Is Volvox aureus a green algae?
[Video] Volvox aureus under the microscope. Volvox is a polyphyletic genus of Chlorophyte green algae in the family Volvocaceae. Volvox is classified in the class Chlorophyceae due to the presence of chlorophyll. There are 20 species of freshwater Volvox. Common species are Volvox aureus, Volvox globator, Volvox carteri, and Volvox barberi, etc.
What is Volvox in biology?
Volvox is a polyphyletic genus of chlorophyte green algae in the family Volvocaceae. It forms spherical colonies of up to 50,000 cells. They live in a variety of freshwater habitats, and were first reported by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1700.
What is Volvox aureus and why is it important?
They are part of the food chain which makes them an important component of the food items for many aquatic organisms such as fish. However, the overgrowth of Volvox aureus could result in a harmful algal bloom. An algal bloom is more frequent in warm waters having a high nitrogen content. [In this image] Algal bloom in Lake Binder, IA.
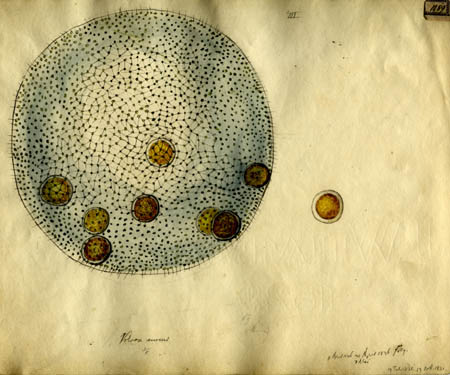
What are motile colonies of Volvox aureus?
Motile colonies of Volvox aureus. Volvox colonies move through their environment by the coordinated movements of their cells' flagella. The dark circles on the colonies are immature daughter colonies.

Where is Volvox aureus found?
Volvox is a genus of freshwater algae found in ponds and ditches, even in shallow puddles.
Is Volvox aureus prokaryotic?
Is Volvox prokaryotic or eukaryotic? Volvox is a genus of colonial green algae. They are eukaryotic.
What disease does Volvox cause?
Answer and Explanation: Volvox does not make people sick in of itself; however, it can harbor a bacteria called Vibrio cholerae, which can cause cholera.
What is Volvox classification?
ChlamydomonadalesGlobe algae / OrderChlamydomonadales, also known as Volvocales, are an order of flagellated or pseudociliated green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae. Chlamydomonadales can form planar or spherical colonies. These vary from Gonium up to Volvox. Wikipedia
What is the function of Volvox?
Volvox can be found in ponds, puddles, and bodies of still fresh water throughout the world. As autotrophs, they contribute to the production of oxygen and serve as food for a number of aquatic organisms, especially the microscopic invertebrates called rotifers.
Is Volvox harmful to humans?
Are Volvox Dangerous to Humans? Volvox are not directly harmful to humans. They are too small to present any harm to us and do not have any weapons or poisons that are capable of hurting us. On the other hand, Volvox are capable of forming algal blooms which can harm the ecosystem.
Is Volvox helpful or harmful?
Volvox are not harmful to humans, (they don't have toxins to make you sick), but they form algae blooms that can harm the ecosystem.
What are the symptoms of algae poisoning?
Exposure to high levels of blue-green algae and their toxins can cause diarrhea, nausea or vomiting; skin, eye or throat irritation; and allergic reactions or breathing difficulties.
Is algae harmful to humans?
Harmful algae and cyanobacteria, sometimes called blue-green algae, can produce toxins (poisons) that can make people and animals sick and affect the environment.
What family is Volvox in?
VolvocaceaeGlobe algae / FamilyThe Volvocaceae are a family of unicellular or colonial biflagellates, including the typical genus Volvox. The family was named by Ehrenberg in 1834, and is known in older classifications as the Volvocidae. All species are colonial and inhabit freshwater environments. Wikipedia
Is Volvox a protozoa or algae?
Volvox (division Chlorophyta) A genus of green algae (sometimes alternatively regarded as protozoa, class Phytomastigophora) in which the cells occur in spherical, motile colonies (coenobia) of 500 to many thousands of cells, according to species. The individual cells resemble those of Chlamydomonas species.
