
What is the Wells score for deep vein thrombosis?
The Wells score is the most widely used clinical decision tool for the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). This tool risk-stratifies patients into 'low', 'intermediate' and 'high' risk categories for DVT, based on a point system. A score of less than two indicates low risk, and above two indicates intermediate/high risk.
What is a Wells score?
The Wells score is a number that reflects your risk of developing deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT happens when a blood clot forms in a vein that’s deep inside your body, usually in your leg.
Is Wells criteria appropriate for DVT diagnosis in trauma patients?
Venous duplex surveillance is used widely for the diagnosis of DVT, however, there is controversy concerning its appropriate use. The Wells criterion is a clinically validated scoring system in an outpatient setting, but its use in trauma patients has not been studied.
How many patients are positive for DVT in the US?
Of the 298 patients studied, a total of 18 patients (6 %) were positive for DVT. Wells score was used to define each patient’s probability of developing DVT, patients were assigned a score and then categorized: -2 to 0 points: low probability, 1 to 2 points as moderate probability, and 3 to 8 points as high probability.
Is Wells score for PE or DVT?
The Wells' Criteria risk stratifies patients for pulmonary embolism (PE), and has been validated in both inpatient and emergency department settings. Its score is often used in conjunctiion with d-dimer testing to evaluate for PE.
What does Wells score stand for?
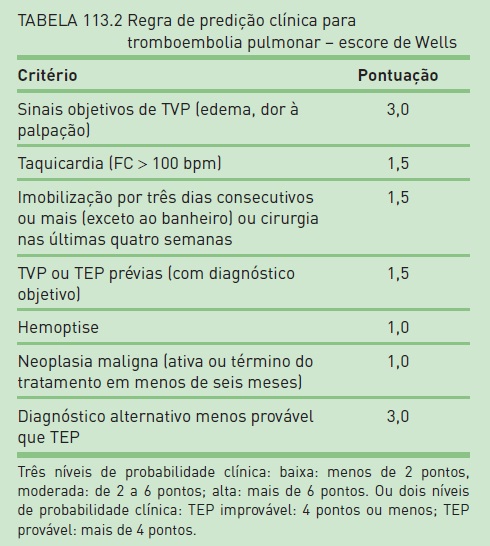
First described in 1998, the Wells score is a clinical prediction score based on simple, noninvasive clinical parameters. It has evolved over the years and been validated and is useful in determining pretest probability for suspected acute PE. The score is calculated based on specific variables (Table 61-1).
What is a 2 level Wells score?
Table 1 Two-level DVT Wells scoreClinical featurePointsLocalised tenderness along the distribution of the deep venous system1Entire leg swollen1Calf swelling at least 3 cm larger than asymptomatic side1Pitting oedema confined to the symptomatic leg19 more rows•Mar 26, 2020
What is a Wells score for PE?
The Wells PE Score is used to evaluate a patient with a suspected PE to establish the probability that this is likely or unlikely. The results of the Wells Score will guide additional investigations and management.
When should the Wells score be used?
The Wells' DVT Criteria can be used in the outpatient and emergency department setting. By risk stratifying to low risk (Wells' Score <2) and a negative d-dimer the clinician can exclude the need for ultrasound (US) to rule out DVT. The Wells' Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Criteria risk stratify patients for DVT.
Is the Wells score useful?
A recently published meta-analysis determined that, except for patients with active cancer, the Wells score is a useful DVT pretest probability predictor in the outpatient, primary care, and emergency department settings, but the inpatient subgroup was not evaluated.
How do you score a DVT?
The Wells score is a number that reflects your risk of developing deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT happens when a blood clot forms in a vein that's deep inside your body, usually in your leg....Three-tier model.ScoreResult3 or higherHigh risk of DVT1 or 2Moderate risk of DVT0 or lessLow risk of DVT
How is leg swelling measured in DVT?
Assess leg and thigh swelling — measure the circumference of the leg 10 cm below the tibial tuberosity and compare with the asymptomatic leg. A difference of more than 3 cm between the extremities increases the probability of DVT. Assess for oedema and dilated collateral superficial veins on the affected side.
When do you do D-dimer Wells score?
SUMMARY. In summary, the data suggest that when patients present in a clinic setting with a suspected first DVT, high-sensitivity D-dimer testing should be combined with Wells scoring to determine which patients need ultrasound imaging and which may be reassured with no further intervention.
What is D-dimer normal range?
A normal D-dimer is considered less than 0.50. A positive D-dimer is 0.50 or greater. Since this is a screening test, a positive D-Dimer is a positive screen.
What can cause elevated D-dimer?
If your results reveal that you have higher-than-normal levels of D-dimer in your blood, it may mean that you have a blood clotting condition....Other conditions and situations that can cause higher-than-normal levels of D-dimer include:Pregnancy.Heart disease.Recent surgery.Trauma.Infection.
