What is volume cycle mode in ventilation?
This mode is used to keep the peak airway pressure at the lowest possible level. This mode is volume-cycled and can be patient triggered-or time-triggered. This is a mode of mechanical ventilation where the machine uses variable pressure to provide pressure support for a patient’s spontaneous breaths.
What is the difference between pressure-controlled and Volume-Cycled Ventilation?
In volume cycled ventilation, tidal volume is set and airway pressures are measured, whereas in press … Pressure-controlled and volume-cycled mechanical ventilation Clin Chest Med. 1996 Sep;17(3):395-410.doi: 10.1016/s0272-5231(05)70323-3. Authors A W McKibben 1 , S A Ravenscraft Affiliation
What are pressure and volume Modes of mechanical ventilation?
Pressure and volume modes of mechanical ventilation are available as options in the current generation of ventilators, giving clinicians many choices when managing a mechanically ventilated patient. In volume cycled ventilation, tidal volume is set and airway pressures are measured, whereas in press …
How does volume control work on a ventilator?
Remember, in volume control, the ventilator will adjust the pressure needed to reach the volume that is set. When the resistance increases, or if compliance drops, in volume control ventilation, this will cause an increase in the peak pressures to overcome the changes in the lungs and deliver the set volume.

What is time cycled ventilation?
Time cycling indicates that the mechanical ventilator breath switches from inspiration to expiration after a set time threshold is reached. This can be accomplished by setting the respiratory rate, inspiratory time, or inspiratory-expiratory ratio.
What is volume ventilation?
Volume control ventilation defines the volume administered to the patient (tidal volume Vt as the control variable). Airway pressure results from the compliance of the lungs and the inhaled volume. A volume-controlled mode thus ensures that the patient will receive a specific tidal volume.
What are the 3 modes of ventilation systems?
Based on the types of respiratory cycles that are offered to the patient, three basic ventilatory modes can be considered. These are: Assist/Control ventilation (A/C), Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV) and Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (SIMV) with PS, a hybrid mode of the first two.
What is the difference between pressure ventilation and volume ventilation?
In summary: In general, volume control favours the control of ventilation, and pressure control favours the control of oxygenation. Volume and pressure control modes have distinct advantages and disadvantages which are mainly related to the flow and pressure patterns of gas delivery.
What are the benefits of volume guarantee ventilation?
Volume guarantee ventilation has been shown in clinical trials to be as safe as pressure limited ventilation with potential benefits including reduction in duration of ventilation, intraventricular haemorrhage and air leak.
What is pressure cycled ventilator?
In volume cycled ventilation, tidal volume is set and airway pressures are measured, whereas in pressure-controlled ventilation, pressure is set and volume is measured. This article reviews the characteristics of these two ventilatory modes and discusses in detail conversion from one mode to the other.
What are the 4 types of ventilation?
What are The Different Types of Ventilation?NATURAL VENTILATION.MECHANISED FANS. In some cases, a natural ventilation solution isn't possible due to the design and location of building. ... EXHAUST VENTILATION. ... SUPPLY VENTILATION. ... BALANCED VENTILATION. ... SMOKE VENTILATION.
What are the 4 phases of ventilation?
There are four stages of mechanical ventilation. There is the trigger phase, the inspiratory phase, the cycling phase, and the expiratory phase.
What are the types of ventilation?
There are three methods that may be used to ventilate a building: natural, mechanical and hybrid (mixed-mode) ventilation.
What are normal PEEP levels?
This, in normal conditions, is ~0.5, while in ARDS it can range between 0.2 and 0.8. This underlines the need for measuring the transpulmonary pressure for a safer application of mechanical ventilation.
Is a BiPap a ventilator?
It is commonly known as “BiPap” or “BPap.” It is a type of ventilator—a device that helps with breathing. During normal breathing, your lungs expand when you breathe in. This is caused by the diaphragm, which is the main muscle of breathing in your chest, going in a downward direction.
What is the difference between SIMV and assist control?
SIMV with pressure support also produced a significantly greater minute volume and ventilatory equivalent than assist-control. There were no significant differences between assist-control and SIMV. All three modes produced a lower ventilatory equivalent and higher oxygen consumption than spontaneous breathing.