How do I identify my Volvox?
Characteristics Features of Volvox The Volvox cell is single, ovoid or spherical in shape which contains two flagella and it appears like a minute floating ball of a pinhead size. The base of the flagella bears single cup-shaped chloroplasts. Each individual cell is attached to each other with cytoplasmic strands.
Is Volvox multicellular or unicellular?
In a way, Volvox exhibits a relatively streamlined type of multicellularity. It possesses just two cell types, and these cells are not organized into tissues or organs.
Is oscillatoria prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
prokaryotesTherefore, Nostoc, Oscillatoria, and Mycobacterium are prokaryotes. Understanding more about Saccharomyces. It is a single-celled eukaryote which is used in baking and brewing and thus called baker's yeast. They have a globular shape, are yellow-green in colour, and belong to kingdom Fungi.
Is spirogyra prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Spirogyra is an alga with a complex cellular structure belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Monera is single-celled prokaryotes and Protists are single-celled eukaryotes.
Is Chlamydomonas prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
eukaryotic algaChlamydomonas reinhardtii is a unicellular eukaryotic alga possessing a single chloroplast that is widely used as a model system for the study of photosynthetic processes.
Learn about this topic in these articles
One of the most-common species, V. aureus, can form harmful algal blooms in warm waters with a high nitrogen content.
Volvox
One of the most-common species, V. aureus, can form harmful algal blooms in warm waters with a high nitrogen content.
What are the characteristics of Volvox?
Volvox Characteristics. Two equal-sized flagella are present in each cell anteriorly. The coordinated movement of flagella enables the colony to move in the water. Each cell performs all the metabolic functions independently such as respiration, photosynthesis, excretion, etc.
What class is Volvox?
Volvox is classified in the class Chlorophyceae due to the presence of chlorophyll. Common species are Volvox aureus, Volvox globator, V. carteri, V. barberi, etc.
What is the color of a volvox pond?
They live in freshwater habitats such as ponds, ditches, etc. The colour of the pond looks greenish due to the rapid growth of volvox.
How many cells are in a volvox?
Volvox. Volvox is a genus of green algae containing around 20 species of freshwater algae. Thousands of cells together form colonies. There are around 500 to 60,000 cells in each colony of volvox. Leeuwenhoek was the first scientist to observe them in 1700.
Is Volvox a colonial algae?
Volvox is a genus of colonial green algae. They are eukaryotic.
Does Volvox aureus produce oxygen?
Volvox significantly contribute to the production of oxygen and also many aquatic organisms feed on them. Volvox aureus may multiply rapidly, resulting in the harmful algal bloom (HAB). HAB is more frequent in warm waters having a high nitrogen content.
Is Volvox haploid or sporophyte?
The life cycle of Volvox is haplontic, i.e. the dominant stage is free-living haploid (n) gametophyte and the sporophyte is represented only by the diploid zygote (2n) Volvox show cell differentiation in terms of reproductive and somatic cells. Most of the species reproduce by both mechanism, asexual under the favourable condition ...
What is a Volvox?
Volvox is a polyphyletic genus of chlorophyte green algae in the family Volvocaceae. It forms spherical colonies of up to 50,000 cells. They live in a variety of freshwater habitats, and were first reported by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1700. Volvox diverged from unicellular ancestors approximately 200 million years ago.
Who first described the genus Volvox?
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek first reported observations of Volvox in 1700. After some drawings of Henry Baker (1753), Linnaeus (1758) would describe the genus Volvox, with two species: V. globator and V. chaos. Volvox chaos is an amoeba now known as ' Chaos (genus) sp.
What is a Volvox colony?
Volvox is a polyphyletic genus in the volvocine green algae clade. Each mature Volvox colony is composed of up to thousands of cells from two differentiated cell types: numerous flagellate somatic cells and a smaller number of germ cells lacking in soma that are embedded in the surface of a hollow sphere or coenobium containing an extracellular ...
How long did it take for a Volvocine green algae to form a multicellular colony?
An estimate using DNA sequences from about 45 different species of volvocine green algae, including Volvox, suggests that the transition from single cells to undifferentiated multicellular colonies took about 35 million years.
