalatine) ganglion receives preganglionic axons from the facial nerve via the greater superficial petrosal nerve and the nerve of the pterygoid canal ( Vidian nerve ). The pterygopalatine ganglion neurons innervate the lacrimal glands, the blood vessels of the eye, the blood vessels and secretory glands of the nasal cavity and palate, and the cerebral blood vessels. Most pterygopalatine ganglion neurons are cholinergic and stimulate secretion of lacrimal, nasal, and palatine glands; VIP and NO are primarily responsible for vasodilation of eye, nasopharynx, and cerebral vessels.
Where does the preganglionic innervation of the nasal airways originate?
Preganglionic parasympathetic innervation of the nasal airways originates from the facial nucleus of the brain stem and the superior salivatory nucleus. Preganglionic fibers follow the greater superficial petrosal nerve and the vidian nerve until they synapse on neurons clustered in the sphenopalatine ganglion (also known as the pterygopalatine ganglion). The preganglionic nerves are cholinergic, and upon stimulation cause nicotinic fast excitatory potentials on the postganglionic neurons.
What is the sagittal graphic of the trigeminal nerve?
Sagittal graphic of the trigeminal nerve shows its three branches exiting the foramina. The ophthalmic division of CNV enters into the orbit via the superior orbital fissure where it divides into frontal, ciliary, and lacrimal branches.
Where are postganglionic fibers located?
Postganglionic fibers are distributed to the nasal mucosa via the branches of the posterior nasal nerve, where they ultimately innervate serous and mucous glands, arteries, veins, and arteriovenous anastomoses.
What is the name of the vein that goes through the pharyngeal plexus?
vidian vein - a vein accompanying the nerve and artery through the pterygoid canal and emptying into the pharyngeal venous plexus. Synonym (s): vein of pterygoid canal
Which artery is located in the sphenoid sinus?
The optic nerve and the internal carotid artery in the sphenoid sinus. (Rhinoscopic Clinic)
What are the structures of the Septacion del Seno Esfenoidal?
These structures include (1) the optic nerve and the internal carotid artery in the superolateral wall, (2) the posterior ethmoid cells in the anterosuperior wall (the Onodi cell), (3) the maxillary nerve in the lateral wall, and (4) the canal of the vidian nerve in the floor.
What is a vidian neurectomy?
A vidian neurectomy is a type of nerve block which involves either severing or removing the vidian nerve and is used to provide relief for patients with chronic rhinitis. Chronic rhinitis is characterized by the inflammation of the lining of the nose, which causes symptoms like nasal congestion, sneezing, itching and runny nose.
Does a vidian nerve neurectomy help with rhinitis?
By severing the vidian nerve, a vidian neurectomy can reduce or eliminate chronic rhinitis symptoms and offer lasting relief to patients.
What nerve is the pterygoid canal?
(Vidian nerve labeled at upper right.) The nerve of the pterygoid canal ( Vidian nerve) is formed by the junction of the greater petrosal nerve and deep petrosal nerve, which passes from the foramen lacerum to ...
Which nerve contains both sympathetic and parasympathetic axons?
The nerve of the pterygoid canal contains axons of both sympathetic and parasympathetic axons, specifically; preganglonic parasympathetic axons from the greater petrosal nerve, a branch of the facial nerve (cell bodies are located in the superior salivatory nucleus)
Which nerve passes through the pterygoid canal?
The nerve of the pterygoid canal ( Vidian nerve) is formed by the junction of the greater petrosal nerve and deep petrosal nerve, which passes from the foramen lacerum to the pterygopalatine fossa through the pterygoid canal .
Which ganglion contains the postganglionic neurons?
The preganglionic parasympathetic axons synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion, which contains the postganglionic neurons which provide secretomotor innervation to the lacrimal gland, as well as the nasal and palatine glands.