
How do you calculate the Vmax of an enzyme?
- y intercept = Vmax.
- gradient = -Km.
- x intercept = Vmax / Km.
What is the difference between kcat and Vmax?
What is the difference between Vmax and kcat? Vmax & Kcat. To determine Kcat, one must obviously know the Vmax at a particular concentration of enzyme, but the beauty of the term is that it is a measure of velocity independent of enzyme concentration, thanks to the term in the denominator. Kcat is thus a constant for an enzyme under given ...
Is there a relationship between Vmax and km?
Vmax is equal to the product of the catalyst rate constant (kcat) and the concentration of the enzyme. Km is the concentration of substrates when the reaction reaches half of Vmax. A small Km indicates high affinity since it means the reaction can reach half of Vmax in a small number of substrate concentration.
What is Vmax enzymes?
Vmax represents the maximum velocity of an enzyme which takes place when all the limited active sites are occupied with substrates. It is determined from the Lineweaver- Burk plot by calculating the reciprocal of the y-intercept. Vmax is proportional to enzyme concentration.
What is Vmax and Km in enzyme kinetics?
Vmax is the reaction rate at the state where the enzyme is fully saturated by the substrate. The key difference between Km and Vmax is that Km measures how easily the enzyme can be saturated by the substrate, whereas Vmax is the maximum rate at which an enzyme is catalyzed when the enzyme is saturated by the substrate.
What is meant by Vmax value?
Vmax: Vmax or a maximum velocity of an enzymatic reaction can be defined as the rate of the reaction at which the enzyme shows the highest turnover. Increasing the substrate concentration indefinitely further does not increase the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction after reaching a certain point.
What does Vmax mean kinetics?
the maximum initial velocityE. Biology definition: Vmax is the maximum initial velocity or rate of a reaction. In enzyme kinetics, Vmax is the maximum velocity of an enzymatically catalyzed reaction when the enzyme is saturated with its substrate.
What does V max and KM mean?
Vmax is the maximum reaction velocity at which all enzymes become saturated with substrate. Km is the substrate concentration at which half of the maximum velocity is achieved.
What does high Vmax mean?
Biomolecules: Enzymes This point is reached when there are enough substrate molecules to completely fill (saturate) the enzyme's active sites. The maximal velocity, or Vmax, is the rate of the reaction under these conditions. Vmax reflects how fast the enzyme can catalyze the reaction.
How is Vmax determined?
Ease of Calculating the Vmax in Lineweaver-Burk Plot Next, you will obtain the rate of enzyme activity as 1/Vo = Km/Vmax (1/[S]) + 1/Vmax, where Vo is the initial rate, Km is the dissociation constant between the substrate and the enzyme, Vmax is the maximum rate, and S is the concentration of the substrate.
What factors affect Vmax?
Although enzymes are catalysts, Vmax does depend on the enzyme concentration, because it is just a rate, mol/sec - more enzyme will convert more substrate moles into product. In standard Michealis-Menten kinetics the reaction constant is proportional to the rate of the decomposition of ES (enzyme-substrate complexes).
How do you find Km and Vmax from Michaelis Menten?
4:025:23B7 Determine Vmax and Michaelis constant (Km) by graphical means ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo if I divide v-max by two that gives me the Michaelis constant for Y and for X if I divide v-maxMoreSo if I divide v-max by two that gives me the Michaelis constant for Y and for X if I divide v-max by two that also gives me the Michaelis constant for X.
What happens to Vmax when enzyme concentration increases?
If you doubled the amount of enzyme, sure the Vmax is going to increase. If you doubled the amount of enzyme, sure the Vmax is going to increase.
Does low Km mean low Vmax?
The value of KM is inversely related to the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate. High values of KM correspond to low enzyme affinity for substrate (it takes more substrate to get to Vmax ). Low KM values for an enzyme correspond to high affinity for substrate.
What does a decrease in Vmax mean?
A lower Vmax means that the enzyme is operating in sub-optimal conditions.
What does a small Vmax mean?
Vmax And Km : Example Question #4 Explanation: In enzyme kinetics, is the concentration of substrate which allows the enzyme to reach (maximum reaction velocity). A small indicates that only a small amount of substrate is needed for the enzyme to become saturated and thus for the reaction to reach maximum velocity.
What does high Km mean?
