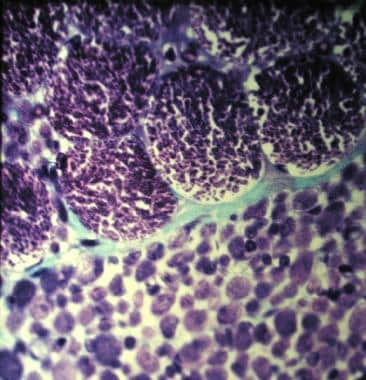
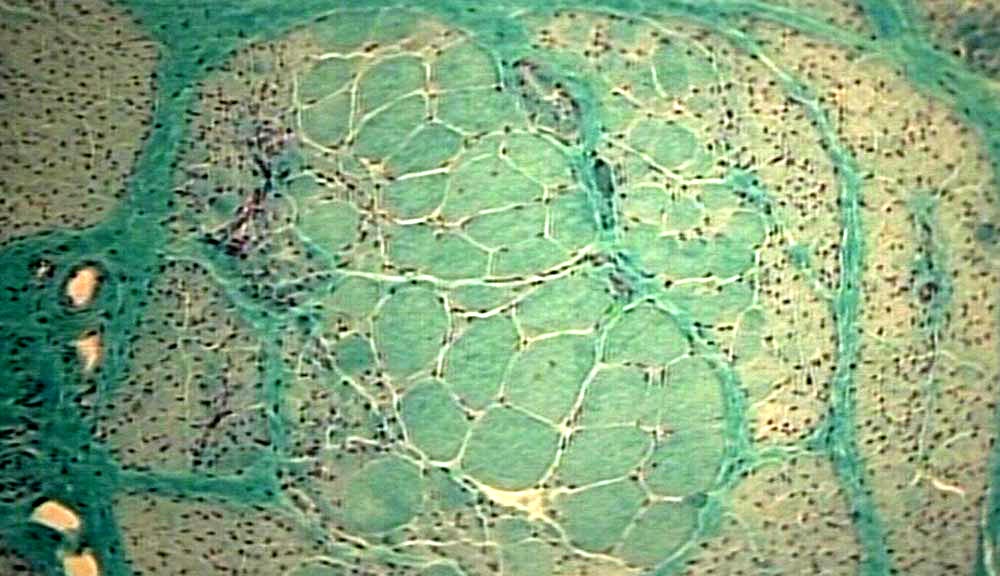
Werdnig-Hoffmann disease (Concept Id: C0043116) Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is characterized by muscle weakness and atrophy resulting from progressive degeneration and irreversible loss of the anterior horn cells in the spinal cord (i.e., lower motor neurons) and the brain stem nuclei. The onset of weakness ranges from before birth to adulthood.
What is Werdnig-Hoffmann disease?
Werdnig-Hoffmann disease is a type of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a rare form of motor neuron disease. It is the most common type of SMA and accounts for about 80% of individuals with this condition. There are 4 types of SMA. Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, also known as SMA1, is the most severe form.
What is Werdnig-Hoffmann disease (SMA1)?
What Is Werdnig-Hoffmann Disease? Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, also called spinal muscular atrophy type 1 (SMA1), is a genetic neuromuscular disorder. It affects the nerve cells controlling the voluntary muscles—the muscles under your conscious control that you can move at will.
What is the prognosis of Werdnig Hoffmann disease (WHD)?
The prognosis for Werdnig Hoffmann disease is very poor. The disease presents before 6 months of age, and it is a progressive muscular disorder that often results in early death. Most patients die prematurely either in infancy or early childhood, often by 2 years of life. This is the most common genetic cause of infant mortality. [7] Complications
What are the treatment options for Werdnig-Hoffmann disease?
Management. No specific therapy is yet available for the treatment of Werdnig-Hoffmann disease. Treatment is not disease-modifying. Affected children should be under the care of a multidisciplinary team with expertise in the management of SMA1.

What is the life expectancy of someone with spinal muscular atrophy?
The life expectancy of patients with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) type I is generally considered to be less than 2 years. Recently, with the introduction of proactive treatments, a longer survival and an improved survival rate have been reported.
Is Hoffman's syndrome hereditary?
Summary. Werdnig-Hoffmann disease (SMA1) affects the nerves controlling voluntary muscles. It is a genetic disease that is inherited.
What are the signs and symptoms of spinal muscular atrophy?
What are the symptoms of spinal muscular atrophy?muscle weakness and decreased muscle tone.limited mobility.breathing problems.problems eating and swallowing.delayed gross motor skills.spontaneous tongue movements.scoliosis (curvature of the spine)
Can SMA disease be cured?