How do you rule out PE?
For that reason, your doctor will likely discuss your medical history, do a physical exam, and order one or more of the following tests.Blood tests. ... Chest X-ray. ... Ultrasound. ... CT pulmonary angiography. ... Ventilation-perfusion scan (V/Q scan) ... Pulmonary angiogram. ... MRI. ... Medications.More items...•
What is Wells clinical prediction rule?
The Wells Clinical Prediction Rule is a diagnostic tool used during review of systems to identify possible deep vein thrombosis (DVT). It is completed by healthcare professionals and can be applied to any patient with a suspected DVT.
What is D-dimer normal range?
A normal D-dimer is considered less than 0.50. A positive D-dimer is 0.50 or greater. Since this is a screening test, a positive D-Dimer is a positive screen.
When is D-dimer used?
D-dimer testing is often ordered when someone goes to the emergency room with symptoms of a serious condition (e.g., chest pain and difficulty in breathing). A D-dimer test may be ordered when someone has symptoms of deep vein thrombosis, such as: Leg pain or tenderness, usually in one leg. Leg swelling, edema.
What laboratory test is most helpful for ruling out a PE?
D-dimer. Your doctor will order a D-dimer blood test to help diagnose or rule out the presence of a pulmonary embolism. The D-dimer test measures the levels of a substance that is produced in your bloodstream when a blood clot breaks down.
What is the Wells score for DVT?
It is a straightforward point-score system with a maximum of eight score points, with one point each given for 1) cancer, 2) paralysis or recent plaster cast, 3) bed rest longer than 3 days or surgery in the previous 4 weeks, 4) pain on palpation of deep veins, 5) swelling of the entire leg, 6) an affected calf more than 3 cm larger in diameter than the unaffected calf, 7) pitting edema of affected side, and 8) dilated superficial veins. Two points are subtracted if an alternative diagnosis is at least as probable as DVT. Low probability is no points, intermediate clinical probability is one to two points; and three or more points is considered high clinical probability of DVT.
Why should a Wells score be calculated?
Wells score should be calculated to risk stratify patients with suspected PE if patient stable
What is the probability of an embolism?
The probability of embolism is high if the patient has typical signs (tachycardia, leg swelling) and risk factors (e. g., cancer, immobilization) and lacks an alternative diagnosis. The probability is low if the presentation is atypical, there are no risk factors, and there is a likely alternative diagnosis (e.g., angina, congestive heart failure).
How many points are subtracted for DVT?
Two points are subtracted if an alternative diagnosis is at least as probable as DVT. Low probability is no points, intermediate clinical probability is one to two points; and three or more points is considered high clinical probability of DVT. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
What are the physical fitness tests in California?
In California, testing is done “to help students in starting life-long habits of regular physical activity.”59 The school-based tests typically used are the 20 m shuttle run or the mile run. The raw data from these tests are entered into standardized equations to estimate maximal oxygen uptake (V̇O 2max ), but none of the data become part of the child's medical record.
What is Wells criteria for DVT?
Wells criteria for DVT is a reliable clinical tool to assess the risk of deep venous thrombosis in trauma patients
What is the cut off score for DVT?
Statistical measures of performance of Wells score in predicting DVT in patients with cut off scores of 2
What is the sensitivity of Wells score?
In patients classified as moderate or higher probability for DVT (cut-off scores of 2), the Wells score was able to detect patients at risk of developing DVT with a specificity of 90 % (95 % CI: 87–94 %), sensitivity of 67 % (95 % CI: 45–88 %), positive predictive value of 31 % (95 % CI: 16–45 %) and NPV of 98 % (95 % CI: 96–99 %) (Table 4).
What is the third leading cause of death in hospitalized trauma patients?
