Here's What You Need To Know About Wave Refraction And Shoaling
- Wave refraction determines its direction as it hits the shore. Wave refraction is a common term in oceanography and it’s used to describe how a wave behaves over different depths.
- Concave refraction versus convex refraction. ...
- Shoaling occurs when the wave reaches shallow waters and grows in height. ...
What is a real life example of refraction?
- A prism uses refraction to form a spectrum of colors from an incident beam of light.
- Refraction is responsible for the ability of the cornea and lens of the eye to form a real image on the retina.
- Spectacles are worn by people with defects of vision use refraction for providing correct vision.
What causes refraction and what is it?
- Bending of light.
- If light is moving from rarer to denser medium then it moves towards the normal.
- If it is moving from denser to rarer medium then it moves away from the normal.
- Change in wavelength of light.
- rarer to denser — wavelength decreases
- denser to rarer — wavelength increases
- Spliting of light ray if it is polychromatic in nature.
How do you calculate refraction?
How do you calculate refraction?
- Figure 1 – Refraction of Light.
- Formula 1 – Snell’s Law. n 1 × sin (θ 1) = n 2 × sin (θ2)
- Formula 2 – Numerical Aperture. NA (numerical aperture) = n × sin (θ)
- Formula 3 – Refractive Index (or Index of Refraction) n = c/η
How does refraction affect what we see?
Refraction makes celestial objects appear higher in the sky. Magic Atmosphere. One of mother nature's favorite magic tricks, refraction is the bending of light as it moves from one substance to another.. It is responsible for a variety of optical phenomena including rainbows, mirages, halos, and sundogs.It is also the reason why stars twinkle at night, your diamond ring sparkles, a straw or ...

What is wave refraction simple definition?
refraction, in physics, the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another caused by its change in speed.
What is wave refraction geography?
Wave refraction refers to what happens to waves when they approach an uneven coastline. Very few coastlines are perfectly straight, and few sea beds have uniform height and shape.
What is wave refraction and why is it important?
Refraction is the reason why surf waves often line up parallel to the beach. Even if waves are coming in from deep water at an angle to the beach, the move to shallower water means that the waves will slow down and curve around (refract) so they are more parallel as the surf hits the beach.
What is wave refraction quizlet?
What is wave refraction? When waves meet a coastline that is an irregular shape waves are refracted, meaning they come increasingly parallel to the coastline.
What is an example of a wave refraction?
Refraction occurs with any kind of wave. For example, water waves moving across deep water travel faster than those moving across shallow water. A light ray that passes through a glass prism is refracted or bent.
What causes refraction waves?
Refraction can increase or decrease the wave height, as well as the speed and strength of a breaking wave. Refraction is the reason why surface waves are always parallel to the shore.
What is the effect of wave refraction?
The effects of wave refraction also tend to concentrate wave energy on headlands or protrusions that stick out of the coastline and tend to defocus or diverge the energy in embayments. This is important for our purposes because the refraction of waves affects erosion, transportation, and deposition along the coastline.
What are three examples of refraction?
“The process of bending of light as it passes from air into glass and vice versa is called refraction of light.”Mirage,bent pencil in glass of water,rainbow,sunset are some examples of refraction of light.
What is difference between reflection and refraction?
Reflection can simply be defined as the bouncing back of light when it strikes the medium on a plane. Refraction can be defined as the process of the shift of light when it passes through a medium leading to the bending of light. The light entering the medium returns to the same medium.
Does wave refraction create wave energy?
Wave energy is concentrated on headlands due to wave refraction; erosion is maximum. Wave energy is dispersed in the bays; deposition is maximum. Headland cliffs are cut back by wave erosion and the bays are filled with sand deposits until the coastline becomes straight.
What is wave refraction and why does it occur in ocean waves?
Refraction is the change in direction of waves as they move between materials with different properties. Water waves are refracted as they move from deep water to shallow water. Water waves travel faster in deep water than in shallow water.
Why does sound refract under water?
Why does sound sometimes refract under water? Sound sometimes refracts underwater due to temperature differences between the surface and under the water. Which is normally greater, the energy in ordinary sound or the energy in ordinary light? Energy of light is greater than energy of sound.
What is wave refraction in the ocean?
Refraction is the change in direction of waves as they move between materials with different properties. Water waves are refracted as they move from deep water to shallow water. Water waves travel faster in deep water than in shallow water.
What is the effect of wave refraction?
The effects of wave refraction also tend to concentrate wave energy on headlands or protrusions that stick out of the coastline and tend to defocus or diverge the energy in embayments. This is important for our purposes because the refraction of waves affects erosion, transportation, and deposition along the coastline.