It's not currently possible to cure spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), but research is ongoing to find new treatments. Treatment and support is available to manage the symptoms and help people with the condition have the best possible quality of life.
What is the treatment for Hoffman's disease?
Treatment / Management There is no cure for Werdnig-Hoffmann disease. Nusinersen is a survival motor neuron-2 (SMN2)-directed antisense oligonucleotide, and FDA approved for the treatment of SMA in adult and pediatric patients. It is administered intrathecally.
Does myopathy affect the brain?
Inclusion body myopathy with early-onset Paget disease and frontotemporal dementia (IBMPFD) is a condition that can affect the muscles, bones, and brain. The first symptom of IBMPFD is often muscle weakness (myopathy), which typically appears in mid-adulthood.
What happens to the body when you have spinal muscular atrophy?
Individuals with SMA have insufficient levels of the SMN protein, which leads to loss of motor neurons in the spinal cord, producing weakness and wasting of the skeletal muscles. This weakness is often more severe in the trunk and upper leg and arm muscles than in muscles of the hands and feet.
What type of doctor do you see for muscle atrophy?
Neurologists. These doctors deal with problems with your nerves or nervous system. A neurologist or pediatric neurologist could be one of the first people you see, since SMA is the loss of specialized nerve cells calls motor neurons.
What is the treatment for spinal muscular atrophy?
The FDA has approved three medications to treat SMA: nusinersen (Spinraza), onasemnogene abeparvovec-xioi (Zolgensma) and risdiplam (Evrysdi). Both are forms of gene therapy that affect the genes involved in SMA.
Is SMA painful?
Overall, pain in this population of SMA patients appears to be comparable to that of people with osteoarthritis or chronic low back pain. Despite SMA patients being generally protected from severe pain, younger SMA patients do experience pain at heightened rates.
What causes SMA in babies?
Most kinds of SMA are caused by a problem with a gene called the SMN1 gene. The gene does not make enough of a protein needed for the motor neurons to work normally. The motor neurons break down and can't send signals to the muscles. A child with SMA gets one copy of the SMN1 gene from each parent.
How many babies are born with SMA?
One in every 6,000 babies is born with SMA. It occurs in both males and females of all races, and can begin in infancy, childhood, or adulthood, three of which affect children.
What causes congenital hypothyroidism in newborns?
The most common cause worldwide is a shortage of iodine in the diet of the mother and the affected infant. Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. Genetic causes account for about 15 to 20 percent of cases of congenital hypothyroidism.
What is Thompson's disease?
Myotonia congenita is an inherited myopathy, a disease that causes problems with the tone and contraction of skeletal muscles. It doesn't cause muscle atrophy (shrinkage); instead, it sometimes can cause muscle enlargement and increased muscle strength.
What type of disease is spinal muscular atrophy?
Description. Spinal muscular atrophy is a genetic disorder characterized by weakness and wasting (atrophy ) in muscles used for movement (skeletal muscles). It is caused by a loss of specialized nerve cells, called motor neurons that control muscle movement.
What is congenital myotonic muscular dystrophy?
Congenital myotonic dystrophy (CMD) is an autosomal dominant neuromuscular disorder with multisystem involvement. It is a subtype of myotonic dystrophy type 1. Features include severe hypotonia and generalized muscle weakness; myotonia is classically absent in infancy.
What is SMA1?
SMA1 is a type of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). SMA generally causes muscles to become weak over time. Children with different types of SMA will have problems controlling head movement, sitting up, and walking. These conditions can also affect swallowing and breathing as the condition worsens.
What is SMA1 gene?
SMA1 is an inherited condition associated with abnormal genes. The abnormal gene associated with SMA1 and all types of SMA is the survival motor neuron (SMN). 3 There have been two SMN genes identified with Werdnig-Hoffmann disease—SMN1 and SMN2.
Why is SMA1 considered severe?
SMA1 is considered severe because it affects the muscles that control breathing. Many children with the condition don’t live past age 2 because of breathing issues. 1 Babies with SMA1 are very weak in the early months and have problems with feeding. Cognitive, mental, and emotional development are generally normal in SMA1.
What is the best treatment for SMN?
Disease-modifying therapies can help stimulate the production of SMN protein. Spinraza (nusinersen) has been approved for pediatric and adult patients. 12 It is injected into the space around the spinal canal. Another medication—Evrysdi (risdiplam)—is prescribed for adults and children older than 2 months and is taken daily by mouth. 4
What organizations help with Werdnig-Hoffman disease?
Many organizations can offer help and support to your family for dealing with and managing Werdnig-Hoffman disease, including Cure SMA, the SMA Foundation, and the Muscular Dystrophy Association .