A small Km indicates that the enzyme requires only a small amount of substrate to become saturated. Hence, the maximum velocity is reached at relatively low substrate concentrations. A large Km indicates the need for high substrate concentrations to achieve maximum reaction velocity.
What does a small Vmax mean?
Vmax And Km : Example Question #4 Explanation: In enzyme kinetics, is the concentration of substrate which allows the enzyme to reach (maximum reaction velocity). A small indicates that only a small amount of substrate is needed for the enzyme to become saturated and thus for the reaction to reach maximum velocity.
What does a decrease in Vmax mean?
A lower Vmax means that the enzyme is operating in sub-optimal conditions.
What is Vmax physics?
vmax = maximum velocity at equilibrium (m/s) A = amplitude of mass (m) k = spring constant (N/m)
What is enzyme kinetics?
Enzyme kinetics is the study of enzyme reactions rates and the conditions which affect them. In this article, we will discuss the structure and function of enzymes, their clinical significance and theories of enzyme kinetics. Enzyme Structure. Enzymes are proteins and usually have a globular tertiary structure.
What is the rate limiting step of an enzyme reaction?
The rate-limiting step of any reaction is its slowest step, and this is what sets the pace of the entire reaction. In enzymatic reactions, the conversion of the enzyme-substrate complex to the product is normally rate-limiting. The rate of this step (and therefore the entire enzymatic reaction) is directly proportional to the concentration of the enzyme-substrate complex.
What happens when an enzyme changes its pH?
Changes in pH can alter critical ionisation states, while changes in temperature can disrupt important bonds, affecting the enzyme’s structure and therefore function. If exposed to severe changes in temperature and/or pH, the shape of the active site may change. This is referred to as enzyme denaturation and means the enzyme will no longer be able to bind its substrate or carry out its biological function.
What happens when a substrate binds to the active site?
Therefore, when the substrate binds to the active site, it is encouraged to continue the reaction and is converted into the transition state, and ultimately the final product of the reaction. This energetically favourable process allows more substrate molecules to be converted into products in a given period of time.
What is the structure of an enzyme?
Enzyme Structure. Enzymes are proteins and usually have a globular tertiary structure. Their structure is highly specific to the reaction they catalyse, and hence the reactants involved, due to the presence of an active site where the reaction itself occurs.
What does it mean when your enzymes are low?
If levels are abnormally low, it may indicate that the enzyme is either non-functional, being produced more slowly than usual or is being broken down quickly, possibly due to a genetic abnormality.
How does pH affect enzymes?
Changes in pH can alter critical ionisation states, while changes in temperature can disrupt important bonds, affecting the enzyme's structure and therefore function . If exposed to severe changes in temperature and/or pH, the shape of the active site may change.
What is the kinetics of an enzyme?
Enzyme kinetics graph showing rate of reaction as a function of substrate concentration for normal enzyme, enzyme with a competitive inhibitor, and enzyme with a noncompetitive inhibitor. For the competitive inhibitor, Vmax is the same as for the normal enzyme, but Km is larger. For the noncompetitive inhibitor, Vmax is lower than for the normal enzyme, but Km is the same.
What is enzyme kinetics graph?
Enzyme kinetics graph showing rate of reaction as a function of substrate concentration.
Why is there extra substrate in enzymes?
The extra substrate makes the substrate molecules abundant enough to consistently “beat” the inhibitor molecules to the enzyme. With a noncompetitive inhibitor, the reaction can never reach its normal , regardless of how much substrate we add.