What is volume trigger in ventilator?
Volume triggering is described by Chatburn (2012) as “the starting of inspiratory flow due to a patient inspiratory effort that generates an inspiratory volume signal larger than a preset threshold”.
How does CPAP ventilation work?
CPAP works by providing a positive pressure of air through the mask and into the airway, which helps to keep the airway open. This helps to prevent breathing difficulties, increase the level of oxygen in the lungs and removes the unwanted gas (carbon dioxide) out of the lungs.
What is the difference between oxygenation and ventilation?
Ventilation and oxygenation are distinct but interdependent physiological processes. While ventilation can be thought of as the delivery system that presents oxygen-rich air to the alveoli, oxygenation is the process of delivering O2 from the alveoli to the tissues in order to maintain cellular activity.
What is a volume control?
noun. the control on a radio, etc, for adjusting the intensity of sound.
What is pressure control ventilation?
pressure control ventilationpositive pressure ventilationin which breaths are augmented by air at a fixed rate and amount of pressure, with tidal volume not being fixed; used particularly for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome.
What is high frequency ventilation?
high-frequency ventilationa technique of mechanical ventilation that uses very high rates (over 80 breaths per minute) and small tidal volumes (equal to or less than dead space); it may either be positive pressure ventilation or be delivered in the form of frequent jets of air. It is used to lower the peak airway pressure applied to the lung, thus decreasing the risk of barotrauma.
What is proportional assist ventilation?
proportional assist ventilationpositive pressure ventilationin which the ventilator can sense the patient's level of inspiratory flow and deliver pressure support to achieve a given tidal volume.
What is negative pressure ventilation?
negative pressure ventilationa type of mechanical ventilation in which negative pressure is generated on the outside of the patient's chest and transmitted to the interior of the thorax in order to expand the lungs and allow air to flow in; used primarily with patients having paralysis of the chest muscles. See also ventilator.
What is IMV ventilation?
intermittent mandatory ventilation(IMV) a type of control mode ventilationin which the patient breathes spontaneously while the ventilator delivers a prescribed tidal volume at specified intervals and allows the patient to breathe spontaneously between cycles. The ventilator rate is set to maintain the patient's PaCO2at desired levels and is reduced gradually to zero as the patient's condition improves. See also intermittent positive-pressure breathing.
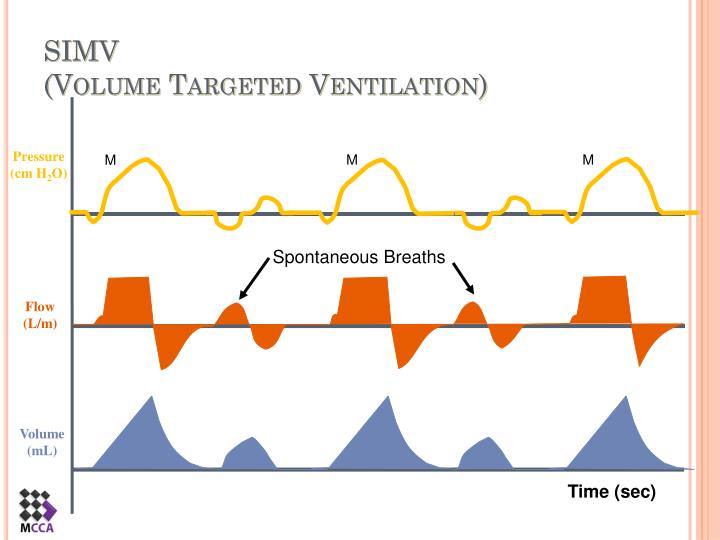
What is SIMV in medical terms?
intermittent mandatory ventilation, synchronized(SIMV) positive pressure ventilationin which the patient breathes spontaneously while the ventilator delivers a positive-pressure breath at intervals that are predetermined but synchronized with the patient's breathing.
What is the exchange of air between the lungs and the outside air?