What causes wave refraction quizlet?
Q: What causes wave refraction? Refraction - as waves approach shore, they bend so wave crests are nearly parallel to shore. Waves refract due to the friction of the continental shelf and the water which slows them down and causes the waves to face more directly to the shore and the wave crests bend.
What is the bending of a wave front as it travels at different speeds over water of different depths?
Refraction is the bending of a wave-front as it travels at different speeds over water of different depths. When different parts of the same wave-front travel at different speeds, the wave bends towards the slower part. The shallower the water, the slower the wave; therefore the wave bends towards the shallower water.
How do waves feel the bottom?
The depth at which the waves start to ‘feel’ the bottom depends on the wavelength of the waves. Longer waves have larger orbital motions. Therefore, the orbital motions of longer waves reach down further below the surface, and longer waves ‘feel’ the bottom before shorter ones.
What happens to the waves when they are shallower?
The shallower the water, the slower the wave; therefore the wave bends towards the shallower water. In the deep ocean, the orbital motions of the particles beneath the waves diminish to nothing way before they reach the sea bed. But once the water starts to get shallower, these orbital motions begin to reach all the way down to the bed, and so, ...
How does bathymetry affect waves?
The way in which the bathymetry affects a wave approaching the coast is by making it bend, through the process of refraction. Refraction can turn, twist and mould the waves into a thousand different shapes and sizes, all depending on the bathymetry.
How does the sea floor affect the waves?
But at some point near the coast, the water becomes shallow enough for the presence of the sea floor to affect the behaviour of the waves. The configuration of the sea floor (the bathymetry), either offshore of a surf spot or below the breakpoint itself, is a vitally important factor in determining the characteristics of the waves when they break.
What is Wave Refraction?
As waves travel over the sea floor at different speeds , they bend and contort, with the bend essentially turning toward its slowest point.
What are the two factors that determine wave refraction?
There are two main factors to consider when talking about wave refraction: focusing and defocusing.
How does bathymetry impact waves?
The bathymetry impacts the wave through a process known as refraction.
How far can a mutant wave reach?
The two swells combine to form one massive, mutant wave that can reach upwards of 20 feet and can break in a just a few feet of water.
Where can you find wave refraction in California?
You can find two examples of wave refraction in California at 1) The Wedge in Newport Beach and 2) at South Ocean beach in San Francisco.
What are waves influenced by?
Waves are influenced by wind, tides, and swell, and while the ocean floor also plays a role, it’s minor at best.
Does bathymetry produce wave refraction?
Depending on the bathymetry, some locations may produce both types of wave refraction.
Why do waves bend in the ocean?
a. The waves are moving faster just in front of the headland, causing the waves to bend.
What is the inverse of wavelength?
a. Wave period is the inverse of wavelength.
What is the depth of the wave base?
a. The depth of the wave base is twice the wavelength of the waves.
What is Refraction?
Refraction is the bending of a wave when it passes from one medium to another. The bending is caused due to the differences in density between the two substances.
What is refraction in optics?
Refraction has many applications in optics and technology. A few of the prominent applications are listed below: A lens uses refraction to form an image of an object for various purposes, such as magnification. Spectacles worn by people with defective vision use the principle of refraction.
How does light ray refract?
A light ray refracts whenever it travels at an angle into a medium of different refractive index. This change in speed results in a change in direction. As an example, consider air travelling into water. The speed of light decreases as it continues to travel at a different angle.
What are the applications of refraction?
Refraction has many applications in optics and technology. A few of the prominent applications are listed below: 1 A lens uses refraction to form an image of an object for various purposes, such as magnification. 2 Spectacles worn by people with defective vision use the principle of refraction. 3 Refraction is used in peepholes of house doors, cameras, movie projectors and telescopes.
What is the difference between reflection and refraction?
If the medium has a smooth surface, then the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Refraction of light is the change in the direction of light as it passes from one medium to another.
What is the refractive index?
What is Refractive Index? Refractive index, also called the index of refraction describes how fast light travels through the material. Refractive Index is dimensionless. For a given material, the refractive index is the ratio between the speed of light in a vacuum (c) and the speed of light in the medium (v).
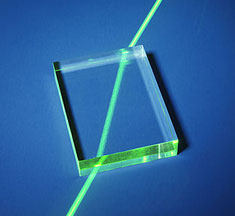
How does light refract in glass?
Refraction of light in glass is shown in the figure above. When light travels from air into glass, the light slows down and changes direction slightly. When light travels from a less dense substance to a denser substance, the refracted light bends more towards the normal line. If the light wave approaches the boundary in a direction that is perpendicular to it, the light ray doesn’t refract in spite of the change in speed.