What is an asexual colony?
An asexual colony includes both somatic (vegetative) cells, which do not reproduce, and large, non-motile gonidia in the interior, which produce new colonies through repeated division. In sexual reproduction two types of gametes are produced. Volvox species can be monoecious or dioecious.
Where to find Volvox algae?
Volvox is a genus of freshwater algae found in ponds and ditches, even in shallow puddles. According to Charles Joseph Chamberlain, "The most favorable place to look for it is in the deeper ponds, lagoons, and ditches which receive an abundance of rain water.
Can Volvox reproduce sexually?
Volvox is facultatively sexual and can reproduce both sexually and asexually. In the lab, asexual reproduction is most commonly observed; the relative frequencies of sexual and asexual reproduction in the wild is unknown.
How many species of Volvox are there?
Volvox, genus of some 20 species of freshwater green algae (division Chlorophyta) found worldwide. Volvox form spherical or oval hollow colonies that contain some 500 to 60,000 cells embedded in a gelatinous wall and that are often just visible with the naked eye. Volvox colonies were first. Volvox, genus of some 20 species ...
How do Volvox reproduce?
Most species of Volvox reproduce both asexually and sexually , and some, such as Volvox carteri, switch primary modes of reproduction at least once each year. Asexual colonies have reproductive cells known as gonidia, which produce small daughter colonies that are eventually released from the parent as they mature. In sexual colonies, developing ova or spermatozoa replace gonidia, and fertilization results in zygotes that form a cyst and are released from the parent colony after its death. Thick-walled zygotes formed late in the summer serve as winter resting stages.
How many cells are in a Volvoxform?
Volvoxform spherical or oval hollow colonies that contain some 500 to 60,000 cells embedded in a gelatinous wall and that are often just visible with the naked eye.
What are the somatic cells of a Volvoxcolonyeach?
The somatic cells of a Volvoxcolonyeach feature two flagella(whiplike appendages), several contractile vacuoles(fluid-regulating organelles), a single chloroplast(the site of photosynthesis), and an eyespotused for light reception.
How many flagella are in a Volvox colony?
The somatic cells of a Volvox colony each feature two flagella (whiplike appendages), several contractile vacuoles (fluid-regulating organelles), a single chloroplast (the site of photosynthesis), and an eyespot used for light reception. Neighbouring cells are often joined together by strands of cytoplasm, which enable cell-to-cell communication, and the colony moves through water by the coordinated movement of the flagella. The photosynthetic colonies are usually organized so that cells with larger eyespots are grouped at one side to facilitate phototaxis (movement toward light) for photosynthesis, and the reproductive cells are grouped at the opposite side.
What is a volvox?
A quick overview. Volvox is a genus of green algae. Volvoxes are free-floating single-cellular algae but typically stay together as spherical colonies (or balls) of 500-50,000 cells. They can live in a variety of freshwater habitats, including ponds, pools, and ditches. Under a microscope, volvoxes look like green marbles slowly rotating, ...
Who discovered Volvox?
Dutch microscopist, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, first reported the Volvox colonies in 1700. Leeuwenhoek also discovered many other microscopic organisms, such as rotifers and paramecia, by using his simple microscopes.
How does Volvox reproduce?
Volvox can reproduce asexually or sexually. The choice between asexual and sexual reproduction depends on the conditions where they live. Asexual reproduction takes place during summer under favorable conditions, which allow a rapid expansion of the volvox population. The color of the pond may turn greenish due to the rapid growth of volvoxes. On the contrary, sexual reproduction occurs at the end of the growing season.
What are the differences between a Volvox and a dioecious?
Some Volvox species are monoecious (only one sex) whilst others are dioecious (with two separate sexes). In dioecious forms, female colonies produce specialized egg cells and male colonies produce packets of spermatozoids, both at the posterior of the colonies. Egg cells lack flagella and remain attached to neighboring cells by the protoplasmic bridges. Sperm cells lack cell walls but have two flagella. Mature sperm cells detach from the parent colony and swim towards egg cells. When a sperm cell fertilizes an egg cell, a thick-walled hypnozygote is formed.