Pulmonology The exchange of air between the lungs and the outside air. See Dead space, High-frequency ventilation, Jet ventilation, Maximum voluntary ventilation, Mechanical ventilation, Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation, Partial ventilation, Staircase ventilation Public health The circulation of air from one space to another, usually understood to mean the replacement of ambient air with fresh air from another source. See General exhaust, Local exhaust, Mechanical exhaust.
What is a ventilator mode?
A ventilator mode is a way of describing how the mechanical ventilator assists the patient with inspiration. The characteristics of a particular mode controls how the ventilator functions. Understanding the different ventilator modes is one of the most important aspects of mechanical ventilation.
What is mechanical ventilation?
A mode of mechanical ventilation in which two levels of continuous positive airway pressure are applied with an intermittent release phase for spontaneous breaths. This mode is often recommended to improve oxygenation and treat refractory hypoxemia.
What is SIMV in respiratory therapy?
It helps to decrease the patient’s mean airway pressure. As a Respiratory Therapist (or student), SIMV and Assist/Control are the two ventilator modes that you should be most familiar with. However, it’s also important to develop an understanding of some of the secondary modes of mechanical ventilation as well.
What is SIMV mode?
SIMV is a mode that is used for weaning as well.
What does it mean when a ventilator is in pressure control mode?
You also have to take into account that the ventilator is in the pressure control mode, which means that the pressure is pre-set. If there is a decrease in lung compliance when the ventilator is operating in the pressure control mode, the machine will continue delivering a constant pressure.
Why is assist/control used in mechanical ventilation?
That is also one of the advantages of using Assist/Control because it keeps the patient’s work of breathing requirement very low.
What is CPAP continuous pressure?
In CPAP, or continuous positive airway pressure, a continuous pressure that is above atmospheric pressure is maintained throughout the breathing cycle.
Is PCV a ventilatory mode?
Volume-controlled ventilation (VCV) and pressure-controlled ventilation (PCV) are not different ventilatory modes, but are different control variables within a mode. Just as the debate over the optimal ventilatory mode continues, so too does the debate over the optimal control variable. VCV offers t …
Is VCV the same as PCV?
Volume-controlled ventilation (VCV) and pressure-controlled ventilation (PCV) are not different ventilatory modes, but are different control variables within a mode. Just as the debate over the optimal ventilatory mode continues, so too does the debate over the optimal control variable. VCV offers the safety of a pre-set tidal volume and minute ventilation but requires the clinician to appropriately set the inspiratory flow, flow waveform, and inspiratory time. During VCV, airway pressure increases in response to reduced compliance, increased resistance, or active exhalation and may increase the risk of ventilator-induced lung injury. PCV, by design, limits the maximum airway pressure delivered to the lung, but may result in variable tidal and minute volume. During PCV the clinician should titrate the inspiratory pressure to the measured tidal volume, but the inspiratory flow and flow waveform are determined by the ventilator as it attempts to maintain a square inspiratory pressure profile. Most studies comparing the effects of VCV and PCV were not well controlled or designed and offer little to our understanding of when and how to use each control variable. Any benefit associated with PCV with respect to ventilatory variables and gas exchange probably results from the associated decelerating-flow waveform available during VCV on many ventilators. Further, the beneficial characteristics of both VCV and PCV may be combined in so-called dual-control modes, which are volume-targeted, pressure-limited, and time-cycled. PCV offers no advantage over VCV in patients who are not breathing spontaneously, especially when decelerating flow is available during VCV. PCV may offer lower work of breathing and improved comfort for patients with increased and variable respiratory demand.
What is pressure controlled ventilatory mode?
Pressure controlled ventilatory mode in which the majority of time is spent at the higher (inspiratory) pressure. Early trials were promising, however the risks of auto PEEP and hemodynamic deterioration due to the decreased expiratory time and increased mean airway pressure generally outweight the small potential for improved oxygenation
What are the characteristics of ventilatory modes?
While modes have classically been divided up into pressure or volume controlled modes, a more modern approach describes ventilatory modes based on three characteristics – the trigger (flow versus pressure), the limit (what determines the size of the breath), and the cycle (what actually ends the breath). In both VCV and PCV, time is the cycle, the difference being in how the time to cessation is determined. PSV, by contrast, has a flow cycle.
What is APRV in CPAP?