Venous thromboembolism (VTE), comprising of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), is the third leading cause of death in hospitalized trauma patients, with an estimated incidence of 5–20 % with prophylaxis [1–3]. This wide range in incidence of VTE is attributed to variability in patients’ risk factors, choice of prophylaxis and modalities of screening and detection of VTE [1, 4]. Thromboprophylaxis in trauma patients is complex for many reasons, one of them being the presence of an early coagulopathy present in 25 % of trauma patients at the time of admission [5], which is further complicated by hypo-perfusion, acidosis and resuscitative measures [4, 6]. This coagulopathy shifts to a pro-thrombotic state early after traumatic injury necessitating thromboembolism prophylaxis. Additionally, these patients have a high bleeding risk associated with the use of anticoagulants and limitation of use of compression devices due to extremity injuries [7]. DVT has been chosen as an important indicator of quality of care and pay for performance criteria, with an underlying assumption that all DVTs are preventable with appropriate detection and prophylaxis [8]. This has led to an increased use of duplex ultrasound scanning for DVT in asymptomatic trauma patients, which may not be cost efficient or at times effective in preventing clinically relevant VTEs in a subset of these patients [7, 9]. Furthermore, there is immense variability in the utilization of duplex ultrasound screening among various trauma centers in the National Trauma Data Base (NTDB) [8]. Currently, screening is suggested for patients who are at high risk of developing DVT and have received suboptimal or no thromboprophylaxis. There are, however multiple opinions on what factors define a high risk trauma patient [1, 8] or what constitutes an optimal regimen for use in screening or prophylaxis against DVTs. Given this clinical dilemma, a means of increasing the pretest probability of screening algorithms is needed to optimize DVT detection and cost-effectiveness. Multiple tools are available to identify high-risk patients in the outpatient setting such as Wells Score, Geneva Score, Minaiti Score and Charlotte rule, of which the Wells score with its modification is the most widely used and accepted scoring system [10–12].
What is the RR of a wells score?
Further analysis revealed that patients with Wells score ≤ 1 had a relative risk (RR) of developing DVT of 0.075 [95 % confidence interval (CI): 0.03–0.19], while the RR of patients with Wells score of 2, 3, and 4 were 13.3 (95 % CI: 5.5–33.3), 13.9 (95 % CI: 6.5–29.8) and, 18.5 (95 % CI: 11.5–29.8) respectively. There was a strong linear correlation between Wells score and incidence of DVT with Pearson coefficient r = 0.94 (95 % CI: 0.64–0.99; R2 = 0.88; p = 0.0016) (Fig. 2a). In patients classified as low probability by their score (cut-off scores of 1), the Wells score was able to rule out the presence of DVT with a sensitivity of 100 % (95 % CI: 100–100 %) as well as a negative predictive value (NPV) of 100 % (95 % CI: 100–100 %) (Table 3).
What is the term for the immobilization of the lower extremities?
Paralysis, paresis, or recent cast immobilization of the lower extremities
When was the Wells score calculated?
Wells scores were calculated retrospectively for all patients who were admitted to the trauma service and underwent Venous Duplex Scanning (VDS) at the author’s institution between 2012 and 2013. Correlation of Wells score with DVT and its efficacy in risk stratifying the patients after trauma was analyzed using linear correlation and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Sensitivity and specificity of Wells score in ruling out or ruling in DVT were calculated in various risk groups.
What is Wells score for DVT?
The Wells score proposes the DVT unlikely and DVT likely sorting of the result, therefore the Wells score for DVT calculator displays a result based on the points each answer is awarded and specifies whether a diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis is likely or not.
How does this Wells score for DVT calculator work?
This is a health tool used to pre test clinical probability of a deep venous thrombosis based on a range of criteria as established in the Wells model. It takes into account the main risk factors for developing DVT such as bed immobilization, surgery or trauma; clinical signs or swelling and edema; as well as the chance of another diagnosis being possible:
What is DVT diagnosis?
This is a very useful risk stratification score and helps the clinician avoid costly clinical determinations such as ultrasound when the probability is low and the D-dimer is negative and in cases where DVT suspicion can be eliminated safely.
Where does venous thrombosis occur?
Is the affection in which one or more blood clots are being formed in the deep veins of the body and these are known as venous thrombosis that usually occurs in the deep large veins of the leg, through the calf or thigh.
What are the risk factors for DVT?
It takes into account the main risk factors for developing DVT such as bed immobilization, surgery or trauma; clinical signs or swelling and edema; as well as the chance of another diagnosis being possible: 1) Lower limb trauma, surgery or plaster – risk of vessel damage and more.
Why do blood vessels clot?
Blood vessel damage is another cause resultant in blood clots from the narrowing of blockage of the vessel, preventing normal blood flow. Blood vessels can be damaged by their own conditions such as vasculitis or during trauma from broken bones or muscle damage or surgery.
Does estrogen increase blood clotting?
Hormone replacement therapy or the contraceptive pill are said to increase blood clotting risk due to the estrogen intake. There are also infectious or inflammatory conditions to be named as risk factors and also thrombophilia, the condition in which the blood clots easily.
What is the Wells score?
The Wells score is the most widely used clinical decision tool for the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). This tool risk-stratifies patients into 'low', 'intermediate' and 'high' risk categories for DVT, based on a point system.
What does a score of less than two mean?
A score of less than two indicates low risk, and above two indicates intermediate/high risk. Active cancer (patient receiving treatment for cancer within 6 months or currently receiving palliative treatment). Paralysis, paresis, or recent plaster or immobilisation of the lower extremeties.
What is the term for the immobilization of the lower extremities?
Paralysis, paresis, or recent plaster or immobilisation of the lower extremeties.