How rare is SMA1?
According to a 2017 report in the Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, SMA1 is extremely rare, with an incidence of around one in 10,000 live births. 15 The report’s authors note that because the condition is so rare, estimating the prevalence can be challenging and limited.
What is the name of the disease that affects the voluntary muscles?
Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, also called spinal muscular atrophy type 1 (SMA1), is a genetic neuromuscular disorder. It affects the nerve cells controlling the voluntary muscles—the muscles under your conscious control that you can move at will.
What is Werdnig Hoffmann disease?
Werdnig Hoffmann Disease. Werdnig-Hoffmann disease is a type of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a rare form of motor neuron disease. It is the most common type of SMA and accounts for about 80% of individuals with this condition.
What is motor neuron disease?
Motor neuron disease is a condition that affects anterior horn cells of the motor neurons. These are the neurons that control voluntary muscle control. These are rare conditions that are often very severe, and no cure is available.
What causes a floppy baby?
Central nervous system abnormalities (i.e., cerebral structural abnormalities) are seen in most cases of the floppy infant. Cerebral pathology should be suspected if alertness is diminished or infantile reflexes persist. Chromosomal disorders, especially Prader--Willi syndrome, may also cause floppy child syndrome. Peroxisomal disorders are suspected if the child loses functions already gained or if there is hepatosplenomegaly. Infantile acid maltase deficiency (Pompe's disease) has to be suspected in the context of (hypertrophic) cardiomegaly.
What are the symptoms of SMA?
Type 1 patients present with severe hypotonia, poor head control, weak cry, poor feeding, diffuse, proximal predominant weakness, and respiratory distress ( Figure 89.1 ). 44 Patients appear alert for their degree of weakness because of absent or minimal facial involvement. 45 Eye muscles and cognitive function are spared, and children with SMA typically have a higher than normal IQ. 46 Tongue atrophy and fasciculations are noted in over half of patients. 6,45 Motor examination reveals severe areflexic hypotonia with the extremities held in a splayed out “frog-leg” like posture. A bell-shaped chest results from paradoxical breathing, i.e., flattening of the upper chest and flaring of the lower chest and abdominal protrusion during inspiration caused by weakness of the intercostal muscles and relative sparing of the diaphragm. 45 Although SMA is usually not considered a multisystem disease, there have been scattered reports of patients with severe type 1 disease associated with various cardiac structural abnormalities and digital vascular necrosis and thrombosis. 47,48
What are the differential diagnostic features of neurologic examination?
Particularly noteworthy differential diagnostic features in the neurological examination include the presence of normal sphincter and sensory functions. Both these functions would be expected to be affected with major spinal cord disease, and sensory function with peripheral nerve disease. The patient's alert state with normal visual and auditory responses rules against a central disorder. Total areflexia and absence of ptosis, ophthalmoplegia, and facial weakness rule against a variety of primary diseases of muscle. Distinction from type II glycogen storage disease (Pompe disease) can be most difficult, but this much less common disease is usually accompanied by prominent involvement of the heart and enlargement of the tongue.
What is Werdnig-Hoffmann disease?
Werdnig-Hoffmann disease is a form of SMA and is otherwise called SMA type 1 (SMA1). It presents in infants. It is an autosomal recessive condition characterised by the degeneration of anterior horn cells, leading to profound symmetrical weakness and wasting of voluntary muscle. Werdnig-Hoffmann disease describes a subset ...
What is SMA in medical terms?
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is an autosomal recessive neuromuscular disease characterised by degeneration of alpha motor neurons in the spinal cord, resulting in progressive proximal muscle weakness and paralysis . Werdnig-Hoffmann disease is a form of SMA and is otherwise called SMA type 1 (SMA1). It presents in infants.
How many clinical subgroups are there in SMA1?
Within SMA1 at least three clinical subgroups can be defined according to the severity of clinical signs: Severe weakness since birth/neonatal period - head control is never achieved. Onset of weakness after the neonatal period but generally within two months - head control is never achieved.
How many people have SMA?
The estimated incidence of SMA is 1 in 6,000 to 1 in 10,000 live births and the carrier frequency of 1/40-1/60. Werdnig-Hoffmann disease (SMA1) is the most severe and common type of SMA and accounts for about 50% of patients diagnosed with SMA.
When does SMA1 start?
Classically, infants with SMA1 have onset of clinical signs before 6 months of age and never acquire the ability to sit unsupported. All children with SMA1 show a combination of severe hypotonia and weakness, with sparing of the facial muscles, invariably associated with a typical respiratory pattern.
What causes paradoxical breathing in children?
Some of these children may also show congenital bone fractures and extremely thin ribs. The spared diaphragm, combined with weakened intercostal muscles, results in paradoxical breathing.