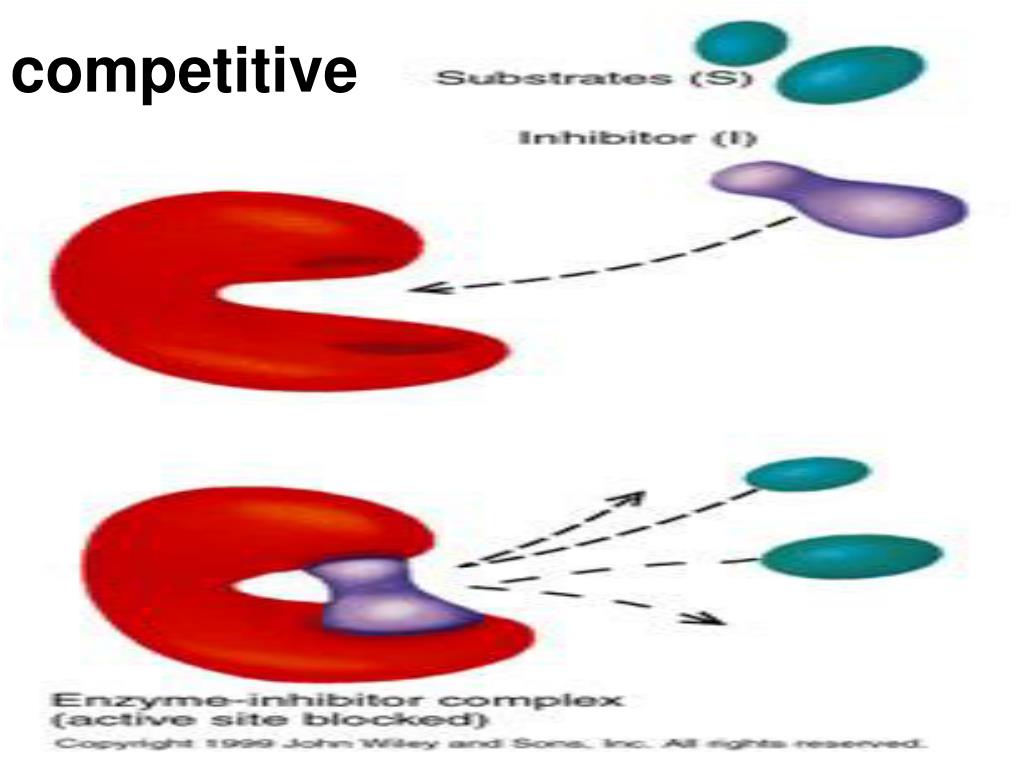
How do competitive inhibitors affect enzymes?
That is, the inhibitor and substrate compete for the enzyme. Competitive inhibition acts by decreasing the number of enzyme molecules available to bind the substrate.
What is the equation for enzymes?
Enzymes that display this behavior can often be described by an equation relating substrate concentration, initial velocity, , and , known as the Michaelis-Menten equation. Enzymes whose kinetics obey this equation are called Michaelis-Menten enzymes.
Why does Km decrease in uncompetitive inhibition?
The apparent Km decreases in uncompetitive inhibition because by binding to the enzyme-substrate complex, uncompetitive inhibitors are "pulling" that complex out from the reactions. This removal of substrate decreases its concentration, and allows the remaining enzyme to work better.
How to tell how an enzyme works?
As a matter of fact, you can tell a remarkable amount about how an enzyme works, and about how it interacts with other molecules such as inhibitors, simply by measuring how quickly it catalyzes a reaction under a series of different conditions.
What is the Km of an enzyme?
Michaelis Constant (Km): Enzymes have varying tendencies to bind their substrates ( affinities ). An enzyme's K m describes the substrate concentration at which half the enzyme's active sites are occupied by substrate. A high K m means a lot of substrate must be present to saturate the enzyme, meaning the enzyme has low affinity for the substrate. On the other hand, a low K m means only a small amount of substrate is needed to saturate the enzyme, indicating a high affinity for substrate. Click on the image at right to see how high K m and low K m enzymes compare. Graphically, the K m is the substrate concentration that gives the enzyme one-half of its V max. Although it may look like the V max drops, if the graph is extended along the x-axis, the V max stays constant for the two enzymes described here.
What are the two constants of enzymes?
Enzymes. In a mathematical description of enzyme action developed by Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten in 1913, two constants, Vmax and Km , play an important role. These constants are important to know, both to understand enzyme activity on the macroscale and to understand the effects of different types of enzyme inhibitors.
What does 108 mean in enzymes?
108 - Indicates how efficiently an enzyme selects its substrate and converts to product.
What curve can be used to estimate V?
The Michaelis-Menten curve can be used to ESTIMATE V
Why is the concentration of ES relatively constant?
i.e. the concentration of ES remains relatively constant because it is produced and broken down at the same rate
Can Michaelis-Menten curve be used to determine KM?
The Michaelis-Menten curve can be used to ESTIMATE Vmax and KM – although not exacting and we don’t use it. Determine the values by a different version of the equation. In 1934, Lineweaver and Burk devised a way to transform the hyperbolic plot into a linear plot.
Is Mhas the same as substrate concentration?
Mhas the same units as substrate concentration, this implies a relationship between K