Airway pressure release ventilation is similar to PCIRV – instead of being a variation of PCV in which the I:E ratio is reversed, APRV is a variation of CPAP that releases pressure temporarily on exhalation. This unique mode of ventilation results in higher average airway pressures. Patients are able to spontaneously ventilate at both low and high pressures, although typically most (or all) ventilation occurs at the high pressure. In the absence of attempted breaths, APRV and PCIRV are identical. As in PCIRV, hemodynamic compromise is a concern in APRV. Additionally, APRV typically requires increased sedation
Why is the expiratory time constant calculated?
Calculates the expiratory time constant in order to guarantee sufficient expiratory time and thus minimize air trapping
What is inverse ratio ventilation?
Inverse Ratio Ventilation (IRV) is a subset of PCV in which inflation time is prolonged ( In IRV, 1:1 , 2:1, or 3:1 may be use . Normal I:E is 1:3). This lowers peak airway pressures but increases mean airway pressures. The result may be improved oxygenation but at the expense of compromised venous return and cardiac output, thus it is not clear that this mode of ventilation leads to improved survival. IRV’s major indication is in patients with ARDS with refractory hypoxemia or hypercapnia in other modes of ventilation [Am J Surg 183: 151, 2002]
What is the tidal volume goal for ARDSnet II?
ARDSnet II: 8.3 vs. 13.2 cm H2O: in patients with acute lung injury and ARDS who receive mechanical ventilation with a tidal-volume goal of 6 ml per kilogram of predicted body weight and an end-inspiratory plateau-pressure limit of 30 cm of water, clinical outcomes are similar whether lower or higher PEEP levels are used [NEJM 351: 327, 2004]
What is a CMV breath?
Also known as continuous mandatory ventilation (CMV). Each breath is either an assist or control breath, but they are all of the same volume. The larger the volume, the more expiratory time required. If the I:E ratio is less than 1:2, progressive hyperinflation may result.
Abstract
Patient-ventilator interaction is a key element in optimizing mechanical ventilation.
Introduction
The goals of mechanical ventilatory support are to provide unloading of the respiratory muscles and medical gas to sustain life. Patient-ventilator interaction is complex and multifactorial, as it is dependent upon respiratory system conditions, various disease states, neural function, and clinical input.
Cycling Mechanisms
The cycling of a mechanical ventilator breath occurs after a set value is reached. These values are often referred to as “cycle variables.” 8 All mechanical ventilator breath types are governed by cycling variables. Four variables are used to determine when to cycle to exhalation: pressure, time, volume, and flow.
Premature Cycling
Most scientific study of mechanical ventilation cycling focuses on delayed cycling. However, premature breath cycling may also have detrimental effects on patient-ventilator synchrony. Premature cycling is simply when the ventilator terminates the breath while the patient requires a longer inspiratory period.
Delayed Cycling
Optimal assistance of spontaneous breaths would require cycling to correspond to the end of the patient's neural inspiratory effort. The presence of active expiratory effort before the cycle criterion is met is termed “delayed cycling” ( Fig. 4 ).
Expiratory Asynchrony
Expiratory asynchrony can be identified as the delay in the relaxation of the expiratory-muscle activity prior to the next mechanical inspiration. Simply, there is an overlap between expiratory and inspiratory activity.
Summary
Substantial progress has been made in the understanding of patient-ventilator interaction. It has become increasingly recognized that cycling is an important determinant of optimal patient-ventilator synchrony. Cycling of the mechanical breath has gained the attention of both ventilator manufacturers and clinicians.
What is volume cycled ventilation?
In volume cycled ventilation, tidal volume is set and airway pressures are measured, whereas in pressure-controlled ventilation, pressure is set and volume is measured. This article reviews the characteristics of these two ventilatory modes and discusses in detail conversion from one mode to the other. Pertinent clinical studies and recent direct comparisons of volume-cycled and pressure-controlled ventilation are reviewed.
What is volume mode in mechanical ventilation?
Pressure and volume modes of mechanical ventilation are available as options in the current generation of ventilators, giving clinicians many choices when managing a mechanically ventilated patient. In volume cycled ventilation, tidal volume is set and airway pressures are measured, whereas in press …