How long do children with Werdnig-Hoffmann disease live?
If no intervention is provided, children with Werdnig-Hoffmann disease generally do not survive beyond the first two years.
What is SMA1 genetic testing?
Genetic testing for spinal muscular atrophy 1 (SMA1) is available. Carrier testing for at-risk relatives and prenatal testing for pregnancies at increased risk are possible , if the disease-causing mutations in the family have been identified. SMA1 is caused by mutations in the SMN1 gene, and extra copies of the SMN2 gene affect the severity of the condition. [11]
What is SMA1?
Spinal muscular atrophy 1 (SMA1), also known as Werdnig Hoffmann disease, is a genetic neuromuscular disorder that affects the nerve cells that control voluntary muscles (motor neurons). Without treatment, symptoms of SMA1 become apparent before 6 months of age and include worsening muscle weakness and poor muscle tone ( hypotonia) due to loss of the lower motor neurons in the spinal cord and brain stem. Feeding and breathing problems are also present. [1] SMA1 is caused by changes (pathogenic variants also called mutations) in the SMN1 gene and is typically inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. [1] [2]
What is SMA1 caused by?
Feeding and breathing problems are also present. [1] . SMA1 is caused by changes (pathogenic variants also called mutations) in the SMN1 gene and is typically inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. [1] [2] Diagnosis of SMA1 is suspected by symptoms and confirmed by genetic testing.
How to diagnose SMA1?
Diagnosis of SMA1 is suspected by symptoms and confirmed by genetic testing. SMA has been added to the list of recommended newborn screening tests in the United States, so that it can be detected prior to symptoms developing. This occurred because treatments are being developed that are changing the course of the disease. In December 2016, nusinersen (Spinraza) became the first FDA approved treatment for SMA1. Continued treatment with nusinersen is allowing many babies with SMA1 to reach and maintain age appropriate developmental milestones, including sitting, crawling, and walking. On average, breathing problems, nutrition problems, and hospital admissions have also decreased. However, response to treatment does vary. Some babies with SMA1 may not respond to the nusinersen at all or may have medical complications that prevent use of the treatment. [3] [4] Other treatments remain supportive. [5] [6]
What is the HPO database?
People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. This information comes from a database called the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) . The HPO collects information on symptoms that have been described in medical resources.
What is the chance of being an unaffected carrier?
50% chance to be an unaffected carrier like each of the parents. 25% chance to not have the condition and not be a carrier. An unaffected sibling of a person with SMA1 has a 2/3 chance to be a carrier. Approximately 2% of cases of SMA1 are not inherited from both parents.
How to find a genetics specialist?
To find a medical professional who specializes in genetics, you can ask your doctor for a referral or you can search for one yourself. Online directories are provided by the American College of Medical Genetics and the National Society of Genetic Counselors. If you need additional help, contact a GARD Information Specialist. You can also learn more about genetic consultations from MedlinePlus Genetics.
Sma1 Symptoms
Causes
- SMA types affect both babies and children. With SMA, there is a breakdown of the nerve cells of the brain and spinal cord, keeping the brain from sending the messages needed to control muscle movement. SMA1 is an inherited condition associated with abnormal genes. The abnormal gene associated with SMA1 and all types of SMA is the survival motor neuron (SMN).3There have bee…
Diagnosis
- A diagnosis is generally made when a parent or caregiver notices symptoms of SMA1 in a baby or child. SMA might also be diagnosed during newborn screening. SMA was added to the federal Recommended Uniform Screening Panel (RUSP) newborn screening guidelines in 2018.5 When a parent or caregiver reports symptoms, a doctor will look at the children’s medical and family hist…
Treatment
- There is no cure for Werdnig-Hoffmann disease.10 However, treatment aims at managing symptoms of the condition. In addition, new gene replacement therapy options have recently been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), as well as disease-modifying therapies.11 Zolgensma (onasemnogene abeparvovec-xioi) is a new type of gene therapy that involves an inf…
Summary
- Werdnig-Hoffmann disease (SMA1) affects the nerves controlling voluntary muscles. It is a genetic disease that is inherited. SMA1 symptoms include problems with controlling head movement, sitting up, and walking, progressing with symptoms of impaired breathing and feeding. The condition appears before the age of 6 months and is often fatal by age 2...
A Word from Verywell
- For the most part, it is widely accepted that babies with Werdnig-Hoffman disease have a reduced lifespan, although this is improving. At some point, your family may need to consider end-of-life careoptions. Make sure you talk to the medical professionals early to help ensure the best possible care for your child as their condition progresses. A diagnosis of SMA1 can be stressful …