How do volvox colonies form?
A typical volvox colony consists of a hollow sphere of cells. Each ball, or coenobium, is formed by a single layer of superficial cells joined together. Each cell is surrounded by a thick mucilaginous wall, forming a gelatinous layer that holds the hollow ball together. In some volvox species, these mucilaginous walls may fill up the internal space of the sphere.#N#These superficial cells are also called vegetative cells or somatic cells. Each vegetative cell sitting on the surface of the sphere bears two flagella. These flagella face the side of the surrounding water and beat to propel the whole colony through the water. This is why a volvox moves like a rolling ball.
How many flagella are there in a volvox?
Each vegetative cell sitting on the surface of the sphere bears two flagella. These flagella face the side of the surrounding water and beat to propel the whole colony through the water. This is why a volvox moves like a rolling ball.
What do volvoxes look like?
Under a microscope, volvoxes look like green marbles slowly rotating, making them one of the most adorable microscopic organisms. [In this image] A mature Volvox carteri colony with many daughter colonies inside under a microscope. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device.
What are the characteristics of a Volvox cell?
Characteristics Features of Volvox 1 The Volvox cell is single, ovoid or spherical in shape which contains two flagella and it appears like a minute floating ball of a pinhead size. 2 The base of the flagella bears single cup-shaped chloroplasts. 3 Each individual cell is attached to each other with cytoplasmic strands. 4 Each individual cell possesses a red eyespot on its surface. 5 Anterior cells of the particular colony of Volvox possess phototactic abilities while the posterior cells perform reproduction. 6 The size of the Volvox colony ranges from 100-6000 µm. 7 We cannot see the Volvox species with the naked eye due to their microscopic size but few colonies are easily visible because of their big size with 1 mm in diameter. 8 Volvox prefers to live in nutrient-rich water bodies such as lakes, pools, canals, ditches, etc. 9 Each cell of the Volvox colony produces mucilage which makes the colony distinct or inconspicuous. 10 They show the flagellar movement. In this case, the flagella of all the cells of the colony perform simultaneous action by which the entire colony rolls over the surface of the water. Besides these, the eyespot controls the movement of the flagella as they are photoreceptive organs. 11 They reproduce both asexually and sexually. 12 They can be dioecious or monoecious. In this case, the male colony produces lots of sperm packets while the female colony releases oogamete or ovum.
Which cells perform reproduction in Volvox?
Anterior cells of the particular colony of Volvox possess phototactic abilities while the posterior cells perform reproduction.
What is the shape of a Volvox cell?
The Volvox cell is single, ovoid or spherical in shape which contains two flagella and it appears like a minute floating ball of a pinhead size. The base of the flagella bears single cup-shaped chloroplasts. Each individual cell is attached to each other with cytoplasmic strands. Each individual cell possesses a red eyespot on its surface.
What type of cell is in a Volvox colony?
The mature Volvox colony contains two separate cell types namely germ cells of the smaller number and numerous flagellated somatic cells . In this case, adult somatic cells have a single layer that contains two flagella which allow the organism to swim in a coordinated fashion in water.
How many cells does a Volvox have?
There are some 20 freshwater species of Volvox which prefer to live in colonies with up to 60,000 cells by making a gelatinous wall. These colonies have an ovoid or spherical hollow shape which may be larger than a pinhead size. Dutch microscopist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek first reported the Volox colonies in 1700.
Why does Volvox occur in the colony?
In the young colony, the vegetative cells are similar in size and green in color. Each motile colony (coenobium) is free-swimming and appears as small pinhead like spherical to ovoid shape with hollow mucilaginous mass which consists of numerous small pear-shaped cells arranged in a single layer joined with one another by delicate strands of cytoplasm within the periphery of the gelatinous colonial matrix. The total number of cells in the colony varies from about 500 ( Volox aureus) to about 2000 or more ( Volvox globate ). Each colony develops the following three types of cells:
When does Volox disappear?
During spring, the surface of the water in which Volox occurs looks green. During early summer, the Volox abruptly disappears and it remains in resting zygote condition. Volvox colony appears in the rainy season.